Hepatotoxicity induced by trastuzumab used for breast cancer adjuvant therapy: a case report
- PMID: 25491149
- PMCID: PMC4307619
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-417
Hepatotoxicity induced by trastuzumab used for breast cancer adjuvant therapy: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Trastuzumab is generally considered a highly safe drug, but there have been cases of infusion reaction and cardiotoxicity. This report will present a rare case of hepatotoxicity induced by trastuzumab used for adjuvant therapy of human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2-positive breast cancer.
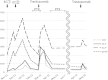
Case presentation: The patient was a 60-year-old Japanese postmenopausal woman with a non-contributory past medical history. She presented for detailed examination of an abnormality in her left breast. She had left breast cancer (T2N1M0, stage IIB) that was positive for estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor and was human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 3+. She began receiving epirubicin and cyclophosphamide therapy but developed hepatotoxicity (aspartate aminotransferase 43 U/L, alanine aminotransferase 104 U/L, alkaline phosphatase 634 U/L, and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase 383 U/L). Thus, the therapy was discontinued after two cycles, and a weekly paclitaxel therapy was begun. After the absence of an adverse event was confirmed, she also began receiving trastuzumab (4 mg/kg) at the second cycle. However, hepatotoxicity (aspartate aminotransferase 267 U/L, alanine aminotransferase 246 U/L, alkaline phosphatase 553 U/L, and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase 240 U/L) developed again, and trastuzumab was discontinued. She received paclitaxel monotherapy for a total of four cycles and subsequently underwent partial mastectomy and axillary dissection. After completing adjuvant radiation therapy (breast, 50 Gy), she received trastuzumab administration (4 mg/kg) but hepatotoxicity (aspartate aminotransferase 47 U/L, alanine aminotransferase 102 U/L, alkaline phosphatase 377 U/L, and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase 91 U/L) recurred. Thus, it was discontinued again. There was no hepatitis B or C virus infection, and a drug-induced lymphocyte stimulation test revealed a positive reaction to trastuzumab (stimulation index: 227%). Thereafter she has used only oral letrozole (2.5mg/day) and no recurrent cancer has been observed.
Conclusions: Although trastuzumab is a highly safe drug, one must be mindful of its risk for hepatotoxicity. Periodic monitoring of liver functions is necessary during trastuzumab therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trastuzumab-induced hepatotoxicity.Ann Pharmacother. 2008 Oct;42(10):1497-501. doi: 10.1345/aph.1L217. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Ann Pharmacother. 2008. PMID: 18780811
-
[Two cases of recurrent breast cancer with regional lymph node metastases showing a complete response to trastuzumab and paclitaxel treatment].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2006 Sep;33(9):1301-3. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2006. PMID: 16969029 Japanese.
-
Successful neoadjuvant therapy with trastuzumab, paclitaxel and epirubicin for an elderly patient with inflammatory breast cancer.Anticancer Res. 2010 Feb;30(2):581-5. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20332474
-
[Liver arterial infusion chemotherapy with adjuvant trastuzumab for the simultaneous treatment of liver and breast cancer-a case report].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2012 Nov;39(11):1707-10. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2012. PMID: 23152024 Review. Japanese.
-
Grade 3 trastuzumab-induced neutropenia in breast cancer patient.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2014 Apr;20(2):154-7. doi: 10.1177/1078155213487394. Epub 2013 Jun 26. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2014. PMID: 23804626 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of hepatotoxicity of chemotherapy and targeted agents.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Jul 15;11(7):3461-3474. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34354855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety profile of trastuzumab originator vs biosimilars: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Sep 18. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03642-x. Online ahead of print. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39292389 Review.
-
Nano-Encapsulation of Coenzyme Q10 in Secondary and Tertiary Nano-Emulsions for Enhanced Cardioprotection and Hepatoprotection in Human Cardiomyocytes and Hepatocytes During Exposure to Anthracyclines and Trastuzumab.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jul 9;15:4859-4876. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S245170. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32764923 Free PMC article.
-
Garlic Extract Alleviates Trastuzumab-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats Through Its Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antihyperlipidemic Effects.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Nov 27;14:6305-6316. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S339092. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34866928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE, Jr, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman PA, Swain SM, Pisansky TM, Fehrenbacher L, Kutteh LA, Vogel VG, Visscher DW, Yothers G, Jenkins RB, Brown AM, Dakhil SR, Mamounas EP, Lingle WL, Klein PM, Ingle JN, Wolmark N. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1673–1684. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052122. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, Gianni L, Baselga J, Bell R, Jackisch C, Cameron D, Dowsett M, Barrios CH, Steger G, Huang CS, Andersson M, Inbar M, Lichinitser M, Láng I, Nitz U, Iwata H, Thomssen C, Lohrisch C, Suter TM, Rüschoff J, Suto T, Greatorex V, Ward C, Straehle C, McFadden E, et al. Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1659–1672. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052306. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vogel CL, Cobleigh MA, Tripathy D, Gutheil JC, Harris LN, Fehrenbacher L, Slamon DJ, Murphy M, Novotny WF, Burchmore M, Shak S, Stewart SJ, Press M. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(3):719–726. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.3.719. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cobleigh MA, Vogel CL, Tripathy D, Robert NJ, Scholl S, Fehrenbacher L, Wolter JM, Paton V, Shak S, Lieberman G, Slamon DJ. Multinational study of the efficacy and safety of humanized anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody in women who have HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer that has progressed after chemotherapy for metastatic disease. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(9):2639–2648. - PubMed
-
- Masood S, Bui MM. Assessment of HER-2/neu overexpression in primary breast cancers and their metastatic lesions: an immunohistochemical study. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2000;30:259–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

