Insulin Hexamer-Caged Gadolinium Ion as MRI Contrast-o-phore
- PMID: 29873848
- PMCID: PMC6347121
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201801388
Insulin Hexamer-Caged Gadolinium Ion as MRI Contrast-o-phore
Abstract
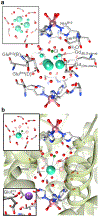
High-relaxivity protein-complexes of GdIII are being pursued as MRI contrast agents in hope that they can be used at much lower doses that would minimize toxic-side effects of GdIII release from traditional contrast agents. We construct here a new type of protein-based MRI contrast agent, a proteinaceous cage based on a stable insulin hexamer in which GdIII is captured inside a water filled cavity. The macromolecular structure and the large number of "free" GdIII coordination sites available for water binding lead to exceptionally high relaxivities per one GdIII ion. The GdIII slowly diffuses out of this cage, but this diffusion can be prevented by addition of ligands that bind to the hexamer. The ligands that trigger structural changes in the hexamer, SCN- , Cl- and phenols, modulate relaxivities through an outside-in signaling that is allosterically transduced through the protein cage. Contrast-o-phores based on protein-caged metal ions have potential to become clinical contrast agents with environmentally-sensitive properties.
Keywords: contrast agent; environmentally sensitive; gadolinium; insulin hexamer; proteins.
© 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
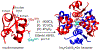
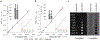
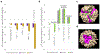
Similar articles
-
GdIII complexes with fast water exchange and high thermodynamic stability: potential building blocks for high-relaxivity MRI contrast agents.Chemistry. 2003 Aug 4;9(15):3555-66. doi: 10.1002/chem.200204612. Chemistry. 2003. PMID: 12898682
-
Gadolinium(III) complexes of mono- and diethyl esters of monophosphonic acid analogue of DOTA as potential MRI contrast agents: solution structures and relaxometric studies.Dalton Trans. 2007 Jan 28;(4):493-501. doi: 10.1039/b612876a. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Dalton Trans. 2007. PMID: 17213936
-
Separation and characterization of the two diastereomers for [Gd(DTPA-bz-NH2)(H2O)]2-, a common synthon in macromolecular MRI contrast agents: their water exchange and isomerization kinetics.Inorg Chem. 2005 May 16;44(10):3561-8. doi: 10.1021/ic048645d. Inorg Chem. 2005. PMID: 15877439
-
Gd-hydroxypyridinone (HOPO)-based high-relaxivity magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents.Acc Chem Res. 2009 Jul 21;42(7):938-47. doi: 10.1021/ar800250h. Acc Chem Res. 2009. PMID: 19505089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclen-based Gd3+ complexes as MRI contrast agents: Relaxivity enhancement and ligand design.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Nov 15;24(22):5663-5684. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.09.069. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27729196 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

