The Influence of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Oenococcus oeni Starters on the Volatile and Sensory Properties of Black Raspberry Wine
- PMID: 38231611
- PMCID: PMC10706081
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12234212
The Influence of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Oenococcus oeni Starters on the Volatile and Sensory Properties of Black Raspberry Wine
Abstract
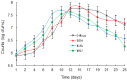
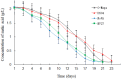
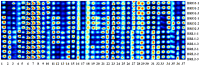
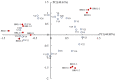
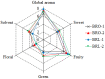
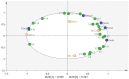
Malolactic fermentation (MLF) by different lactic acid bacteria has a significantly influence on the aromatic and sensory properties of wines. In this study, four strains including two Oenococcus oeni (commercial O-Mega and native DS04) and two Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (commercial NoVA and native NV27) were tested for their performances over MLF and effects on the basic composition, volatile components and sensory property of black raspberry wine. Results of microbial growth kinetics showed Lactiplantibacillus strains had higher fermentation efficiency than Oenococcus. The volatile compounds were determined by GC-IMS; NoVA and NV27 had higher production of volatile esters, and DS04 synthesized more amounts of acetate esters and several alcohols. In terms of sensory evaluation, NV27 and DS04 showed great aroma properties due to the enhanced fruity and sweet aroma. Furthermore, PLS was used for the establishment of the relationship between volatiles and sensory odors and sensory data interpretation.
Keywords: GC-IMS; Lactiplantibacillus; Oenococcus; black raspberry wine; sensory evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors of this work, Changsen Wang, Shuyang Sun, Haoran Zhou and Zhenzhen Cheng, declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Torulaspora delbrueckii and malolactic fermentation on fermentation kinetics and sensory property of black raspberry wines.Food Microbiol. 2020 Oct;91:103551. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2020.103551. Epub 2020 May 26. Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32539970
-
Changes in the volatile profile of Pinot noir wines caused by Patagonian Lactobacillus plantarum and Oenococcus oeni strains.Food Res Int. 2018 Apr;106:22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.12.032. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Food Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29579921
-
Effects of inoculation timing and mixed fermentation with Pichia fermentans on Oenococcus oeni viability, fermentation duration and aroma production during wine malolactic fermentation.Food Res Int. 2022 Sep;159:111604. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111604. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35940798
-
Genomic variations of Oenococcus oeni strains and the potential to impact on malolactic fermentation and aroma compounds in wine.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Nov;92(3):441-7. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3546-2. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21870044 Review.
-
Improving Oenococcus oeni to overcome challenges of wine malolactic fermentation.Trends Biotechnol. 2015 Sep;33(9):547-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jul 18. Trends Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26197706 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous expression of the Oenococcus oeni two-component signal transduction response regulator in the Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WCFS1 strain enhances acid stress tolerance.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Sep 28;24(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03498-9. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39342090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang S., Xing X., Chu Q., Sun S., Wang P. Impact of co-culture of Lactobacillus plantarum and Oenococcus oeni at different ratios on malolactic fermentation, volatile and sensory characteristics of mulberry wine. LWT. 2022;169:113995. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113995. - DOI
-
- Lucio O., Pardo I., Heras J., Krieger-Weber S., Ferrer S. Use of starter cultures of Lactobacillus to induce malolactic fermentation in wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2017;23:15–21. doi: 10.1111/ajgw.12261. - DOI
-
- Brizuela N., Tymczyszyn E.E., Semorile L.C., La Hens D.V., Delfederico L., Hollmann A., Bravo-Ferrada B. Lactobacillus plantarum as a malolactic starter culture in winemaking: A new (old) player? Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019;38:10–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ejbt.2018.12.002. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

