Impact of indigenous Oenococcus oeni and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum species co-culture on Cabernet Sauvignon wine malolactic fermentation: Kinetic parameters, color and aroma
- PMID: 38633743
- PMCID: PMC11021843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101369
Impact of indigenous Oenococcus oeni and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum species co-culture on Cabernet Sauvignon wine malolactic fermentation: Kinetic parameters, color and aroma
Abstract
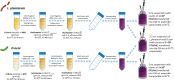
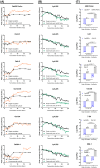
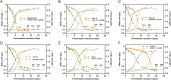
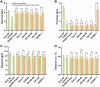
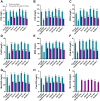
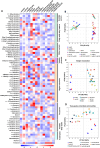
Malolactic fermentation (MLF) is a crucial process to enhance wine quality, and the utilization of indigenous microorganisms has the potential to enhance wine characteristics distinct to a region. Here, the MLF performance of five indigenous Oenococcus oeni strains and six synthetic microbial communities (SynComs), were comparatively evaluated in Cabernet Sauvignon wine. In terms of malate metabolism rate and wine aroma diversity, the strain of O. oeni Oe114-46 demonstrated comparable MLF performance to the commercial strain of O. oeni Oe450 PreAc. Furthermore, the corresponding SynComs (Oe144-46/LpXJ25) exhibited improved fermentation properties, leading to increased viable cell counts of both species, more rapid and thorough MLF, and increased concentrations of important aroma compounds, such as linalool, 4-terpinenol, α-terpineol, diethyl succinate, and ethyl lactate. These findings highlight the remarkable MLF performance of indigenous O. oeni and O. oeni-L. plantarum microbial communities, emphasizing their immense potential in improving MLF efficiency and wine quality.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum; Malolactic fermentation; Oenococcus oeni; Two-species microbial community.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of inoculation timing and mixed fermentation with Pichia fermentans on Oenococcus oeni viability, fermentation duration and aroma production during wine malolactic fermentation.Food Res Int. 2022 Sep;159:111604. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111604. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35940798
-
Advantages of Using Blend Cultures of Native L. plantarum and O. oeni Strains to Induce Malolactic Fermentation of Patagonian Malbec Wine.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 6;9:2109. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02109. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30237792 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative functional analysis of malate metabolism genes in Oenococcus oeni and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum at low pH and their roles in acid stress response.Food Res Int. 2022 Jul;157:111235. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111235. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35761547
-
Genomic variations of Oenococcus oeni strains and the potential to impact on malolactic fermentation and aroma compounds in wine.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Nov;92(3):441-7. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3546-2. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21870044 Review.
-
Improving Oenococcus oeni to overcome challenges of wine malolactic fermentation.Trends Biotechnol. 2015 Sep;33(9):547-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jul 18. Trends Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26197706 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

