Host Defense Peptide LL-37-Mediated Chemoattractant Properties, but Not Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine IL-1RA Production, Is Selectively Controlled by Cdc42 Rho GTPase via G Protein-Coupled Receptors and JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
- PMID: 30158931
- PMCID: PMC6104452
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01871
Host Defense Peptide LL-37-Mediated Chemoattractant Properties, but Not Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine IL-1RA Production, Is Selectively Controlled by Cdc42 Rho GTPase via G Protein-Coupled Receptors and JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
Abstract
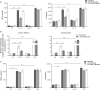
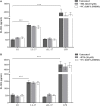
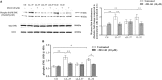
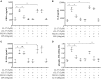
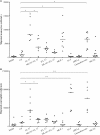
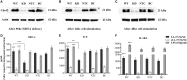
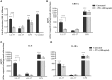
The human host defense peptide LL-37 promotes immune activation such as induction of chemokine production and recruitment of leukocytes. Conversely, LL-37 also mediates anti-inflammatory responses such as production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, e.g., IL-1RA, and the control of pro-inflammatory cytokines, e.g., TNF. The mechanisms regulating these disparate immunomodulatory functions of LL-37 are not completely understood. Rho GTPases are GTP-binding proteins that promote fundamental immune functions such as chemokine production and recruitment of leukocytes. However, recent studies have shown that distinct Rho proteins can both negatively and positively regulate inflammation. Therefore, we interrogated the role of Rho GTPases in LL-37-mediated immunomodulation. We demonstrate that LL-37-induced production of chemokines, e.g., GRO-α and IL-8 is largely dependent on Cdc42/Rac1 Rho GTPase, but independent of the Ras pathway. In contrast, LL-37-induced production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1RA is not dependent on either Cdc42/Rac1 RhoGTPase or Ras GTPase. Functional studies confirmed that LL-37-induced recruitment of leukocytes (monocytes and neutrophils) is also dependent on Cdc42/Rac1 RhoGTPase activity. We demonstrate that Cdc42/Rac1-dependent bioactivity of LL-37 involves G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling, but not p38 or ERK MAPK signaling. We further show that LL-37 specifically enhances the activity of Cdc42 Rho GTPase, and that the knockdown of Cdc42 suppresses LL-37-induced production of chemokines without altering the peptide's ability to induce IL-1RA. This is the first study to demonstrate the role of Rho GTPases in LL-37-mediated responses. We demonstrate that LL-37 facilitates chemokine production and leukocyte recruitment engaging Cdc42/Rac1 Rho GTPase via GPCR and the JNK MAPK pathway. In contrast, LL-37-mediated anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1RA production is independent of either Rho or Ras GTPase. The results of this study suggest that Cdc42 Rho GTPase may be the molecular switch that controls the opposing functions of LL-37 in the process of inflammation.
Keywords: Cdc42 RhoGTPase; JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase; LL-37; cathelicidin; cell migration; host defense peptide; inflammation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human cathelicidin LL-37 and its derivative IG-19 regulate interleukin-32-induced inflammation.Immunology. 2014 Sep;143(1):68-80. doi: 10.1111/imm.12291. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24666281 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc42 downregulates MMP-1 expression by inhibiting the ERK1/2 pathway.J Cell Sci. 2005 Mar 15;118(Pt 6):1173-83. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01707. Epub 2005 Feb 22. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15728253
-
Intracellular receptor for human host defense peptide LL-37 in monocytes.J Immunol. 2009 Aug 15;183(4):2688-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802586. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19605696
-
Reprint of Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Dec;17(4):1185-97. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24263067 Review.
-
Impact of LL-37 on anti-infective immunity.J Leukoc Biol. 2005 Apr;77(4):451-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0704380. Epub 2004 Nov 29. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15569695 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory Peptides as Vaccine Adjuvants and Antimicrobial Agents.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;17(2):201. doi: 10.3390/ph17020201. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399416 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages immunomodulation induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis and oral antimicrobial peptides.Odontology. 2023 Oct;111(4):778-792. doi: 10.1007/s10266-023-00798-w. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Odontology. 2023. PMID: 36897441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cathelicidin and Calprotectin Are Disparately Altered in Murine Models of Inflammatory Arthritis and Airway Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01932. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973796 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Biological Activities for a Novel 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline Conjugate with Dipeptide Derivatives: Insights from Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 12;8(51):48843-48854. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05961. eCollection 2023 Dec 26. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38162790 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of IL-17A/F and TNF-α uniquely alters the bronchial epithelial cell proteome to enhance proteins that augment neutrophil migration.J Inflamm (Lond). 2022 Dec 14;19(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12950-022-00323-w. J Inflamm (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36517803 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

