Cereal β-d-Glucans in Food Processing Applications and Nanotechnology Research
- PMID: 38338635
- PMCID: PMC10855322
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13030500
Cereal β-d-Glucans in Food Processing Applications and Nanotechnology Research
Abstract
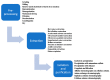
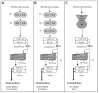
Cereal (1,3)(1,4)-β-d-glucans, known as β-d-glucans, are cell wall polysaccharides observed in selected plants of grasses, and oats and barley are their good natural sources. Thanks to their physicochemical properties β-d-glucans have therapeutic and nutritional potential and a specific place for their functional characteristics in diverse food formulations. They can function as thickeners, stabilizers, emulsifiers, and textural and gelation agents in beverages, bakery, meat, and extruded products. The objective of this review is to describe the primary procedures for the production of β-d-glucans from cereal grains, to define the processing factors influencing their properties, and to summarize their current use in the production of novel cereal-based foods. Additionally, the study delves into the utilization of β-d-glucans in the rapidly evolving field of nanotechnology, exploring potential applications within this technological realm.
Keywords: cereals; extraction; food application; nanotechnology; processing; β-d-glucans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
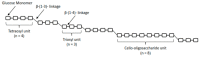
Similar articles
-
Beta-glucans from oats and/or barley in a ready-to-eat cereal manufactured via pressure cooking and reduction of blood-glucose rise after consumption: evaluation of a health claim pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006.EFSA J. 2021 Apr 8;19(4):e06493. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6493. eCollection 2021 Apr. EFSA J. 2021. PMID: 33854576 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review on cereal β-glucan: extraction, characterization, causes of degradation, and food application.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(21):3693-3704. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1706444. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31899946 Review.
-
Beta-Glucans of Cereals: Functional and Technological Properties.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 28;15(9):2124. doi: 10.3390/nu15092124. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Over-expression of specific HvCslF cellulose synthase-like genes in transgenic barley increases the levels of cell wall (1,3;1,4)-β-d-glucans and alters their fine structure.Plant Biotechnol J. 2011 Feb;9(2):117-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00532.x. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011. PMID: 20497371
-
Characterization of β-Glucans from Cereal and Microbial Sources and Their Roles in Feeds for Intestinal Health and Growth of Nursery Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;13(13):2236. doi: 10.3390/ani13132236. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the Hidden Potential of Barley (Hordeum vulgare): An Important Review.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;13(17):2421. doi: 10.3390/plants13172421. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273905 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiozzi V., Eliopoulos C., Markou G., Arapoglou D., Agriopoulou S., El Enshasy H.A., Varzakas T. Biotechnological Addition of β-Glucans from Cereals, Mushrooms and Yeasts in Foods and Animal Feed. Processes. 2021;9:1889. doi: 10.3390/pr9111889. - DOI
-
- Li X., Cheung P.C.K. Application of Natural β-Glucans as Biocompatible Functional Nanomaterials. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2019;8:315–319. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2019.11.005. - DOI
-
- Tosh S.M., Brummer Y., Wood P.J., Wang Q., Weisz J. Evaluation of Structure in the Formation of Gels by Structurally Diverse (1→3)(1→4)-β-d-Glucans from Four Cereal and One Lichen Species. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004;57:249–259. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.05.009. - DOI
-
- Cui W., Wood P.J. Relationships between Structural Features, Molecular Weight, and Rheological Properties of Cereal β-d-Glucans. In: Nishinari K., editor. Hydrocoll. Elsevier Science; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2000. pp. 159–168. - DOI
-
- Izydorczyk M.S., Macri L.J., MacGregor A.W. Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Barley Non-Starch Polysaccharides—I. Water-Extractable β-Glucans and Arabinoxylans. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998;35:249–258. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(97)00137-9. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

