Research advances in the identification of regulatory mechanisms of surfactin production by Bacillus: a review
- PMID: 38566071
- PMCID: PMC10988940
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02372-7
Research advances in the identification of regulatory mechanisms of surfactin production by Bacillus: a review
Abstract
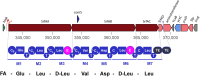
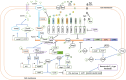
Surfactin is a cyclic hexalipopeptide compound, nonribosomal synthesized by representatives of the Bacillus subtilis species complex which includes B. subtilis group and its closely related species, such as B. subtilis subsp subtilis, B. subtilis subsp spizizenii, B. subtilis subsp inaquosorum, B. atrophaeus, B. amyloliquefaciens, B. velezensis (Steinke mSystems 6: e00057, 2021) It functions as a biosurfactant and signaling molecule and has antibacterial, antiviral, antitumor, and plant disease resistance properties. The Bacillus lipopeptides play an important role in agriculture, oil recovery, cosmetics, food processing and pharmaceuticals, but the natural yield of surfactin synthesized by Bacillus is low. This paper reviews the regulatory pathways and mechanisms that affect surfactin synthesis and release, highlighting the regulatory genes involved in the transcription of the srfAA-AD operon. The several ways to enhance surfactin production, such as governing expression of the genes involved in synthesis and regulation of surfactin synthesis and transport, removal of competitive pathways, optimization of media, and fermentation conditions were commented. This review will provide a theoretical platform for the systematic genetic modification of high-yielding strains of surfactin.
Keywords: Bacillus; Regulatory mechanism; Surfactin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid detection and characterization of surfactin-producing Bacillus subtilis and closely related species based on PCR.Curr Microbiol. 2004 Sep;49(3):186-91. doi: 10.1007/s00284-004-4314-7. Curr Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15386102
-
[Construction and optimization of engineered Bacillus subtilis for surfactin production].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020 Nov 25;36(11):2377-2386. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200156. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 33244932 Chinese.
-
Phylogenomic characterization and pangenomic insights into the surfactin-producing bacteria Bacillus subtilis strain RI4914.Braz J Microbiol. 2022 Dec;53(4):2051-2063. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00815-0. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Braz J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36083529 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of peptide antibiotic production in Bacillus.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):631-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01154.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 7682277 Review.
-
Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999 May;51(5):553-63. doi: 10.1007/s002530051432. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999. PMID: 10390813 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation of a novel Bacillus subtilis HF1 strain that is rich in lipopeptide homologs and has strong effects on the resistance of plant fungi and growth improvement of broilers.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 1;15:1433598. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1433598. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39411434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borriss R. Use of plant-associated bacillus strains as biofertilizers and biocontrol agents in agriculture. In: Maheshwari D, editor. Bacteria in Agrobiology: Plant Growth Responses. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2011. pp. 41–76.
-
- Yamamoto T. One hundred years of Bacillus thuringiensis research and development: discovery to transgenic crops. J Insect Biotechnol Sericolo. 2001;70:1–23.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

