Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus protects against alcohol-induced liver damage by modulating inflammatory mediators in mice and HepG2 cells
- PMID: 25690093
- PMCID: PMC4344618
- DOI: 10.3390/md13021051
Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus protects against alcohol-induced liver damage by modulating inflammatory mediators in mice and HepG2 cells
Abstract
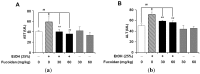
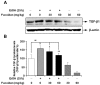
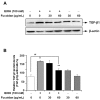
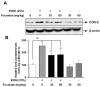
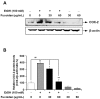
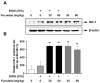
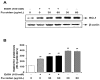
Fucoidan is an l-fucose-enriched sulfated polysaccharide isolated from brown algae and marine invertebrates. In this study, we investigated the protective effect of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus on alcohol-induced murine liver damage. Liver injury was induced by oral administration of 25% alcohol with or without fucoidan (30 mg/kg or 60 mg/kg) for seven days. Alcohol administration increased serum aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase levels, but these increases were suppressed by the treatment of fucoidan. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), a liver fibrosis-inducing factor, was highly expressed in the alcohol-fed group and human hepatoma HepG2 cell; however, the increase in TGF-β1 expression was reduced following fucoidan administration. Treatment with fucoidan was also found to significantly reduce the production of inflammation-promoting cyclooygenase-2 and nitric oxide, while markedly increasing the expression of the hepatoprotective enzyme, hemeoxygenase-1, on murine liver and HepG2 cells. Taken together, the antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects of fucoidan on alcohol-induced liver damage may provide valuable insights into developing new therapeutics or interventions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fucoidan extracted from Fucus evanescens prevents endotoxin-induced damage in a mouse model of endotoxemia.Mar Drugs. 2014 Jan 31;12(2):886-98. doi: 10.3390/md12020886. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24492521 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus on liver fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway-mediated inhibition of extracellular matrix and autophagy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Feb 12;10:619-30. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S98740. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 26929597 Free PMC article.
-
COMPARATIVE EFFECT OF FUCOIDAN FROM ALGA FUCUS VESICULOSUS AND ITS FRACTIONS, OBTAINED BY ANION-EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY, ON CELL LINES HeLa G-63, Hep G2 AND CHANG LIVER.Tsitologiia. 2017;59(2):148-55. Tsitologiia. 2017. PMID: 30199163 English, Russian.
-
The potent activity of sulfated polysaccharide, ascophyllan, isolated from Ascophyllum nodosum to induce nitric oxide and cytokine production from mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells: Comparison between ascophyllan and fucoidan.Nitric Oxide. 2011 Nov 30;25(4):407-15. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2011.10.001. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Nitric Oxide. 2011. PMID: 22024029
-
Potential Beneficial Actions of Fucoidan in Brain and Liver Injury, Disease, and Intoxication-Potential Implication of Sirtuins.Mar Drugs. 2020 May 5;18(5):242. doi: 10.3390/md18050242. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32380741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Fucoidan in Alleviating Histamine-Induced Liver Injury: Insights from Mice Studies.Foods. 2024 May 14;13(10):1523. doi: 10.3390/foods13101523. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38790823 Free PMC article.
-
Triterpenoids Extracted From Antrodia cinnamomea Mycelia Attenuate Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in C57BL/6 Mice via Suppression Inflammatory Response.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jul 3;11:1113. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01113. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32719658 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Potential of Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum against Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Vitro and Vivo.Nutrients. 2019 Apr 27;11(5):963. doi: 10.3390/nu11050963. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31035540 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Effects of Antrodia cinnamomea: The Modulation of Oxidative Stress Signaling in a Mouse Model of Alcohol-Induced Acute Liver Injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7841823. doi: 10.1155/2017/7841823. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28337253 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of fucoidan on ethanol-induced liver injury and steatosis in mice and the underlying mechanism.Food Nutr Res. 2021 Apr 20;65. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v65.5384. eCollection 2021. Food Nutr Res. 2021. PMID: 33994911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park S.H., Kim C.H., Kim D.J., Park J.H., Kim T.O., Yang S.Y., Moon Y.S., Kim T.N., Kim H.K., Park H.Y., et al. Prevalence of alcoholic liver disease among Korean adults: results from the fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2009. Subst. Use Misuse. 2011;46:1755–1762. doi: 10.3109/10826084.2011.620053. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

