Telomerase antagonist imetelstat increases radiation sensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 28099140
- PMCID: PMC5355123
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14618
Telomerase antagonist imetelstat increases radiation sensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
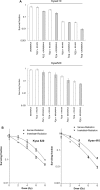
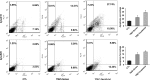
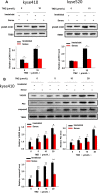
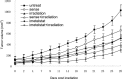
The morbidity and mortality of esophageal cancer is one of the highest around the world and the principal therapeutic method is radiation. Thus, searching for sensitizers with lower toxicity and higher efficiency to improve the efficacy of radiation therapy is critical essential. Our research group has previously reported that imetelstat, the thio-phosphoramidate oligonucleotide inhibitor of telomerase, can decrease cell proliferation and colony formation ability as well as increase DNA breaks induced by radiation in esophageal cancer cells. Further study in this project showed that imetelstat significantly sensitized esophageal cancer cells to radiation in vitro. Later study showed that imetelstat leads to increased cell apoptosis. We also measured the expression level of several DNA repair and apoptosis signaling proteins. pS345 CHK1, γ-H2AX, p53 and caspase3 expression were up-regulated in imetelstat treated cells, identifying these factors as molecular markers. Mouse in vivo model using imetelstat at clinically achievable concentrations and fractionated irradiation scheme yielded results demonstrating radiosensitization effect. Finally, TUNEL assay, caspase 3 and Ki67 staining in tumor tissue proved that imetelstat sensitized esophageal cancer to radiation in vivo through promoting cell apoptosis and inhibiting cell proliferation. Our study supported imetelstat increase radiation sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through inducing cell apoptosis and the specific inhibitor of telomerase might serve as a potential novel therapeutic tool for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma therapy.
Keywords: apoptosis; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; radiosensitization; telomerase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Telomerase antagonist imetelstat inhibits esophageal cancer cell growth and increases radiation-induced DNA breaks.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Dec;1823(12):2130-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22906540
-
Effect of telomerase inhibition on preclinical models of malignant rhabdoid tumor.Cancer Genet. 2014 Sep;207(9):403-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Cancer Genet. 2014. PMID: 25441685
-
The HSP90 inhibitor alvespimycin enhances the potency of telomerase inhibition by imetelstat in human osteosarcoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(6):949-57. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1040964. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25920748 Free PMC article.
-
Imetelstat (GRN163L)--telomerase-based cancer therapy.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010;184:221-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-01222-8_16. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20072842 Review.
-
Telomerase inhibitors for the treatment of brain tumors and the potential of intranasal delivery.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2010 Apr;12(2):168-75. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20373260 Review.
Cited by
-
Telomerase inhibition decreases esophageal squamous carcinoma cell migration and invasion.Oncol Lett. 2020 Sep;20(3):2870-2880. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11810. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32782603 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-138-5p Suppresses Cell Growth and Migration in Melanoma by Targeting Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase.Genes (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;12(12):1931. doi: 10.3390/genes12121931. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946880 Free PMC article.
-
The CINs of Polo-Like Kinase 1 in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 13;12(10):2953. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102953. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting hallmarks of cancer to enhance radiosensitivity in gastrointestinal cancers.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 May;17(5):298-313. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0247-2. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32005946 Review.
-
Establishment and characterization of an immortalized bovine intestinal epithelial cell line.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad215. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad215. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37351870 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

