C-reactive protein for diagnosing late-onset infection in newborn infants
- PMID: 30640979
- PMCID: PMC6373636
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012126.pub2
C-reactive protein for diagnosing late-onset infection in newborn infants
Abstract
Background: Late-onset infection is the most common serious complication associated with hospital care for newborn infants. Because confirming the diagnosis by microbiological culture typically takes 24 to 48 hours, the serum level of the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein (CRP) measured as part of the initial investigation is used as an adjunctive rapid test to guide management in infants with suspected late-onset infection.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of serum CRP measurement in detecting late-onset infection in newborn infants.
Search methods: We searched electronic databases (MEDLINE, Embase, and Science Citation Index to September 2017), conference proceedings, previous reviews, and the reference lists of retrieved articles.
Selection criteria: We included cohort and cross-sectional studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of serum CRP levels for the detection of late-onset infection (occurring more than 72 hours after birth) in newborn infants.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed eligibility for inclusion, evaluated the methodological quality of included studies, and extracted data to estimate diagnostic accuracy using hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) models. We assessed heterogeneity by examining variability of study estimates and overlap of the 95% confidence interval (CI) in forest plots of sensitivity and specificity.
Main results: The search identified 20 studies (1615 infants). Most were small, single-centre, prospective cohort studies conducted in neonatal units in high- or middle-income countries since the late 1990s. Risk of bias in the included studies was generally low with independent assessment of index and reference tests. Most studies used a prespecified serum CRP threshold level as the definition of a 'positive' index test (typical cut-off level between 5 mg/L and 10 mg/L) and the culture of a pathogenic micro-organism from blood as the reference standard.At median specificity (0.74), sensitivity was 0.62 (95% CI 0.50 to 0.73). Heterogeneity was evident in the forest plots but it was not possible to conduct subgroup or meta-regression analyses by gestational ages, types of infection, or types of infecting micro-organism. Covariates for whether studies used a predefined threshold or not, and whether studies used a standard threshold of between 5 mg/L and 10 mg/L, were not statistically significant.
Authors' conclusions: The serum CRP level at initial evaluation of an infant with suspected late-onset infection is unlikely to be considered sufficiently accurate to aid early diagnosis or select infants to undergo further investigation or treatment with antimicrobial therapy or other interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
JVEB: none.
NM: none.
JC: none.
WM: none.
Figures
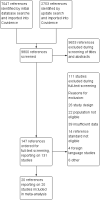

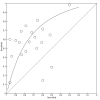

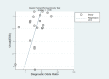
Comment in
-
Commentary on "C-Reactive Protein for the Diagnosis of Late-Onset Infections in Newborn Infants".Neonatology. 2020;117(6):767-770. doi: 10.1159/000510671. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Neonatology. 2020. PMID: 33454717 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Assessment of C-Reactive Protein Diagnostic Test Accuracy for Late-Onset Infection in Newborn Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Mar 1;174(3):260-268. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5669. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32011640 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide for the diagnosis of haemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 8;12(12):CD013129. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013129.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36478359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and lactate dehydrogenase for the diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 21;4(4):CD012645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012645. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28431197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulse oximetry screening for critical congenital heart defects.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 1;3(3):CD011912. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011912.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29494750 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Defining necrotizing enterocolitis: current difficulties and future opportunities.Pediatr Res. 2020 Aug;88(Suppl 1):10-15. doi: 10.1038/s41390-020-1074-4. Pediatr Res. 2020. PMID: 32855506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic scores derived in saliva are associated with gestational age at birth.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Jun 29;16(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01701-2. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38951914 Free PMC article.
-
Vital signs as physiomarkers of neonatal sepsis.Pediatr Res. 2022 Jan;91(2):273-282. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01709-x. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 34493832 Review.
-
Effect of Anti-Infective Reconstituted Bone Xenograft Combined with External Fixator on Serum CRP and PCT Levels and Prognosis of Patients with Bone Infection after Lower Extremity Long Bone Trauma.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 30;2021:5979514. doi: 10.1155/2021/5979514. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9851029. doi: 10.1155/2023/9851029. PMID: 34504538 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Antibiotic Discontinuation 24 h After Neonatal Late-Onset Sepsis Work-Up-A Validated Decision Tree Model.Front Pediatr. 2021 Aug 19;9:693882. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.693882. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34490157 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Aminullah 2001 {published data only}
-
- Aminullah A, Sjachroel DN, Hadinegoro SR, Madiyono B. The role of plasma C‐reactive protein in the evaluation of antibiotic treatment in suspected neonatal sepsis. Medical Journal of Indonesia 2001;10(1):16‐21.
Benitz 1998 {published data only}
-
- Benitz WE, Han MY, Madan A, Ramachandra P. Serial serum C‐reactive protein levels in the diagnosis of neonatal infection. Pediatrics 1998;102(4):E41. [PUBMED: 9755278] - PubMed
Bohnhorst 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bohnhorst B, Lange M, Bejo L, Bartels DB, Hoy L, Peter C. Value of clinical symptoms and combination rules of procalcitonin, C‐reactive protein, and interleukin 6 in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Klinische Padiatrie 2010;222:S5.
Boo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Boo NY, Nor Azlina AA, Rohana J. Usefulness of a semi‐quantitative procalcitonin test kit for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Singapore Medical Journal 2008;49(3):204‐8. - PubMed
Bustos 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bustos BR, Araneda CH. Procalcitonin for the diagnosis of late onset sepsis in newborns of very low birth weight [Procalcitonina para el diagnóstico de la sepsis tardía en recién nacidos de muy bajo peso de nacimiento]. Revista Chilena de Infectologia 2012;29(5):511‐6. [DOI: 10.4067/S0716-10182012000600005; PUBMED: 23282492] - DOI - PubMed
Chan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Chan DK, Ho LY. Usefulness of C‐reactive protein in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Singapore Medical Journal 1997;38(6):252‐5. [PUBMED: 9294338] - PubMed
Choo 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Decembrino 2015 {published and unpublished data}
Doellner 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Doellner H, Arntzen KJ, Haereid PE, Aag S, Austgulen R. Interleukin‐6 concentrations in neonates evaluated for sepsis. Journal of Pediatrics 1998;132(2):295‐9. [PUBMED: 9506644] - PubMed
-
- Doellner H, Vatten L, Austgulen R. Early diagnostic markers for neonatal sepsis: comparing C‐reactive protein, interleukin‐6, soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors and soluble adhesion molecules. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2001;54(12):1251‐7. [PUBMED: 11750194] - PubMed
Fendler 2008 {published data only}
Hisamuddin 2015 {published and unpublished data}
Jacquot 2009 {published data only}
Kipfmueller 2015 {published data only}
Kordek 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kordek A, Loniewska B, Podraza W, Nikodemski T, Rudnicki J. Usefulness of estimation of blood procalcitonin concentration versus C‐reactive protein concentration and white blood cell count for therapeutic monitoring of sepsis in neonates. Postepy Higieny i Medycyny Doswiadczalnej (Online) 2014;68:1516‐23. [PUBMED: 25531715] - PubMed
Kumar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kumar R. Validation of C‐Reactive Protein [Masters thesis]. Nairobi: University of Nairobi, 2006.
-
- Kumar R, Musoke R, Macharia WM, Revathi G. Validation of C‐reactive protein in the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis in a tertiary care hospital in Kenya. East African Medical Journal 2010;87(6):255‐61. [PUBMED: 23057268] - PubMed
Ng 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ng PC, Cheng SH, Chui KM, Fok TF, Wong MY, Wong W, et al. Diagnosis of late onset neonatal sepsis with cytokines, adhesion molecule, and C‐reactive protein in preterm very low birthweight infants. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 1997;77(3):F221‐7. [PUBMED: 9462194] - PMC - PubMed
Pynn 2015 {published data only}
Seibert 1990 {published data only}
-
- Seibert K, Yu VY, Doery JC, Embury D. The value of C‐reactive protein measurement in the diagnosis of neonatal infection. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 1990;26(5):267‐70. [PUBMED: 2265018] - PubMed
Sherwin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sherwin C, Broadbent R, Young S, Worth J, McCaffrey F, Medlicott NJ, et al. Utility of interleukin‐12 and interleukin‐10 in comparison with other cytokines and acute‐phase reactants in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. American Journal of Perinatology 2008;25(10):629‐36. [DOI: 10.1055/s-0028-1090585; PUBMED: 18850512] - DOI - PubMed
Verboon‐Maciolek 2006 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Aboud 2010 {published data only}
-
- Aboud MI, Waise MW, Shakerdi LA. Procalcitonin as a marker of neonatal sepsis in intensive care units. Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences 2010;35(3):205‐10.
Adhikari 1986 {published data only}
-
- Adhikari M, Coovadia HM, Coovadia YM, Smit SY, Moosa A. Predictive value of C‐reactive protein in neonatal septicaemia. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 1986;6(1):37‐40. [PUBMED: 2428291] - PubMed
Adib 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Adib M, Ostadi V, Navaei F, Saheb Fosoul F, Oreizi F, Shokouhi R, et al. Evaluation of CD11b expression on peripheral blood neutrophils for early detection of neonatal sepsis. Iranian Journal of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 2007;6(2):93‐6. [PUBMED: 17563410] - PubMed
Adly 2014 {published data only}
Ahmed 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ahmed Z, Ghafoor T, Waqar T, Ali S, Aziz S, Mahmud S. Diagnostic value of C‐reactive protein and haematological parameters in neonatal sepsis. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons‐‐Pakistan : JCPSP 2005;15(3):152‐6. [DOI: ; PUBMED: 15808093] - PubMed
Ahmed 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ahmed A, Baki A, Begum T, Nahar N. Evaluation of procalcitonin as a marker of neonatal sepsis. Intensive Care Medicine 2013;39:S75.
Ainbender 1982 {published data only}
-
- Ainbender E, Cabatu EE, Guzman DM, Sweet AY. Serum C‐reactive protein and problems of newborn infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1982;101(3):438‐40. [PUBMED: 7108668] - PubMed
Alexejew 1990 {published data only}
-
- Alexejew B, Hendrick W, Braun W, Domula M, Winiecki P. The significance of various hematological parameters for the early diagnosis of bacterial infections in premature and full‐term neonates. 3. Discussion of the study results. Padiatrie und Grenzgebiete 1990;29(6):455‐79. - PubMed
Aliefendioglu 2014 {published data only}
Alt 1982 {published data only}
-
- Alt R, Willard D, Messer J, Metais P, Goester C, Mark JJ. Value of C‐reactive protein in neonatal bacterial infections [Interet de la c reactive proteine dans les infections bacteriennes neonatales]. Archives Francaises de Pediatrie 1982;39(10):811‐3. [PUBMED: 7168617] - PubMed
Al‐Zwaini 2009 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Zwaini EJ. C‐reactive protein: a useful marker for guiding duration of antibiotic therapy in suspected neonatal septicaemia?. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal 2009;15(2):269‐75. [PUBMED: 19554972] - PubMed
Amato 1984 {published data only}
-
- Amato M, Ruckstuhl C, Muralt G. Serum C‐reactive protein in preterm infants [C‐reaktives protein im serum fruhgeborener]. Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift 1984;114(12):412‐4. [PUBMED: 6719082] - PubMed
Ammo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ammo K, Salacity G. CRP and ESR as a diagnostic marker in detection of neonatal sepsis. Pakistan Paediatric Journal 2008;32(1):15‐22.
Ananina 1963 {published data only}
-
- Ananina NV. Significance of the electrophoretic investigation of the blood proteins and C‐reactive protein in the diagnosis of sepsis in the newborn. Pediatriia 1963;42:19‐24. [PUBMED: 14148317] - PubMed
Ang 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ang AT, Ho NK, Chia SE. The usefulness of CRP and I/T ratio in early diagnosis of infections in Asian newborns. Journal of the Singapore Paediatric Society 1990;32(3‐4):159‐63. [PUBMED: 2133755] - PubMed
Anwer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Anwer SK, Mustafa S. Rapid identification of neonatal sepsis. Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2000;50(3):94‐8. [PUBMED: 10795470] - PubMed
Apostolou 2002 {published data only}
Arani 2013 {published data only}
-
- Arani MH, Movahedian A, Arani MG, Adinah M, Mosayebi Z. Predictive value of interleukin‐6 (IL6) in term neonates with early sepsis during 2010‐2011. Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology 2013;6(10):e8580.
Arati 2014 {published data only}
-
- Arati K, Nagarathnamma T, Benakappa A. Comparative evaluation of blood culture, estimation of immunoglobulin M (IgM) and C‐reactive protein detection in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. International Journal of Current Research 2014;6(2):5094‐7.
Arayici 2014 {published data only}
-
- Arayici S, Kadioglu Simsek G, Conploat FE, Oncel M, Uras N, Oguz S, et al. Can base excess be used for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis in preterm newborns?. Archives of Diseases in Childhood 2014;99:A418‐9.
Arnon 2004 {published data only}
Arnon 2005 {published data only}
Arnon 2007 {published data only}
Athhan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Athhan F, Akagunduz B, Genel F, Bak M, Can D. Procalcitonin: a marker of neonatal sepsis. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2002;48(1):10‐4. [PUBMED: 11866330] - PubMed
Athiraman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Athiraman N, Agarwal R, Krishnamoorthy S, Guy M. Can we rely on procalcitonin in the diagnosis of late onset neonatal sepsis?. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 2011;96(Suppl 1):Fa40.
Ayazi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ayazi P, Mahyar A, Daneshi MM, Jahanihashemi H, Esmailzadehha N, Mosaferirad N. Comparison of serum IL‐1beta and C reactive protein levels in early diagnosis and management of neonatal sepsis. Le Infezioni in Medicina 2014;22(4):296‐301. [PUBMED: 25551845] - PubMed
Aydin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Aydin B, Zenciroglu A, Dilli D, Erol S, Ozyazici E, Karadag N, et al. The predictive values on mean platelet volume (MPV) in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2012;97(Suppl 2):A338.
Aydin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Aydin B, Dilli D, Zenciroglu A, Kaya O, Bilaloglu E, Okumus N, et al. Comparison of a rapid bed‐side test with a central laboratory analysis for C‐reactive protein in newborn infants with suspicion of sepsis. Clinical Laboratory 2013;59(9‐10):1045‐51. [PUBMED: 24273927] - PubMed
Baptista‐Gonzales 1989 {published data only}
-
- Baptista‐Gonzales HA, Ibarra‐Camacho A, Cedillo RE, Torres‐Alipi BI. Usefulness of C‐reactive protein for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Boletin Medico del Hospital Infantil de Mexico 1989;46(8):543‐6. [PUBMED: 2803537] - PubMed
Baruti‐Gafurri 2010 {published data only}
Batfalsky 2012 {published data only}
-
- Batfalsky A, Lohr A, Heussen N, Neunhoeffer F, Orlikowsky TW. Diagnostic value of an interleukin‐6 bedside test in term and preterm neonates at the time of clinical suspicion of early‐ and late‐onset bacterial infection. Neonatology 2012;102(1):37‐44. [DOI: 10.1159/000336632; PUBMED: 22507910] - DOI - PubMed
Beceiro Mosquera 2009 {published data only}
-
- Beceiro Mosquera J, Sivera Monzo CL, Oria de Rueda Salguero O, Olivas Lopez de Soria C, Herbozo Nory C. Usefulness of a rapid serum interleukin‐6 teste combined with C‐reactive protein to predict sepsis in newborns with suspicion of infection [Utilidad de un test rápido de interleuquina‐6 sérico combinado con proteína C reactiva para predecir la sepsis en recién nacidos con sospecha de infección]. Anales de Pediatria (Barcelona, Spain : 2003) 2009;71(6):483‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2009.07.027; PUBMED: 19811958] - DOI - PubMed
Berger 1995 {published data only}
-
- Berger C, Uehlinger J, Ghelfi D, Blau N, Fanconi S. Comparison of C‐reactive protein and white blood cell count with differential in neonates at risk for septicaemia. European Journal of Pediatrics 1995;154(2):138‐44. [PUBMED: 7720743] - PubMed
Berrington 2014 {published data only}
-
- Berrington JE, Hearn RI, Hall C, Stewart CJ, Cummings SP, Embleton ND. Proportionate reduction in uncertainty of late onset infection in preterm infants by neutrophil CH64 measurement. Fetal and Pediatric Pathology 2014;33(1):16‐22. [DOI: 10.3109/15513815.2013.842270; PUBMED: 24093544] - DOI - PubMed
Bhandari 2008 {published data only}
Bhargava 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bhargava M, Sindhuri U, Saluja S, Saraf A, Dayanand S, Simon‐Lopez R. Volume, conductivity, and scatter properties of leukocytes (VCS Technology) is a highly sensitive and specific predictor of blood culture proven neonatal sepsis. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology 2011;33(Suppl 1):55‐6.
Bhargava 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bhargava M. Utility of automated blood cell analyzer‐derived indices (VCS technology) in the rapid diagnosis of infectious, inflammatory, and neoplastic disorders part I: neonatal sepsis, malaria, and dengue. Indian Journal of Hematology & Blood Transfusion 2013;29(4):244.
Blanco 1996 {published data only}
-
- Blanco A, Solis G, Arranz E, Coto GD, Ramos A, Telleria J. Serum levels of CD14 in neonatal sepsis by Gram‐positive and Gram‐negative bacteria. Acta Paediatrica 1996;85(6):728‐32. [PUBMED: 8816213] - PubMed
Blommendahl 2002 {published data only}
-
- Blommendahl J, Janas M, Laine S, Miettinen A, Ashorn P. Comparison of procalcitonin with CRP and differential white blood cell count for diagnosis of culture‐proven neonatal sepsis. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2002;34(8):620‐2. [PUBMED: 12238581] - PubMed
Boonkasidecha 2013 {published data only}
-
- Boonkasidecha S, Panburana J, Chansakulporn S, Benjasuwantep B, Kongsomboon K. An optimal cut‐off point of serum C‐reactive protein in prediction of neonatal sepsis. Chotmaihet Thangphaet [Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand] 2013;96(Suppl 1):S65‐70. [PUBMED: 23724458] - PubMed
Boskabadi 2010 {published data only}
Bressan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bressan S, Andreola B, Cattelan F, Zangardi T, Perilongo G, Dalt L. Predicting severe bacterial infections in well‐appearing febrile neonates: laboratory markers accuracy and duration of fever. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2010;29(3):227‐32. [DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181b9a086; PUBMED: 19949364] - DOI - PubMed
Buck 1994 {published data only}
-
- Buck C, Bundschu J, Gallati H, Bartmann P, Pohlandt F. Interleukin‐6: a sensitive parameter for the early diagnosis of neonatal bacterial infection. Pediatrics 1994;93(1):54‐8. [PUBMED: 8265324] - PubMed
Bustos Betanzo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bustos Betanzo RO. Procalcitonin, C‐reactive protein and leukocyte count in very‐low birth weight infants with late neonatal sepsis. Anales de Pediatria (Barcelona, Spain : 2003) 2007;66(5):541‐2. [PUBMED: 17517212] - PubMed
Catal 2014 {published data only}
-
- Catal F, Tayman C, Tonbul A, Akca H, Kara S, Tatli MM, et al. Mean platelet volume (MPV) may simply predict the severity of sepsis in preterm infants. Clinical Laboratory 2014;60(7):1193‐200. [PUBMED: 25134389] - PubMed
Ceccon 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ceccon M, Vaz FA, Diniz EM, Okay TS. Analysis of the use of interleukin 6 and 8 and C‐reactive protein for the diagnosis and therapeutic follow‐up of newborns with late onset sepsis admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Pediatric Research 2003;53(4):312A‐3A.
-
- Ceccon ME, Vaz FA, Diniz EM, Okay TS. Interleukin 6 and C‐reactive protein for the diagnosis of late onset sepsis in the newborn infant [Interleucina 6 e proteína c reativa no diagnóstico de sepse tardia no recém‐nascido]. Revista de Associacao Medica Brasileira 2006;52(2):79‐85. [PUBMED: 16767331] - PubMed
Cekmez 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cekmez F, Canpolat FE, Cetinkaya M, Aydinoz S, Aydemir G, Karademir F, et al. Diagnostic value of resistin and visfatin, in comparison with C‐reactive protein, procalcitonin and interleukin‐6 in neonatal sepsis. European Cytokine Network 2011;22(2):113‐7. [DOI: 10.1684/ecn.2011.0283; PUBMED: 21636351] - DOI - PubMed
Celik 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Celik IH, Demirel G, Uras N, Oguz ES, Erdeve O, Dilme U. The role of serum interleukin‐6 and C‐reactive protein levels for differentiating aetiology of neonatal sepsis. Archivos Argentinos de Pediatria 2015;113(6):534‐7. - PubMed
Celik 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Celik HT, Portakal O, Yigit S, HasCelik G, Korkmaz A, Yurdakok M. Comparison of the efficacy of serum C‐reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukin‐6 levels and new leukocyte parameters in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 2014;52(Suppl 1):S856.
-
- Celik HT, Portakal O, Yigit S, Hascelik G, Korkmaz A. Yurdakoek M. Efficacy of new lycocyte parameters versus serum C‐reactive protein, procalcitonin, and interleukin‐6 in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Pediatrics International 2016;58(2):119‐25. [DOI: 10.1111/ped.12754; PUBMED: 26190096] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Celik T, Portakal O, Yigit S, Hascelik G, Korkmaz A, Yurdakok M. Comparison of the efficacy of C‐reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukin‐6 levels and new leukocyte parameters in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2012;97:A12. - PubMed
Cesur 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cesur S, Irmak H, Esras Z, Yasar H, Sengul A, Dilme U, et al. Prognostic value of serum TNF‐alpha, IL‐10, leptin, and CRP levels in newborns with septicemia. Mikrobiyoloji Bulteni 2009;43(3):607‐12. [PUBMED: 20084913] - PubMed
Cetinkaya 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cetinkaya M, Ozkan H, Koksal N, Celebi S, Hacimustafaoglu M. Comparison of serum amyloid A concentrations with those of C‐reactive protein and procalcitonin in diagnosis and follow‐up of neonatal sepsis in premature infants. Journal of Perinatology 2009;29(3):225‐31. [DOI: 10.1038/jp.2008.207; PUBMED: 19078972] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Köksal N, Harmanci R, Cetinkaya M, Hacimustafaoğlu M. Role of procalcitonin and CRP in diagnosis and follow‐up of neonatal sepsis. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2007;49(1):21‐9. [PUBMED: 17479640] - PubMed
Chen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chen HL, Hung CH, Tseng HI, Yang RC. Plasma IP‐10 as a predictor of serious bacterial infection in infants less than 4 months of age. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2009;55(2):103‐8; Corrected and republished in: Journal of Tropical Pediatrics: 2011: 57(2): 145‐51. [DOI: 10.1093/tropej/fmn092; PUBMED: 18952629] - DOI - PubMed
Davis 2015 {published data only}
Dhanalakshmi 2015 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Dorado Moles 2007 {published data only}
-
- Dorado Moles MJ, Figueredo Delgado MA, Fernández Pérez C, Moro Serrano M. T lymphocyte immunophenotype as a diagnostic marker of late‐onset neonatal sepsis [Inmunofenotipificación de linfocitos T como marcador diagnóstico de sepsis neonatal tardía]. Anales de Pediatria (Barcelona, Spain : 2003) 2007;67(6):536‐43. [PUBMED: 18053517] - PubMed
Duhan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Duhan A, Berwal A, Raikwar P, Punia A, Beniwal K, Kamra HT. Utility of haematological parameters in detection of neonatal sepsis. JKIMSU 2016;5(3):98‐106.
Edgar 1994 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Edgar JD, Wilson DC, McMillan SA, Crockard AD, Halliday MI, Gardiner KR, et al. Predictive value of soluble immunological mediators in neonatal infection. Clinical Science 1994;87(2):165‐71. [PUBMED: 7924161] - PubMed
Edgar 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Edgar JD, Gabriel V, Gallimore JR, McMillan SA, Grant J. A prospective study of the sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic performance of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1, highly sensitive C‐reactive protein, soluble E‐selectin and serum amyloid A in the diagnosis of neonatal infection. BMC Pediatrics 2010;10:22. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-10-22; PUBMED: 20398379] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
El Shimi 2017 {published data only}
El‐Sonbaty 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- El‐Sonbaty MM, AlSharany W, Youness ER, Mohamed NA, Abdel‐Hamid TA, Abdel‐Razek ARA. Diagnostic utility of biomarkers in diagnosis of early stages of neonatal sepsis in neonatal intensive care unit in Egypt. Egyptian Pediatric Association Gazette 2016;64(2):91‐6.
Enguix 2001 {published data only}
-
- Enguix A, Rey C, Concha A, Medina A, Coto D, Dieguez MA. Comparison of procalcitonin with C‐reactive protein and serum amyloid for the early diagnosis of bacterial sepsis in critically ill neonates and children. Intensive Care Medicine 2001;27(1):211‐5. [PUBMED: 11280637] - PubMed
Escobar 2015 {published data only}
-
- Escobar LA, Ruiz JS, Gil‐Ruiz Gil‐Esparza MA, Cardenas Rebollo JM, Diaz‐Parreno AS, Llana Martin I. C‐reactive protein utility as an indicator of proven neonatal sepsis. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 2015;43:338.
Fattah 2017 {published data only}
-
- Fattah MA, Omer AF, Asaif S, Manlulu R, Karar T, Ahmed A, et al. Utility of cytokine, adhesion molecule and acute phase proteins in early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Journal of Natural Science, Biology, and Medicine 2017;8(1):32‐9. [DOI: 10.4103/0976-9668.198362; PUBMED: 28250672] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Franz 1999 {published data only}
-
- Franz AR, Kron M, Pohlandt F, Steinbach G. Comparison of procalcitonin with interleukin 8, C‐reactive protein and differential white blood cell count for the early diagnosis of bacterial infections in newborn infants. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1999;18(8):666‐71. [PUBMED: 10462333] - PubMed
-
- Franz AR, Sieber S, Pohlandt F, Kron M, Steinbach G. Whole blood interleukin 8 and plasma interleukin 8 levels in newborn infants with suspected bacterial infection. Acta Paediatrica 2004;93(5):648‐53. [PUBMED: 15174789] - PubMed
-
- Franz AR, Steinbach G, Kron M, Pohlandt F. Reduction of unnecessary antibiotic therapy in newborn infants using interleukin‐8 and C‐reactive protein as markers of bacterial infections. Pediatrics 1999;104(3 Pt 1):447‐53. [PUBMED: 10469768] - PubMed
Ganesan 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Garland 2003 {published data only}
-
- Garland SM, Bowman ED. Reappraisal of C‐reactive protein as a screening tool for neonatal sepsis. Pathology 2003;35(3):240‐3. [PUBMED: 14506969] - PubMed
Goldfinch 2015 {published data only}
-
- Goldfinch C, Komran T, Kotsanas D, Burgner D, Tan K. Should inflammatory markers inform the decision to perform a lumbar puncture in infants with suspected neonatal sepsis?. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2015;51(Suppl 1):84.
Gorbe 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Gura 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gura A, Oygur N, Ongun H, Saka O, Yegin O. E‐selectin as an early indicator and follow‐up parameter in late neonatal sepsis [Yenidogan gec sepsisinde erken tani ve tedavi kriteri olarak E‐selektin]. Cocuk Saglili ve Hastalkiklari Dergisi 2003;46(4):261‐6.
Hegadi 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hegadi SS, Kalpana S. Comparative evaluation of blood culture and C‐reactive protein detection in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences 2015;6(2):B1366‐71.
Khair 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Khair KB, Rahman MA, Sultana T, Roy CK, Rahman MQ, Ahmed AN. Early diagnosis of neonatal septicemia by hematologic scoring system, C‐reactive protein and serum haptoglobin. Mymensingh Medical Journal : MMJ 2012;21(1):85‐92. [PUBMED: 22314460] - PubMed
Khassawneh 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Kite 1988 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Kocabas 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kocabas E, Sarikcioglu A, Aksaray N, Seydaoglu G, Seyhun Y, Yaman A. Role of procalcitonin, C‐reactive protein, interleukin‐6, interleukin‐8 and tumor necrosis factor‐alpha in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2007;49(1):7‐20. [PUBMED: 17479639] - PubMed
Krauel 1987 {published data only}
-
- Krauel J, Salvado A, Mira A, Orellana N, Calvet I, Molina V, et al. Simultaneous determination of total and immature neutrophil C‐reactive protein in normal, diseased, and infected newborn infants. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1987;27(4):257‐60. [PUBMED: 3426018] - PubMed
Krediet 1992 {published data only}
-
- Krediet T, Gerards L, Fleer A, Stekelenburg G. The predictive value of CRP and I/T‐ratio in neonatal infection. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 1992;20(6):479‐85. [PUBMED: 1293275] - PubMed
Kuster 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kuster H, Weiss M, Willeitner AE, Detlefsen S, Jeremias I, Zbojan J, et al. Interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist and interleukin‐6 for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis 2 days before clinical manifestation. Lancet 1998;352(9136):1271‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)08148-3; PUBMED: 9788457] - DOI - PubMed
Laborada 2003 {published data only}
Lai 2015 {published data only}
Liu 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Lu 2016 {published data only}
-
- Lu Q, Duan H, Yu J, Yao Y. Are global coagulation and platelet parameters useful markers for predicting late‐onset neonatal sepsis?. Clinical Laboratory 2016;62(1‐2):73‐9. [PUBMED: 27012035] - PubMed
-
- Yao Y, Tu Y, Lu Q. Values of C‐reactive protein, percentage of neutrophils and mean platelet volume in early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics] 2015;17(5):425‐9. [PUBMED: 26014688] - PubMed
Magudumana 2000 {published data only}
-
- Magudumana MO, Ballot DE, Cooper PA, Trusler J, Cory BJ, Viljoen E, et al. Serial interleukin 6 measurements in the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2000;46(5):267‐71. [PUBMED: 11077934] - PubMed
Manucha 2002 {published data only}
-
- Manucha V, Rusia U, Sikka M, Faridi MM, Madan N. Utility of haematological parameters and C‐reactive protein in the detection of neonatal sepsis. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2002;38(5):459‐64. [PUBMED: 12354261] - PubMed
Matesanz 1980 {published data only}
-
- Matesanz JL, Malaga S, Santos F, Nuno F, Ramos A, Crespo M. Diagnostic value of C reactive protein in neonatal sepsis. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1980;13(8):671‐8. [PUBMED: 7436148] - PubMed
Mehr 2001 {published data only}
Mustafa 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mustafa S, Farooqui S, Waheed S, Mahmood K. Evaluation of C‐reactive protein as early indicator of blood culture positivity in neonates. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences 2005;21(1):69‐73.
Nakamura 1989 {published data only}
-
- Nakamura H, Uetani Y, Nagata T, Yamasaki T. Serum C‐reactive protein in the early diagnosis of neonatal septicemia and bacterial meningitis. Acta Paediatrica Japonica; Overseas Edition 1989;31(5):567‐71. [PUBMED: 2515735] - PubMed
Noto 2012 {published data only}
-
- Noto A, Fanos V, Puxeddu E, Irmesi R, Puddu M, Ottonello G, et al. Soluble CD14‐subtype (sCD14‐ST) presepsin in critically ill preterm and term newborns for the early assessment of neonatal sepsis: preliminary results. Clinical Chemistry 2012;58(10 Suppl 1):A142‐3.
Nuntnarumit 2002 {published data only}
-
- Nuntnarumit P, Pinkaew O, Kitiwanwanich S. Predictive values of serial C‐reactive protein in neonatal sepsis. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2002;85(Suppl 4):S1151‐8. [PUBMED: 12549789] - PubMed
Okulu 2015 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Omran 2018 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Park 2014 {published data only}
Perez Solis 2006 {published data only}
-
- Perez Solis D, Lopez Sastre JB, Coto Cotallo GD, Dieguez Junquera MA, Deschamps Mosquera EM, Crespo Hernandez M. Procalcitonin for the diagnosis of nosocomial neonatal sepsis [Procalcitonina para el diagnóstico de sepsis neonatal de origen nosocomial]. Anales de Pediatria (Barcelona, Spain : 2003) 2006;64(4):349‐53. [PUBMED: 16606572] - PubMed
Pourcyrous 1989 {published data only}
-
- Pourcyrous M, Bada H, Jennings W, Korones S. C‐reactive protein‐ the most useful acute phase reactants for the early diagnosis of neonatal bacterial infection. Pediatric Research 1989;25(4):A280.
Prasad 2015 {published data only}
-
- Prasad A, Arora P, Chavan R. Role of hematological profile in early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis – one year cross sectional study in a tertiary care centre. Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion 2015;31(1 Suppl 1):S18.
Qin 2017 {published data only}
Russell 1992 {published data only}
Sakha 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sakha K, Husseini MB, Seyyedsadri N. The role of the procalcitonin in diagnosis of neonatal sepsis and correlation between procalcitonin and C‐reactive protein in these patients. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences 2008;11(14):1785‐90. [PUBMED: 18817217] - PubMed
Sarafidis 2017 {published data only}
Sharma 1993 {published data only}
-
- Sharma A, Kutty CV, Sabharwal U, Rathee S, Mohan H. Evaluation of sepsis screen for diagnosis of neonatal septicemia. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1993;60(4):559‐63. [PUBMED: 8262592] - PubMed
Stein 2015 {published data only}
Topuz 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Topuz S, Ovali F. Comparison of C‐reactive protein and procalcitonin in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Nobel Medicus 2012;8(1):72‐6.
Turner 2006 {published data only}
Tyagi 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Tyagi T, Kelkar A, Doshi P, Mani NS. Utility of VCS parameters for early detection of neonatal sepsis. Indian Journal of Hematology & Blood Transfusion 2016;32(Suppl 2):S420.
Ussat 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ussat M, Vogtman C, Gebauer C, Pulzer F, Thome U, Knuepfer M. The role of elevated central‐peripheral temperature difference in early detection of late‐onset sepsis in preterm infants. Early Human Development 2015;91(12):677‐81. [DOI: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2015.09.007; PUBMED: 26513628] - DOI - PubMed
Vazzalwar 2005 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Wu 2013 {published data only}
Yao 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yao A, Liu J, Chang J, Deng C, Hu Y, Yu F, et al. Clinical practice of procalcitonin and hypersensitive C‐reactive protein test in neonatal infection. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2016;29(2 Suppl):753‐6. [PUBMED: 27113303] - PubMed
Ye 2017 {published data only}
Zarkesh 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zarkesh M, Sedaghat F, Heidarzadeh A, Tabrizi M, Bolooki‐Moghadam K, Ghesmati S. Diagnostic value of IL‐6, CRP, WBC, and absolute neutrophil count to predict serious infection in febrile infants. Acta Medica Iranica 2015;53(7):408‐11. [PUBMED: 26520627] - PubMed
Zhao 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zhao FX, Liu GH, Zhang J. Value of IL‐6 and IL‐8 in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics] 2015;17(12):1311‐5. [PUBMED: 26695671] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ohlin 2010 {published data only}
Additional references
Bassler 2009
-
- Bassler D, Stoll BJ, Schmidt B, Asztalos EV, Roberts RS, Robertson CM, et al. Using a count of neonatal morbidities to predict poor outcome in extremely low birth weight infants: added role of neonatal infection. Pediatrics 2009;123(1):313‐8. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2008-0377; NCT00009646; PUBMED: 19117897] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Benjamin 2001
-
- Benjamin DK Jr, Miller W, Garges H, Benjamin DK, McKinney RE Jr, Cotton M, et al. Bacteremia, central catheters, and neonates: when to pull the line. Pediatrics 2001;107(6):1272‐6. [PUBMED: 11389242] - PubMed
Berrington 2012
Beynon 2013
Butler‐O'Hara 2012
de Man 2000
-
- Man P, Verhoeven BA, Verbrugh HA, Vos MC, Anker JN. An antibiotic policy to prevent emergence of resistant bacilli. Lancet 2000;355(9208):973‐8. [PUBMED: 10768436] - PubMed
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58:882‐93. - PubMed
Dong 2015
Ehl 1997
-
- Ehl S, Gering B, Bartmann P, Hogel J, Pohlandt F. C‐reactive protein is a useful marker for guiding duration of antibiotic therapy in suspected neonatal bacterial infection. Pediatrics 1997;99(2):216‐21. [PUBMED: 9024449] - PubMed
Ehl 1999
-
- Ehl S, Gehring B, Pohlandt F. A detailed analysis of changes in serum C‐reactive protein levels in neonates treated for bacterial infection. European Journal of Pediatrics 1999;158(3):238‐42. [PUBMED: 10094447] - PubMed
Fowlie 1998
Gilfillan 2017
Gordon 2006
-
- Gordon A, Isaacs D. Late onset neonatal Gram‐negative bacillary infection in Australia and New Zealand: 1992‐2002. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2006;25(1):25‐9. [PUBMED: 16395098] - PubMed
Haque 2005
Hedegaard 2015
Hofer 2013
-
- Hofer N, Müller W, Resch B. Chapter 4: the role of C‐reactive protein in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. In: Resch B editor(s). Neonatal Bacterial Infection. London: InTech, 2013.
Hornik 2012
-
- Hornik CP, Fort P, Clark RH, Watt K, Benjamin DK Jr, Smith PB, et al. Early and late onset sepsis in very‐low‐birth‐weight infants from a large group of neonatal intensive care units. Early Human Development 2012;88(Suppl 2):S69‐74. [DOI: 10.1016/S0378-3782(12)70019-1; PUBMED: 22633519] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Leeflang 2014
Malik 2003
-
- Malik A, Hui CP, Pennie RA, Kirpalani H. Beyond the complete blood cell count and C‐reactive protein: a systematic review of modern diagnostic tests for neonatal sepsis. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(6):511‐6. [DOI: 10.1001/archpedi.157.6.511; PUBMED: 12796229] - DOI - PubMed
McGuire 2004
Muller‐Pebody 2011
-
- Muller‐Pebody B, Johnson AP, Heath PT, Gilbert RE, Henderson KL, Sharland M, iCAP Group (Improving Antibiotic Prescribing in Primary Care). Empirical treatment of neonatal sepsis: are the current guidelines adequate?. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 2011;96(1):F4‐8. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.2009.178483; PUBMED: 20584804] - DOI - PubMed
Naaktgeboren 2016
Oeser 2013
Oeser 2014
Pammi 2015
-
- Pammi M, Weiman LE. Late‐onset sepsis in preterm infants: update on strategies for therapy and prevention. Expert Review of Anti‐infective Therapy 2015;13(4):487‐504. - PubMed
Pammi 2017
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(10):982‐90. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.02.022; PUBMED: 16168343] - DOI - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rutter 2001
-
- Rutter CM, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta‐analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(19):2865‐84. [PUBMED: 11568945] - PubMed
Shah 2014
Shalabi 2015
Shane 2013
Shane 2014
-
- Shane AL, Stoll BJ. Neonatal sepsis: progress towards improved outcomes. Journal of Infection 2014;68 Suppl 1:S24‐32. [PUBMED: 24140138] - PubMed
Singh 2012
Steel 1994
Stoll 2003
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N. Infections in VLBW infants: studies from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Seminars in Perinatology 2003;27(4):293‐301. [PUBMED: 14510320] - PubMed
Stoll 2004
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams‐Chapman I, Fanaroff AA, Hintz SR, Vohr B, et al. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low‐birth‐weight infants with neonatal infection. JAMA 2004;292(19):2357‐65. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.292.19.2357; PUBMED: 15547163] - DOI - PubMed
Tsai 2014a
-
- Tsai MH, Chu SM, Lee CW, Hsu JF, Huang HR, Chiang MC, et al. Recurrent late‐onset sepsis in the neonatal intensive care unit: incidence, clinical characteristics and risk factors. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2014;20(11):O928‐35. [DOI: 10.1111/1469-0691.12661; PUBMED: 24796697] - DOI - PubMed
Tsai 2014b
Van den Bruel 2011
-
- Bruel A, Thompson MJ, Haj‐Hassan T, Stevens R, Moll H, Lakhanpaul M, et al. Diagnostic value of laboratory tests in identifying serious infections in febrile children: systematic review. BMJ 2011;342:d3082. [PUBMED: 21653621] - PubMed
van den Hoogen 2010
Vergnano 2005
Vergnano 2011
Verstraete 2015
Volanakis 2001
-
- Volanakis JE. Human C‐reactive protein: expression, structure, and function. Molecular Immunology 2001;38(2‐3):189‐97. [PUBMED: 11532280] - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS‐2 Group. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529‐36. [DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009; PUBMED: 22007046] - DOI - PubMed
Wilczynski 2007
Wong 2012
Zaidi 2005
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

