A novel variant c.7104 + 6T > A of ABCA12 linked to autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis verified by minigene splicing assay
- PMID: 39748812
- PMCID: PMC11693441
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1505924
A novel variant c.7104 + 6T > A of ABCA12 linked to autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis verified by minigene splicing assay
Abstract
Background: Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) is a group of genetic skin disorders characterized by abnormal keratinization, leading to significant health issues and reduced quality of life. ARCI encompasses harlequin ichthyosis (HI), congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (CIE), and lamellar ichthyosis (LI). While all ARCI genes are linked to LI and CIE, HI is specifically associated with severe mutations in the ABCA12 gene. Milder forms like LI and CIE usually involve at least one non-truncating ABCA12 variant.
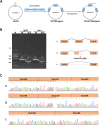
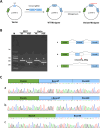
Methods: Whole-exome sequencing (WES) was performed on fetal and parental DNA, and ABCA12 gene variants were validated by Sanger sequencing. The functional effect of the novel variant c.7104 + 6T > A was evaluated using an in vitro minigene system, with splicing analysis conducted via PCR and Sanger sequencing.
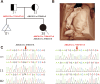
Results: A compound heterozygous variation in the ABCA12 gene, comprising c.5784G > A (p.W1928*) and c.7104 + 6T > A, was identified in the fetus, inherited from the father and mother, respectively. According to ACMG guidelines, the c.7104 + 6T > A variant is classified as a Variant of Uncertain Significance (VUS). Computational predictions suggested that this variant affects splicing. A minigene assay further confirmed that the c.7104 + 6T > A variant in ABCA12 leads to two types of aberrant mRNA splicing: a 69-base pair deletion (c.7036_7104del, p.Val2346_Glu2368del) and skipping of Exon 47, both of which result in a premature stop codon and a truncated protein.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study identified a novel genetic variant, c.7104 + 6T > A in ABCA12, as the cause of ARCI in a fetus, thereby enriched the known ABCA12 mutation spectrum.
Keywords: ABCA12 gene; autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI); mRNA splicing; minigene assay; variant.
© 2024 Zhu, Zhou, Zhang, Chen, Zhang, Huang, Shi and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic investigations of autosomal recessive inherited ichthyosis impressed by fetal ultrasound: Exome sequencing and haplotype linkage analysis.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Jan;64(1):53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2024.03.026. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2025. PMID: 39794051
-
Genedrive kit for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism m.1555A>G in neonates and their mothers: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(75):1-75. doi: 10.3310/TGAC4201. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487741 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of school-based family asthma educational programs on the quality of life and number of asthma exacerbations of children aged five to 18 years diagnosed with asthma: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):69-81. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2335. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571284
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

