Large-scale discovery of novel genetic causes of developmental disorders
- PMID: 25533962
- PMCID: PMC5955210
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14135
Large-scale discovery of novel genetic causes of developmental disorders
Abstract
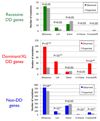
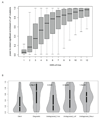
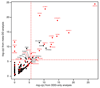
Despite three decades of successful, predominantly phenotype-driven discovery of the genetic causes of monogenic disorders, up to half of children with severe developmental disorders of probable genetic origin remain without a genetic diagnosis. Particularly challenging are those disorders rare enough to have eluded recognition as a discrete clinical entity, those with highly variable clinical manifestations, and those that are difficult to distinguish from other, very similar, disorders. Here we demonstrate the power of using an unbiased genotype-driven approach to identify subsets of patients with similar disorders. By studying 1,133 children with severe, undiagnosed developmental disorders, and their parents, using a combination of exome sequencing and array-based detection of chromosomal rearrangements, we discovered 12 novel genes associated with developmental disorders. These newly implicated genes increase by 10% (from 28% to 31%) the proportion of children that could be diagnosed. Clustering of missense mutations in six of these newly implicated genes suggests that normal development is being perturbed by an activating or dominant-negative mechanism. Our findings demonstrate the value of adopting a comprehensive strategy, both genome-wide and nationwide, to elucidate the underlying causes of rare genetic disorders.
Figures
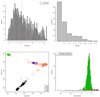
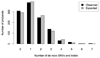
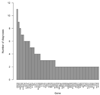
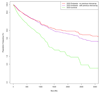


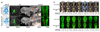
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and architecture of de novo mutations in developmental disorders.Nature. 2017 Feb 23;542(7642):433-438. doi: 10.1038/nature21062. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28135719 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diagnosis of developmental disorders in the DDD study: a scalable analysis of genome-wide research data.Lancet. 2015 Apr 4;385(9975):1305-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61705-0. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 25529582 Free PMC article.
-
Whole exome sequencing in family trios reveals de novo mutations in PURA as a cause of severe neurodevelopmental delay and learning disability.J Med Genet. 2014 Dec;51(12):806-13. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102798. Epub 2014 Oct 23. J Med Genet. 2014. PMID: 25342064 Free PMC article.
-
[XXX syndrome].Nihon Rinsho. 2006 Jun 28;Suppl 2:522-4. Nihon Rinsho. 2006. PMID: 16817456 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
De novo MEIS2 mutation causes syndromic developmental delay with persistent gastro-esophageal reflux.J Hum Genet. 2016 Sep;61(9):835-8. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.54. Epub 2016 May 26. J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27225850 Review.
Cited by
-
Variants in the degron of AFF3 are associated with intellectual disability, mesomelic dysplasia, horseshoe kidney, and epileptic encephalopathy.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 May 6;108(5):857-873. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.04.001. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33961779 Free PMC article.
-
A High-Quality Blue Whale Genome, Segmental Duplications, and Historical Demography.Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Mar 1;41(3):msae036. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae036. Mol Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38376487 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitating collaboration in rare genetic disorders through effective matchmaking in DECIPHER.Hum Mutat. 2015 Oct;36(10):941-9. doi: 10.1002/humu.22842. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Hum Mutat. 2015. PMID: 26220709 Free PMC article.
-
A synonymous UPF3B variant causing a speech disorder implicates NMD as a regulator of neurodevelopmental disorder gene networks.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Aug 29;29(15):2568-2578. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa151. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32667670 Free PMC article.
-
The frontiers of sequencing in undiagnosed neurodevelopmental diseases.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020 Dec;65:76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020. PMID: 32599523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- OMIM. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM. 2014 <http://omim.org>
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

