Enhancer-binding proteins with a forkhead-associated domain and the sigma54 regulon in Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body development
- PMID: 15668379
- PMCID: PMC549468
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409371102
Enhancer-binding proteins with a forkhead-associated domain and the sigma54 regulon in Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body development
Abstract
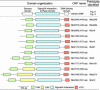
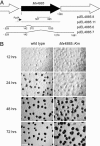
In response to starvation, Myxococcus xanthus initiates a developmental program that results in the formation of spore-filled, multicellular fruiting bodies. Many developmentally regulated genes in M. xanthus are transcribed from sigma(54) promoters, and these genes require enhancer-binding proteins. Here we report the finding of an unusual group of 12 genes encoding sigma(54)-dependent enhancer-binding proteins containing a forkhead-associated (FHA) domain as their N-terminal sensory domain. FHA domains in other proteins recognize phosphothreonine residues. An insertion mutation in one of these genes, Mx4885, caused a cell autonomous aggregation and sporulation defect. In-frame deletion mutants showed that the FHA domain is necessary for proper Mx4885 function. The altered pattern of developmental gene expression in the mutant implied that Mx4885 is on the pathway of response to the morphogenetic C-signal. Immunoblots specific for C-signal and FruA imply that the site of Mx4885 action is downstream of FruA synthesis on the C-signal transduction pathway. Mx4885 may help to coordinate the level of intracellular phosphorylated FruA (FruA-P) with the level of C-signal displayed on the signal donor cell. Because FHA domains respond to phosphothreonine-containing proteins, these results suggest a regulatory link to the abundant Ser/Thr protein kinases in M. xanthus.
Figures

Comment in
-
Eukaryotic-like signaling and gene regulation in a prokaryote that undergoes multicellular development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2681-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500157102. Epub 2005 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15710872 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Eukaryotic-like signaling and gene regulation in a prokaryote that undergoes multicellular development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2681-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500157102. Epub 2005 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15710872 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The enhancer binding protein Nla6 regulates developmental genes that are important for Myxococcus xanthus sporulation.J Bacteriol. 2015 Apr;197(7):1276-87. doi: 10.1128/JB.02408-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25645554 Free PMC article.
-
SigB, SigC, and SigE from Myxococcus xanthus homologous to sigma32 are not required for heat shock response but for multicellular differentiation.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Apr;3(2):287-93. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11321585
-
Dual regulation with Ser/Thr kinase cascade and a His/Asp TCS in Myxococcus xanthus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:111-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792684 Review.
-
Cell-cell interactions that direct fruiting body development in Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):363-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80301-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991. PMID: 1840894 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factor MrpC binds to promoter regions of hundreds of developmentally-regulated genes in Myxococcus xanthus.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 16;15:1123. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1123. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25515642 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of sensory complexity recorded in a myxobacterial genome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Oct 10;103(41):15200-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607335103. Epub 2006 Oct 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17015832 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxyethylarginine synthase genes show complex cross-regulation in Streptomyces clavuligerus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Jan;79(1):240-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02600-12. Epub 2012 Oct 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23104404 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations of the act promoter in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2007 Mar;189(5):1836-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.01618-06. Epub 2006 Dec 22. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17189369 Free PMC article.
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthase is involved in biosynthesis of isovaleryl-CoA in the myxobacterium Myxococcus xanthus during fruiting body formation.J Bacteriol. 2006 Sep;188(18):6524-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.00825-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16952943 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

