Absence of a paternally inherited FOXP2 gene in developmental verbal dyspraxia
- PMID: 17033973
- PMCID: PMC1698557
- DOI: 10.1086/508902
Absence of a paternally inherited FOXP2 gene in developmental verbal dyspraxia
Abstract
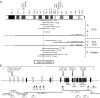
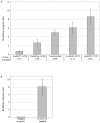
Mutations in FOXP2 cause developmental verbal dyspraxia (DVD), but only a few cases have been described. We characterize 13 patients with DVD--5 with hemizygous paternal deletions spanning the FOXP2 gene, 1 with a translocation interrupting FOXP2, and the remaining 7 with maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 7 (UPD7), who were also given a diagnosis of Silver-Russell Syndrome (SRS). Of these individuals with DVD, all 12 for whom parental DNA was available showed absence of a paternal copy of FOXP2. Five other individuals with deletions of paternally inherited FOXP2 but with incomplete clinical information or phenotypes too complex to properly assess are also described. Four of the patients with DVD also meet criteria for autism spectrum disorder. Individuals with paternal UPD7 or with partial maternal UPD7 or deletion starting downstream of FOXP2 do not have DVD. Using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, we show the maternally inherited FOXP2 to be comparatively underexpressed. Our results indicate that absence of paternal FOXP2 is the cause of DVD in patients with SRS with maternal UPD7. The data also point to a role for differential parent-of-origin expression of FOXP2 in human speech development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Speech and language impairment and oromotor dyspraxia due to deletion of 7q31 that involves FOXP2.Am J Med Genet A. 2006 Mar 1;140(5):509-14. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31110. Am J Med Genet A. 2006. PMID: 16470794
-
Genetic screening for maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 7 in prenatal and postnatal growth retardation of unknown cause.Pediatrics. 2002 Mar;109(3):441-8. doi: 10.1542/peds.109.3.441. Pediatrics. 2002. PMID: 11875139
-
No evidence for additional imprinting defects in Silver-Russell syndrome patients with maternal uniparental disomy 7 or 11p15 epimutation.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Dec;20(12):1329-31. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2007.20.12.1329. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 18341093
-
Epigenetics in Silver-Russell syndrome.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Jun;22(3):403-14. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2008.01.012. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18538282 Review.
-
Deletion of 7q31.1 supports involvement of FOXP2 in language impairment: clinical report and review.Am J Med Genet A. 2007 Apr 15;143A(8):791-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31632. Am J Med Genet A. 2007. PMID: 17330859 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the impact of FOXP1 mutations on developmental verbal dyspraxia.Eur J Hum Genet. 2009 Oct;17(10):1354-8. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.43. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19352412 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of genetic mechanisms regulating cortical neurogenesis.Dev Neurobiol. 2022 Jul;82(5):428-453. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22891. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Dev Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35670518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exome sequencing in sporadic autism spectrum disorders identifies severe de novo mutations.Nat Genet. 2011 Jun;43(6):585-9. doi: 10.1038/ng.835. Epub 2011 May 15. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21572417 Free PMC article.
-
miR-9 and miR-140-5p target FoxP2 and are regulated as a function of the social context of singing behavior in zebra finches.J Neurosci. 2013 Oct 16;33(42):16510-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0838-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24133256 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a de novo FOXP1 mutation and incidental discovery of inherited genetic variants contributing to a case of autism spectrum disorder and epilepsy.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Jul;7(7):e00751. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.751. Epub 2019 May 20. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31111659 Free PMC article.
References
Web Resources
-
- Chromosome 7 Annotation Project, http://www.chr7.org/ (for clinical tables, see http://www.chr7.org/clinical.php)
-
- Database of Genomic Variants, http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for markers HSC274–HSC279 [accession numbers BV123532, BV123533, BV123528, BV123529, BV123530, and BV123531, respectively])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for DVD, SRS, ADS, and WBS)
References
-
- Lai CS, Fisher SE, Hurst JA, Levy ER, Hodgson S, Fox M, Jeremiah S, Povey S, Jamison DC, Green ED, Vargha-Khadem F, Monaco AP (2000) The SPCH1 region on human 7q31: genomic characterization of the critical interval and localization of translocations associated with speech and language disorder. Am J Hum Genet 67:357–368 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hurst JA, Baraitser M, Auger E, Graham F, Norell S (1990) An extended family with a dominantly inherited speech disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol 32:352–355 - PubMed
-
- Shu W, Cho JY, Jiang Y, Zhang M, Weisz D, Elder GA, Schmeidler J, De Gasperi R, Sosa MA, Rabidou D, Santucci AC, Perl D, Morrisey E, Buxbaum JD (2005) Altered ultrasonic vocalization in mice with a disruption in the Foxp2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9643–964810.1073/pnas.0503739102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

