Quantitative Phase Imaging as Sensitive Screening Method for Nanoparticle-Induced Cytotoxicity Assessment
- PMID: 38667312
- PMCID: PMC11049110
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13080697
Quantitative Phase Imaging as Sensitive Screening Method for Nanoparticle-Induced Cytotoxicity Assessment
Abstract
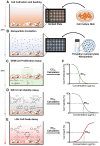
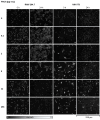
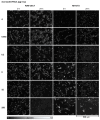
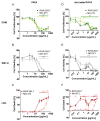
The assessment of nanoparticle cytotoxicity is challenging due to the lack of customized and standardized guidelines for nanoparticle testing. Nanoparticles, with their unique properties, can interfere with biochemical test methods, so multiple tests are required to fully assess their cellular effects. For a more reliable and comprehensive assessment, it is therefore imperative to include methods in nanoparticle testing routines that are not affected by particles and allow for the efficient integration of additional molecular techniques into the workflow. Digital holographic microscopy (DHM), an interferometric variant of quantitative phase imaging (QPI), has been demonstrated as a promising method for the label-free assessment of the cytotoxic potential of nanoparticles. Due to minimal interactions with the sample, DHM allows for further downstream analyses. In this study, we investigated the capabilities of DHM in a multimodal approach to assess cytotoxicity by directly comparing DHM-detected effects on the same cell population with two downstream biochemical assays. Therefore, the dry mass increase in RAW 264.7 macrophages and NIH-3T3 fibroblast populations measured by quantitative DHM phase contrast after incubation with poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles for 24 h was compared to the cytotoxic control digitonin, and cell culture medium control. Viability was then determined using a metabolic activity assay (WST-8). Moreover, to determine cell death, supernatants were analyzed for the release of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH assay). In a comparative analysis, in which the average half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of the nanocarriers on the cells was determined, DHM was more sensitive to the effect of the nanoparticles on the used cell lines compared to the biochemical assays.
Keywords: digital holographic microscopy; in vitro; label-free cytotoxicity testing; nanoparticles; quantitative phase imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Gallium Scan.2022 Dec 26. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2022 Dec 26. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 33620825 Free Books & Documents.
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging.2023 Nov 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Nov 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726046 Free Books & Documents.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Interventions to reduce harm from continued tobacco use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 13;10(10):CD005231. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005231.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27734465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- OECD . OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; Paris, France: 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

