Using anti-poly(ethylene glycol) bioparticles for the quantitation of PEGylated nanoparticles
- PMID: 27991598
- PMCID: PMC5171718
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39119
Using anti-poly(ethylene glycol) bioparticles for the quantitation of PEGylated nanoparticles
Abstract
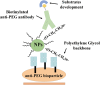
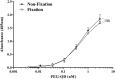
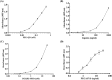
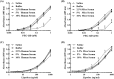
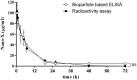
Attachment of polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules to nanoparticles (PEGylation) is a widely-used method to improve the stability, biocompatibility and half-life of nanomedicines. However, the evaluation of the PEGylated nanomedicine pharmacokinetics (PK) requires the decomposition of particles and purification of lead compounds before analysis by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry, etc. Therefore, a method to directly quantify un-decomposed PEGylated nanoparticles is needed. In this study, we developed anti-PEG bioparticles and combined them with anti-PEG antibodies to generate a quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for direct measurement of PEGylated nanoparticles without compound purification. The anti-PEG bioparticles quantitative ELISA directly quantify PEG-quantum dots (PEG-QD), PEG-stabilizing super-paramagnetic iron oxide (PEG-SPIO), Lipo-Dox and PEGASYS and the detection limits were 0.01 nM, 0.1 nM, 15.63 ng/mL and 0.48 ng/mL, respectively. Furthermore, this anti-PEG bioparticle-based ELISA tolerated samples containing up to 10% mouse or human serum. There was no significant difference in pharmacokinetic studies of radiolabeled PEG-nanoparticles (Nano-X-111In) through anti-PEG bioparticle-based ELISA and a traditional gamma counter. These results suggest that the anti-PEG bioparticle-based ELISA may provide a direct and effective method for the quantitation of any whole PEGylated nanoparticles without sample preparation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optimization of an Anti-poly(ethylene glycol) (anti-PEG) Cell-Based Capture System To Quantify PEG and PEGylated Molecules.Anal Chem. 2016 Dec 20;88(24):12371-12379. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03614. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Anal Chem. 2016. PMID: 28193011
-
Sensitivity of PEGylated interferon detection by anti-polyethylene glycol (PEG) antibodies depends on PEG length.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Aug 21;24(8):1408-13. doi: 10.1021/bc3006144. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 23837865
-
Sensitive quantification of PEGylated compounds by second-generation anti-poly(ethylene glycol) monoclonal antibodies.Bioconjug Chem. 2010 Jul 21;21(7):1264-70. doi: 10.1021/bc100067t. Bioconjug Chem. 2010. PMID: 20536171
-
Analytical measurement of PEGylated molecules.Bioconjug Chem. 2012 May 16;23(5):881-99. doi: 10.1021/bc200478w. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Bioconjug Chem. 2012. PMID: 22242549 Review.
-
Antibodies against polyethylene glycol in human blood: A literature review.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2020 Mar-Apr;102:106678. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2020.106678. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2020. PMID: 31981619 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Mobility Spectrometry-Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Multiple Ion Monitoring Coupled with in Source-Collision Induced Dissociation: A New Strategy for the Quantitative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Polymer Excipients in Rat Plasma.Molecules. 2023 Jun 15;28(12):4782. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124782. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375337 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a highly sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) through use of poly-protein G-expressing cell-based microplates.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 14;8(1):17868. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36192-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30552393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chao T. C. et al.. A dose-escalating pilot study of sterically stabilized, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Lipo-Dox) in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Invest 21, 837–847 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

