Ccr4p is the catalytic subunit of a Ccr4p/Pop2p/Notp mRNA deadenylase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 11889048
- PMCID: PMC125913
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.6.1427
Ccr4p is the catalytic subunit of a Ccr4p/Pop2p/Notp mRNA deadenylase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
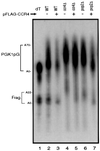
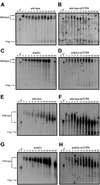
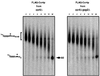
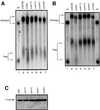
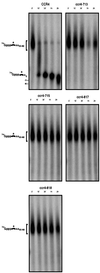
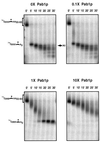
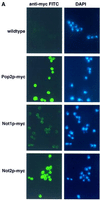
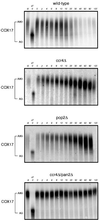
The major pathways of mRNA turnover in eukaryotic cells are initiated by shortening of the poly(A) tail. Recent work has identified Ccr4p and Pop2p as components of the major cytoplasmic deadenylase in yeast. We now demonstrate that CCR4 encodes the catalytic subunit of the deadenylase and that Pop2p is dispensable for catalysis. In addition, we demonstrate that at least some of the Ccr4p/Pop2p-associated Not proteins are cytoplasmic, and lesions in some of the NOT genes can lead to defects in mRNA deadenylation rates. The Ccr4p deadenylase is inhibited in vitro by addition of the poly(A) binding protein (Pab1p), suggesting that dissociation of Pab1p from the poly(A) tail may be rate limiting for deadenylation in vivo. In addition, the rapid deadenylation of the COX17 mRNA, which is controlled by a member of the Pumilio family of deadenylation activators Puf3p, requires an active Ccr4p/Pop2p/Not deadenylase. These results define the Ccr4p/Pop2p/Not complex as the cytoplasmic deadenylase in yeast and identify positive and negative regulators of this enzyme complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PUF protein-mediated deadenylation is catalyzed by Ccr4p.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jan 5;282(1):109-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609413200. Epub 2006 Nov 7. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17090538
-
PUF proteins bind Pop2p to regulate messenger RNAs.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Jun;13(6):533-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1100. Epub 2006 May 21. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16715093
-
The transcription factor associated Ccr4 and Caf1 proteins are components of the major cytoplasmic mRNA deadenylase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cell. 2001 Feb 9;104(3):377-86. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00225-2. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11239395
-
Global control of gene expression in yeast by the Ccr4-Not complex.Gene. 2003 Aug 14;313:1-16. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00672-3. Gene. 2003. PMID: 12957374 Review.
-
Ccr4-Not is at the core of the eukaryotic gene expression circuitry.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Dec;43(6):1253-8. doi: 10.1042/BST20150167. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 26614669 Review.
Cited by
-
The enzyme activities of Caf1 and Ccr4 are both required for deadenylation by the human Ccr4-Not nuclease module.Biochem J. 2015 Jul 1;469(1):169-76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150304. Epub 2015 May 6. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25944446 Free PMC article.
-
CCR4-associated factor CAF1 is an essential factor for spermatogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(13):5808-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.13.5808-5820.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15199137 Free PMC article.
-
The role of deadenylation in the degradation of unstable mRNAs in trypanosomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Sep;37(16):5511-28. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp571. Epub 2009 Jul 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19596809 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of deadenylation-dependent decay.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Mar-Apr;2(2):167-83. doi: 10.1002/wrna.40. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of the CCR4-Not complex in translation and dynamics of co-translation events.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Nov 27;15(1):e1827. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1827. Online ahead of print. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 38009591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beelman C.A. and Parker,R. (1995) Degradation of mRNA in eukaryotes. Cell, 81, 179–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

