Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer's disease progression
- PMID: 31488882
- PMCID: PMC6796854
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-019-0216-x
Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer's disease progression
Abstract
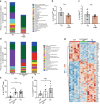
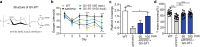
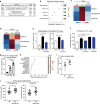
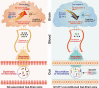
Recently, increasing evidence has suggested the association between gut dysbiosis and Alzheimer's disease (AD) progression, yet the role of gut microbiota in AD pathogenesis remains obscure. Herein, we provide a potential mechanistic link between gut microbiota dysbiosis and neuroinflammation in AD progression. Using AD mouse models, we discovered that, during AD progression, the alteration of gut microbiota composition leads to the peripheral accumulation of phenylalanine and isoleucine, which stimulates the differentiation and proliferation of pro-inflammatory T helper 1 (Th1) cells. The brain-infiltrated peripheral Th1 immune cells are associated with the M1 microglia activation, contributing to AD-associated neuroinflammation. Importantly, the elevation of phenylalanine and isoleucine concentrations and the increase of Th1 cell frequency in the blood were also observed in two small independent cohorts of patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to AD. Furthermore, GV-971, a sodium oligomannate that has demonstrated solid and consistent cognition improvement in a phase 3 clinical trial in China, suppresses gut dysbiosis and the associated phenylalanine/isoleucine accumulation, harnesses neuroinflammation and reverses the cognition impairment. Together, our findings highlight the role of gut dysbiosis-promoted neuroinflammation in AD progression and suggest a novel strategy for AD therapy by remodelling the gut microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
XYW, GQS, TF, JZ, XKC, JY, SSC, YXG, LFR, GQZ, SYY, WL, CD, DBY and CRG are full-time employees of Shanghai Green Valley Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
The microbiome: A target for Alzheimer disease?Cell Res. 2019 Oct;29(10):779-780. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0227-7. Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31488883 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Omission of previous publications by an author should be corrected.Cell Res. 2020 Sep;30(9):819. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0344-3. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32632254 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Geng et al. reply.Cell Res. 2020 Sep;30(9):820. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0377-7. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32661309 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Sodium oligomannate alters gut microbiota, reduces cerebral amyloidosis and reactive microglia in a sex-specific manner.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Feb 17;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00700-w. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 38365827 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia and gut microbiota: A double-edged sword in Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Nov;101:102515. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102515. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39321881 Review.
-
Sodium Oligomannate: First Approval.Drugs. 2020 Mar;80(4):441-444. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01268-1. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32020555 Review.
-
New mechanism of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: The activation of NLRP3 inflammasome mediated by gut microbiota.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 8;100:109884. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109884. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32032696
-
The Gut Microbiota Modulates Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease: Elucidating Crucial Factors and Mechanistic Underpinnings.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Oct;30(10):e70091. doi: 10.1111/cns.70091. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39460538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trimethylamine N-oxide: role in cell senescence and age-related diseases.Eur J Nutr. 2023 Mar;62(2):525-541. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-03011-w. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Eur J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36219234 Review.
-
A phase II randomized trial of sodium oligomannate in Alzheimer's dementia.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020 Sep 14;12(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00678-3. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32928279 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evolving Technologies in Gastrointestinal Microbiome Era and Their Potential Clinical Applications.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 7;9(8):2565. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082565. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32784731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of microbe-derived ɣ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in gut and brain barrier integrity and GABAergic signaling in Alzheimer's disease.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2371950. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2371950. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39008552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox signaling and Alzheimer's disease: from pathomechanism insights to biomarker discovery and therapy strategy.Biomark Res. 2020 Sep 11;8:42. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00218-z. eCollection 2020. Biomark Res. 2020. PMID: 32944245 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

