Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia - The Molecular Mechanisms
- PMID: 27065949
- PMCID: PMC4815176
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00029
Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia - The Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
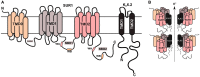
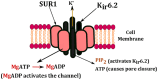
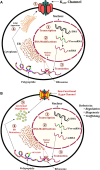
Under normal physiological conditions, pancreatic β-cells secrete insulin to maintain fasting blood glucose levels in the range 3.5-5.5 mmol/L. In hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (HH), this precise regulation of insulin secretion is perturbed so that insulin continues to be secreted in the presence of hypoglycemia. HH may be due to genetic causes (congenital) or secondary to certain risk factors. The molecular mechanisms leading to HH involve defects in the key genes regulating insulin secretion from the β-cells. At this moment, in time genetic abnormalities in nine genes (ABCC8, KCNJ11, GCK, SCHAD, GLUD1, SLC16A1, HNF1A, HNF4A, and UCP2) have been described that lead to the congenital forms of HH. Perinatal stress, intrauterine growth retardation, maternal diabetes mellitus, and a large number of developmental syndromes are also associated with HH in the neonatal period. In older children and adult's insulinoma, non-insulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome and post bariatric surgery are recognized causes of HH. This review article will focus mainly on describing the molecular mechanisms that lead to unregulated insulin secretion.
Keywords: KATP channels; congenital hyperinsulinism; glucose; hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia; insulin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in the diagnosis and management of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia.Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Feb;5(2):101-12. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet1046. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19165222 Review.
-
The Diagnosis and Management of Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;7(2):86-97. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.1891. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26316429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of congenital hyperinsulinism.J Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Apr;54(2):R119-29. doi: 10.1530/JME-15-0016. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25733449 Review.
-
Noninsulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycaemia in adults--a spotlight on its genetics.Endokrynol Pol. 2015;66(4):344-54. doi: 10.5603/EP.2015.0044. Endokrynol Pol. 2015. PMID: 26323472 Review.
-
Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Diagnosis and Treatment Update.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017 Dec 30;9(Suppl 2):69-87. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.2017.S007. Epub 2017 Dec 27. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 29280746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nesidioblastosis in Pregnancy: Navigating the Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges of a Rare Condition.Cureus. 2024 Oct 21;16(10):e71985. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71985. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39434931 Free PMC article.
-
Both Low Blood Glucose and Insufficient Treatment Confer Risk of Neurodevelopmental Impairment in Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Multinational Cohort Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 Jul 10;8:156. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00156. eCollection 2017. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28740482 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Cause of Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia: Kabuki Syndrome.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2021 Nov 25;13(4):452-455. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2020.2020.0065. Epub 2020 Aug 24. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 32830475 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-sensing receptor expression in insulin-negative, intrapancreatic insulinoma.Br J Surg. 2022 Sep 9;109(10):1015-1016. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znac173. Br J Surg. 2022. PMID: 35909304 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Microtubules in Pancreatic β Cells: Convoluted Roadways Toward Precision.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 8;10:915206. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.915206. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35874834 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

