Niemann-Pick C variant detection by altered sphingolipid trafficking and correlation with mutations within a specific domain of NPC1
- PMID: 11349231
- PMCID: PMC1226123
- DOI: 10.1086/320599
Niemann-Pick C variant detection by altered sphingolipid trafficking and correlation with mutations within a specific domain of NPC1
Abstract
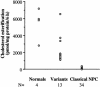
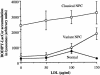
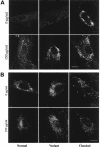
Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a fatal, autosomal recessive lipidosis characterized by lysosomal accumulation of unesterified cholesterol and multiple neurological symptoms, such as vertical supranuclear ophthalmoplegia, progressive ataxia, and dementia. More than 90% of cases of NPC are due to a defect in Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1), a late endosomal, integral membrane protein that plays a role in cholesterol transport or homeostasis. Biochemical diagnosis of NPC has relied on the use of patient skin fibroblasts in an assay to demonstrate delayed low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-derived cholesterol esterification and a cytological technique-filipin staining-to demonstrate the intracellular accumulation of cholesterol. A small percentage of patients, referred to as "NPC variants," present with clinical symptoms of NPC but show near-normal results of these biochemical tests, making laboratory confirmation of NPC disease problematic. Here, we demonstrate that NPC-variant fibroblast samples can be detected as sphingolipid storage disease cells, using a fluorescent sphingolipid analog, BODIPY-lactosylceramide. This lipid accumulated in endosomes/lysosomes in variant cells preincubated with LDL cholesterol but targeted to the Golgi complex in normal cells under these conditions. The reproducibility of this technique was validated in a blinded study. In addition, we performed mutation analysis of the NPC1 gene in NPC variant and "classical" NPC cell samples and found a high incidence of specific mutations within the cysteine-rich region of NPC1 in variants. We also found that 5 of the 12 variant cell samples had no apparent defect in NPC1 but were otherwise indistinguishable from other variant cells. This is a surprising result, since, in general, approximately 90% of patients with NPC possess defects in NPC1. Our findings should be useful for the detection of NPC variants and also may provide significant new insight regarding NPC1 genotype/phenotype correlations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Niemann-Pick C1 disease: correlations between NPC1 mutations, levels of NPC1 protein, and phenotypes emphasize the functional significance of the putative sterol-sensing domain and of the cysteine-rich luminal loop.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jun;68(6):1373-85. doi: 10.1086/320606. Epub 2001 May 1. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11333381 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 58 novel mutations in Niemann-Pick disease type C: correlation with biochemical phenotype and importance of PTC1-like domains in NPC1.Hum Mutat. 2003 Oct;22(4):313-25. doi: 10.1002/humu.10255. Hum Mutat. 2003. PMID: 12955717
-
Niemann-Pick type C disease: NPC1 mutations associated with severe and mild cellular cholesterol trafficking alterations.Hum Genet. 2001 Jul;109(1):24-32. doi: 10.1007/s004390100531. Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11479732
-
Niemann-Pick type C mutations cause lipid traffic jam.Traffic. 2000 Mar;1(3):218-25. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010304.x. Traffic. 2000. PMID: 11208105 Review.
-
The NPC1 protein: structure implies function.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Oct 11;1685(1-3):8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2004.08.006. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15465421 Review.
Cited by
-
Misdiagnosis of Niemann-Pick disease type C as Gaucher disease.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010 Dec;33 Suppl 3(0 3):S429-33. doi: 10.1007/s10545-010-9214-3. Epub 2010 Sep 30. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010. PMID: 20882348 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of the effect of disease causing and benign mutations in position Q92 on cholesterol binding by the NPC1 n-terminal domain.Proteins. 2018 Nov;86(11):1165-1175. doi: 10.1002/prot.25597. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Proteins. 2018. PMID: 30183109 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Systems Approach Reveals Sphingolipid Metabolism Pathway Dysregulation in Association with Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease.Biology (Basel). 2018 Feb 9;7(1):16. doi: 10.3390/biology7010016. Biology (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29425116 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagenesis of the putative sterol-sensing domain of yeast Niemann Pick C-related protein reveals a primordial role in subcellular sphingolipid distribution.J Cell Biol. 2004 Feb 16;164(4):547-56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200310046. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14970192 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry imaging of lipids: untargeted consensus spectra reveal spatial distributions in Niemann-Pick disease type C1.J Lipid Res. 2018 Dec;59(12):2446-2455. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D086090. Epub 2018 Sep 28. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 30266834 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for NPC [MIM 257220] and NPC2 [MIM 601015])
References
-
- Carstea ED, Morris JA, Coleman KG, Loftus SK, Zhang D, Cummings C, Gu J, et al (1997) Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science 277:228–231 - PubMed
-
- Chen CS, Patterson MC, Wheatley CL, O’Brien JF, Pagano RE (1999) Broad screening test for sphingolipid storage diseases based on alterations in lipid trafficking. Lancet 354:901–905 - PubMed
-
- Cruz JC, Sugii S, Yu C, Chang TY (2000) Role of Niemann-Pick type C1 protein in intracellular trafficking of low density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol. J Biol Chem 275:4013–4021 - PubMed
-
- Davies JP, Ioannou YA (2000) Topological analysis of Niemann-Pick C1 protein reveals that the membrane orientation of the putative sterol-sensing domain is identical to those of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase and sterol regulatory element binding protein cleavage-activating protein. J Biol Chem 275:24367–24374 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

