Mutations in CD96, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, cause a form of the C (Opitz trigonocephaly) syndrome
- PMID: 17847009
- PMCID: PMC2227933
- DOI: 10.1086/522014
Mutations in CD96, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, cause a form of the C (Opitz trigonocephaly) syndrome
Abstract
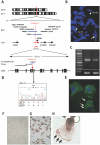
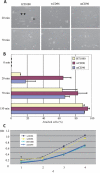
The C syndrome is characterized by trigonocephaly and associated anomalies, such as unusual facies, psychomotor retardation, redundant skin, joint and limb abnormalities, and visceral anomalies. In an individual with the C syndrome who harbors a balanced chromosomal translocation, t(3;18)(q13.13;q12.1), we discovered that the TACTILE gene for CD96, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, was disrupted at the 3q13.3 breakpoint. In mutation analysis of nine karyotypically normal patients given diagnoses of the C or C-like syndrome, we identified a missense mutation (839C-->T, T280M) in exon 6 of the CD96 gene in one patient with the C-like syndrome. The missense mutation was not found among 420 unaffected Japanese individuals. Cells with mutated CD96 protein (T280M) lost adhesion and growth activities in vitro. These findings indicate that CD96 mutations may cause a form of the C syndrome by interfering with cell adhesion and growth.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Opitz trigonocephaly C syndrome in a boy with a de novo balanced reciprocal translocation t(3;18)(q13.13;q12.1).Am J Med Genet A. 2006 Aug 1;140(15):1655-7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31341. Am J Med Genet A. 2006. PMID: 16835930
-
Screening of CD96 and ASXL1 in 11 patients with Opitz C or Bohring-Opitz syndromes.Am J Med Genet A. 2016 Jan;170A(1):24-31. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37418. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Am J Med Genet A. 2016. PMID: 26768331
-
Trisomy of 3pter in a patient with apparent C (trigonocephaly) syndrome.Am J Med Genet. 2000 Oct 2;94(4):311-5. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20001002)94:4<311::aid-ajmg9>3.0.co;2-u. Am J Med Genet. 2000. PMID: 11038445
-
Clinical findings in a patient with FGFR1 P252R mutation and comparison with the literature.Am J Med Genet. 2000 Jul 3;93(1):22-8. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20000703)93:1<22::aid-ajmg5>3.0.co;2-u. Am J Med Genet. 2000. PMID: 10861678 Review.
-
Baraitser-Winter cerebrofrontofacial syndrome.Clin Genet. 2017 Jul;92(1):3-9. doi: 10.1111/cge.12864. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Clin Genet. 2017. PMID: 27625340 Review.
Cited by
-
2011 William Allan Award introduction: John M. Opitz.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Mar 9;90(3):390-1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.01.011. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22405083 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Establishment of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay system for determining soluble CD96 and its application in the measurement of sCD96 in patients with viral hepatitis B and hepatic cirrhosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Feb;155(2):207-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03829.x. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19040604 Free PMC article.
-
De novo nonsense mutations in ASXL1 cause Bohring-Opitz syndrome.Nat Genet. 2011 Jun 26;43(8):729-31. doi: 10.1038/ng.868. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21706002
-
Bohring-Opitz (Oberklaid-Danks) syndrome: clinical study, review of the literature, and discussion of possible pathogenesis.Eur J Hum Genet. 2011 May;19(5):513-9. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.234. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21368916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Causes of Craniosynostosis: An Update.Mol Syndromol. 2019 Feb;10(1-2):6-23. doi: 10.1159/000492266. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Mol Syndromol. 2019. PMID: 30976276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Web Resources
-
- Database of Genomic Variants, http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/
-
- Ensembl Genome Browser, http://www.ensembl.org/index.html
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for CD96 [accession number NM_198196] and ZBED2 [accession number NM_024508.3])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.gov/Omim/ (for C syndrome, C-like syndrome, and cleft lip/palate–ectodermal dysplasia syndrome)
References
-
- Opitz JM, Johnson RC, McCreadie SR, Smith DW (1969) The C syndrome of multiple congenital anomalies. Birth Defects 5:161–166
-
- Gorlin RJ, Cohen MM Jr, Hennekam RCM (2001) Syndromes of the head and neck, 4th ed. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1145–1147
-
- Bohring A, Oudesluijs GG, Grange DK, Zampino G, Thierry P (2006) New cases of Bohring-Opitz syndrome, update, and critical review of the literature. Am J Med Genet A 140:1257–1263 - PubMed
-
- Osaki M, Makita Y, Miura J, Abe N, Noguchi S, Miyamoto A (2006) A Japanese boy with apparent Bohring-Opitz or “C-like” syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 140:897–899 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

