Structure of fosfomycin resistance protein FosA from transposon Tn2921
- PMID: 15075406
- PMCID: PMC2286755
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.03585004
Structure of fosfomycin resistance protein FosA from transposon Tn2921
Abstract
The crystal structure of fosfomycin resistance protein FosA from transposon Tn2921 has been established at a resolution of 2.5 A. The protein crystallized without bound Mn(II) and K+, ions crucial for efficient catalysis, providing a structure of the apo enzyme. The protein maintains the three-dimensional domain-swapped arrangement of the paired betaalphabetabetabeta-motifs observed in the genomically encoded homologous enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA1129). The basic architecture of the active site is also maintained, despite the absence of the catalytically essential Mn(II). However, the absence of K+, which has been shown to enhance enzymatic activity, appears to contribute to conformational heterogeneity in the K(+)-binding loops.
Figures


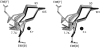
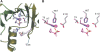
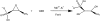
Similar articles
-
Phosphonoformate: a minimal transition state analogue inhibitor of the fosfomycin resistance protein, FosA.Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 2;43(43):13666-73. doi: 10.1021/bi048767h. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15504029
-
Crystal structure of a genomically encoded fosfomycin resistance protein (FosA) at 1.19 A resolution by MAD phasing off the L-III edge of Tl(+).J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Sep 18;124(37):11001-3. doi: 10.1021/ja026879v. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 12224946
-
EPR study of substrate binding to the Mn(II) active site of the bacterial antibiotic resistance enzyme FosA: a better way to examine Mn(II).J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Mar 13;124(10):2318-26. doi: 10.1021/ja012480f. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 11878987
-
Functional analysis of active site residues of the fosfomycin resistance enzyme FosA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 6;280(18):17786-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501052200. Epub 2005 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15741169
-
Mechanistic imperatives for the evolution of glutathione transferases.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998 Oct;2(5):618-23. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(98)80093-8. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998. PMID: 9818188 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthetic gene cluster of cetoniacytone A, an unusual aminocyclitol from the endosymbiotic Bacterium Actinomyces sp. Lu 9419.Chembiochem. 2009 Jan 26;10(2):304-14. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800527. Chembiochem. 2009. PMID: 19101977 Free PMC article.
-
Is a New Standard Needed for Diffusion Methods for In Vitro Susceptibility Testing of Fosfomycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa?Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Dec 7;60(2):1158-61. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02237-15. Print 2016 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26643341 Free PMC article.
-
Crossroads of Antibiotic Resistance and Biosynthesis.J Mol Biol. 2019 Aug 23;431(18):3370-3399. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.06.033. Epub 2019 Jul 6. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31288031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative epimerization in C(7)N-aminocyclitol biosynthesis is catalyzed by ValD, a large protein of the vicinal oxygen chelate superfamily.Chem Biol. 2009 May 29;16(5):567-76. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.04.006. Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19477421 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking peptidoglycan recycling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa attenuates intrinsic resistance to fosfomycin.Microb Drug Resist. 2014 Jun;20(3):231-7. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2014.0036. Epub 2014 May 12. Microb Drug Resist. 2014. PMID: 24819062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong, R.N. 2000. Mechanistic diversity in a metalloenzyme superfamily. Biochemistry 39 13625–13632. - PubMed
-
- Bernat, B.A. and Armstrong, R.N. 2001. Elementary steps in the acquisition of Mn2+ by the fosfomycin resistance protein (FosA). Biochemistry 40 12712–12718. - PubMed
-
- Bernat, B.A., Laughlin, L.T., and Armstrong, R.N. 1997. Fosfomycin resistance protein (FosA) is a manganese metalloglutathione transferase related to glyoxalase I and the extradiol dioxygenases. Biochemistry 36 3050–3055. - PubMed
-
- ———. 1998. Regiochemical and stereochemical course of the reaction catalyzed by the fosfomycin resistance protein, FosA. J. Org. Chem. 63 3778–3780.
-
- ———. 1999. Elucidation of a monovalent cation dependence and characterization of the divalent cation binding site of the fosfomycin resistance protein, FosA. Biochemistry 387462–7469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

