Safety and Efficacy of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors vs. Erythropoietin-Stimulating Agents in Treating Anemia in Renal Patients (With or Without Dialysis): A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
- PMID: 38021836
- PMCID: PMC10659060
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.47430
Safety and Efficacy of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors vs. Erythropoietin-Stimulating Agents in Treating Anemia in Renal Patients (With or Without Dialysis): A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Abstract
Hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase domain inhibitors (HIF-PHIs) are a novel group of drugs used to treat renal anemia, but their benefits vary among different trials. Our meta-analysis aims to assess the safety and efficacy of HIF-PHI versus erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA) in managing anemia among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), regardless of their dialysis status. PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar were queried to discover eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs). To quantify the specific effects of HIF-PHI, we estimated pooled mean differences (MDs) and relative risks (RR) with 95% CIs. Our meta-analysis involved 22,151 CKD patients, with 11,234 receiving HIF-PHI and 10,917 receiving ESA from 19 different RCTs. The HIF-PHI used included roxadustat, daprodustat, and vadadustat. HIF-PHI yielded a slight but significant increase in change in mean hemoglobin (Hb) levels (MD: 0.06, 95% CI (0.00, 0.11); p = 0.03), with the maximum significant increase shown in roxadustat followed by daprodustat as compared to ESA. There was a significant decrease in efficacy outcomes such as change in mean iron (MD: -1.54, 95% CI (-3.01, -0.06); p = 0.04), change in mean hepcidin (MD: -21.04, 95% CI (-28.92, -13.17); p < 0.00001), change in mean ferritin (MD: -16.45, 95% CI (-27.17,-5.73); p = 0.03) with roxadustat showing maximum efficacy followed by daprodustat. As for safety, HIF-PHI showed significantly increased incidence in safety outcomes such as diarrhea (MD: 1.3, 95% CI (1.11, 1.51); p = 0.001), adverse events leading to withdrawal (MD: 2.03, 95% CI (1.5, 2.74), p = 0.00001) among 25 various analyzed outcomes. This meta-analysis indicates that HIF-PHIs present a potentially safer and more effective alternative to ESAs, with increased Hb levels and decreased iron usage in CKD patients without significantly increasing adverse events. Therefore, in these patients, we propose HIF-PHI alongside renal anemia treatment.
Keywords: and efficacy; anemia; dialysis; erythropoietin stimulating agents; hypoxic inducible factors prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors; kidney; renal; safety; treatment; without dialysis.
Copyright © 2023, Damarlapally et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
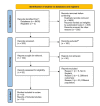
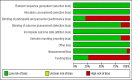
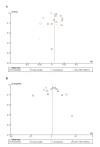

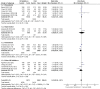
Similar articles
-
A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitors in dialysis chronic kidney disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Mar 27;15(6):2237-2274. doi: 10.18632/aging.204611. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36988549 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors vs. erythropoiesis-stimulating agents on iron metabolism in non-dialysis-dependent anemic patients with CKD: A network meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 16;14:1131516. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1131516. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37008953 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of outcomes on hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors (HIF-PHIs) in anaemia associated with chronic kidney disease: network meta-analyses in dialysis and non-dialysis dependent populations.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Dec 7;17(1):sfad298. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad298. eCollection 2024 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38250252 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor vs epoetin and darbepoetin for anemia in chronic kidney disease patients not undergoing dialysis: A network meta-analysis.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:105020. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105020. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32561478 Review.
-
Future perspectives of anemia management in chronic kidney disease using hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Nov;239:108272. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108272. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36031160 Review.
Cited by
-
Growing concerns about using hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for the treatment of renal anemia.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Feb 28;17(3):sfae051. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae051. eCollection 2024 Mar. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 38516524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal anemia: from relative insufficiency of EPO to imbalance of erythropoiesis and eryptosis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Nov;56(11):3559-3568. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04146-x. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38982020 Review.
References
-
- Evolution of treatment for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Vaught K, Kerber S. J Ren Nutr. 2020;30:0. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
