Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) Metabolic, Satiety, and Mood State Effects at Rest and during Prolonged Exercise
- PMID: 28809814
- PMCID: PMC5579675
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9080882
Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) Metabolic, Satiety, and Mood State Effects at Rest and during Prolonged Exercise
Abstract
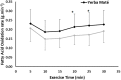
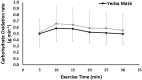
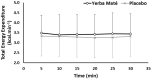
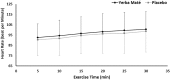
Yerba Maté (YM), has become a popular herb ingested for enhancing metabolic health and weight-loss outcomes. No studies have tested the combined metabolic, satiety, and psychomotor effects of YM during exercise. We tested whether YM ingestion affects fatty acid oxidation (FAO), profile of mood state score (POMS), and subjective appetite scale (VAS), during prolonged moderate exercise. Twelve healthy active females were randomized to ingest either 2 g of YM or placebo (PLC) in a repeated-measures design. Participants rested for 120 min before performing a 30-min cycling exercise corresponding to individuals' crossover point intensity (COP). FAO, determined using indirect calorimetry, was significantly higher during the 30-min exercise in YM vs. PLC (0.21 ± 0.07 vs. 0.17 ± 0.06 g/min, p < 0.05). VAS scores for hunger, prospective eating, and desire to eat were all reduced (p < 0.05). Whereas, POMS measures of focus, energy, and concentration were all increased (p < 0.05). There was no significant time-effect for any of the measured variables, nor was there any interaction effects between YM treatment and time. Combining YM intake with prolonged exercise at targeted "fat-loss"' intensities augments FAO and improves measures of satiety and mood state. Such positive combined metabolic, satiety, and psychomotor effects may provide an important role for designing future fat and weight-loss lifestyle interventions.
Keywords: appetite; endurance-exercise; fat-loss; metabolism; psychomotor; thermogenic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Yerba Maté (Illex Paraguariensis) ingestion augments fat oxidation and energy expenditure during exercise at various submaximal intensities.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014 Sep 2;11:42. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-11-42. eCollection 2014. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014. PMID: 25342955 Free PMC article.
-
Acute effectiveness of a "fat-loss" product on substrate utilization, perception of hunger, mood state and rate of perceived exertion at rest and during exercise.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Nov 25;12:44. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0105-8. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26612980 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolic and Performance Effects of Yerba Mate on Well-trained Cyclists.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018 Apr;50(4):817-826. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001482. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018. PMID: 29117073 Clinical Trial.
-
The positive effects of yerba maté (Ilex paraguariensis) in obesity.Nutrients. 2015 Jan 22;7(2):730-50. doi: 10.3390/nu7020730. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 25621503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yerba Mate Tea (Ilex paraguariensis): a comprehensive review on chemistry, health implications, and technological considerations.J Food Sci. 2007 Nov;72(9):R138-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00535.x. J Food Sci. 2007. PMID: 18034743 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Mercury Content in Various Types of Tea (Camellia sinensis) and Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis).Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 1;19(9):5491. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095491. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564885 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Supplementation of Yerba Mate Extract Did Not Change Muscle Strength in Physically Active Men Following the Strength Muscle Test: A Pilot Clinical Trial.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 24;14(13):2619. doi: 10.3390/nu14132619. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807800 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Yerba Mate-A Long but Current History.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 21;13(11):3706. doi: 10.3390/nu13113706. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34835962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-food Interactions in the Era of Molecular Big Data, Machine Intelligence, and Personalized Health.Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2022 Nov 14;13(1):27-50. doi: 10.2174/2212798412666220620104809. Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2022. PMID: 36173075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Appetite-Suppressing and Satiety-Increasing Bioactive Phytochemicals: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 17;11(9):2238. doi: 10.3390/nu11092238. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31533291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastos D.H.M., De Oliveira D.M., Matsumoto R.L.T., Carvalho P.O., Ribeiro M.L. Yerba maté: Pharmacological properties, research and biotechnology. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2007;1:37–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

