Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from a phase III trial
- PMID: 24019545
- PMCID: PMC5569677
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.47.4940
Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from a phase III trial
Abstract
Purpose: Tivozanib is a potent and selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1), -2, and -3. This phase III trial compared tivozanib with sorafenib as initial targeted therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
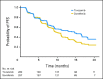
Patients and methods: Patients with metastatic RCC, with a clear cell component, prior nephrectomy, measurable disease, and 0 or 1 prior therapies for metastatic RCC were randomly assigned to tivozanib or sorafenib. Prior VEGF-targeted therapy and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor were not permitted. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS) by independent review.
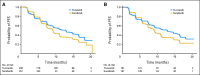
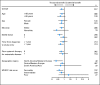
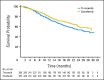
Results: A total of 517 patients were randomly assigned to tivozanib (n = 260) or sorafenib (n = 257). PFS was longer with tivozanib than with sorafenib in the overall population (median, 11.9 v 9.1 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.797; 95% CI, 0.639 to 0.993; P = .042). One hundred fifty-six patients (61%) who progressed on sorafenib crossed over to receive tivozanib. The final overall survival (OS) analysis showed a trend toward longer survival on the sorafenib arm than on the tivozanib arm (median, 29.3 v 28.8 months; HR, 1.245; 95% CI, 0.954 to 1.624; P = .105). Adverse events (AEs) more common with tivozanib than with sorafenib were hypertension (44% v 34%) and dysphonia (21% v 5%). AEs more common with sorafenib than with tivozanib were hand-foot skin reaction (54% v 14%) and diarrhea (33% v 23%).
Conclusion: Tivozanib demonstrated improved PFS, but not OS, and a differentiated safety profile, compared with sorafenib, as initial targeted therapy for metastatic RCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Preserving the sanctity of overall survival for drugs approved on the basis of progression-free survival: tivozanib as a case study.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Oct 20;31(30):3746-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.4869. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24019543 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of tivozanib treatment after sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: crossover of a phase 3 study.Eur J Cancer. 2018 May;94:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29547835 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized phase III trial of temsirolimus versus sorafenib as second-line therapy after sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Mar 10;32(8):760-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.3961. Epub 2013 Dec 2. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24297950 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tivozanib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (TIVO-3): a phase 3, multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label study.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Jan;21(1):95-104. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30735-1. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31810797 Clinical Trial.
-
Profile of tivozanib and its potential for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013 Jun 21;7:519-27. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S31442. Print 2013. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013. PMID: 23818763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First-line therapy for treatment-naive patients with advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of published randomized controlled trials.Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Jun;27(5):383-97. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000335. Anticancer Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26886011 Review.
Cited by
-
Tivozanib in renal cell carcinoma: a new approach to previously treated disease.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 May 22;12:1758835920923818. doi: 10.1177/1758835920923818. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32547647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A phase II study of tivozanib in patients with metastatic and nonresectable soft-tissue sarcomas.Ann Oncol. 2017 Jan 1;28(1):121-127. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw444. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27771610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma and their targeted therapies: a review.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4(5):941-961. doi: 10.37349/etat.2023.00175. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023. PMID: 37970211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tivozanib mediated inhibition of c-Kit/SCF signaling on Tregs and MDSCs and reversal of tumor induced immune suppression correlates with survival of HCC patients.Oncoimmunology. 2020 Sep 30;9(1):1824863. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1824863. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 33101775 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of tivozanib on patient outcomes in treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Aug 16;11:7779-7785. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S206105. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31496820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costa LJ, Drabkin HA: Renal cell carcinoma: New developments in molecular biology and potential for targeted therapies Oncologist 12:1404–1415,2007 - PubMed
-
- Escudier B Eisen T Stadler WM, etal: Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma N Engl J Med 356:125–134,2007 - PubMed
-
- Rini BI Escudier B Tomczak P, etal: Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): A randomised phase 3 trial Lancet 378:1931–1939,2011 - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ Hutson TE Tomczak P, etal: Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma N Engl J Med 356:115–124,2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

