Effects of Different Cultivation Parameters on the Production of Surfactin Variants by a Bacillus subtilis Strain
- PMID: 30340314
- PMCID: PMC6222309
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102675
Effects of Different Cultivation Parameters on the Production of Surfactin Variants by a Bacillus subtilis Strain
Abstract
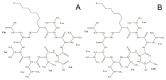
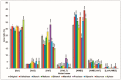
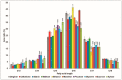
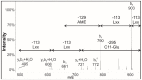
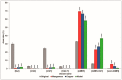
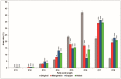
Surfactins are lipopeptide-type biosurfactants produced mainly by Bacillus species, consisting of a peptide loop of seven amino acids and a hydrophobic fatty acid chain (C12⁻C16). These molecules have been proven to exhibit various biological activities; thus, their therapeutic and environmental applications are considered. Within the surfactin lipopeptide family, there is a wide spectrum of different homologues and isomers; to date, more than 30 variants have been described. Since the newest members of these lipopeptides were described recently, there is no information that is available on their characteristic features, e.g., the dependence of their production from different cultivation parameters. This study examined the effects of both the different carbon sources and various metal ions on the surfactin production of a selected B. subtilis strain. Among the applied carbon sources, fructose and xylose had the highest impacts on the ratio of the different variants, regarding both the peptide sequences and the lengths of the fatty acids. Furthermore, the application of metal ions Mn2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ in the media completely changed the surfactin variant compositions of the fermenting broths leading to the appearance of methyl esterified surfactin forms, and resulted in the appearance of novel surfactin variants with fatty acid chains containing no more than 11 carbon atoms.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; HPLC-ESI-MS; cyclic lipopeptides; surfactin production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural Analysis of the Lipopeptide Produced by the Bacillus subtilis Mutant R2-104 with Mutagenesis.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016 Jul;179(6):973-85. doi: 10.1007/s12010-016-2044-5. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27020566
-
Ion trap mass spectrometry of surfactins produced by Bacillus subtilis SZMC 6179J reveals novel fragmentation features of cyclic lipopeptides.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2016 Jul 15;30(13):1581-90. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7592. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2016. PMID: 27321846
-
Effects of different amino acids in culture media on surfactin variants produced by Bacillus subtilis TD7.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012 Apr;166(8):2091-100. doi: 10.1007/s12010-012-9636-5. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22415784
-
Surfactin: biosynthesis, genetics and potential applications.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;672:316-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-5979-9_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20545293 Review.
-
Chemical structure, property and potential applications of biosurfactants produced by Bacillus subtilis in petroleum recovery and spill mitigation.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 3;16(3):4814-37. doi: 10.3390/ijms16034814. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25741767 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of the Medium Composition and the Culture Conditions on Surfactin Biosynthesis by a Native Bacillus subtilis natto BS19 Strain.Molecules. 2021 May 18;26(10):2985. doi: 10.3390/molecules26102985. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34069825 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial surfactants: A journey from fundamentals to recent advances.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 4;13:982603. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.982603. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35992692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome Shuffling of Bacillus velezensis for Enhanced Surfactin Production and Variation Analysis.Curr Microbiol. 2020 Jan;77(1):71-78. doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01807-4. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Curr Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31720755
-
Characterization and Cytotoxic Effect of Biosurfactants Obtained from Different Sources.ACS Omega. 2020 Nov 24;5(48):31381-31390. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04933. eCollection 2020 Dec 8. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33324849 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and structural features of micelles formed by surfactin homologues.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 7;11:1211319. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1211319. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37485321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W.-C., Juang R.-S., Wei Y.-H. Applications of a lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, produced by microorganisms. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015;103:158–169. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2015.07.009. - DOI
-
- From C., Hormazabal V., Hardy S.P., Granum P.E. Cytotoxicity in Bacillus mojavensis is abolished following loss of surfactin synthesis: Implications for assessment of toxicity and food poisoning potential. Inter. J. Food Microbiol. 2007;117:43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.01.013. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

