Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Profiling of Volatile Metabolites Produced by Some Bacillus spp. and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial and Antibiotic Activities
- PMID: 38005278
- PMCID: PMC10673538
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227556
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Profiling of Volatile Metabolites Produced by Some Bacillus spp. and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial and Antibiotic Activities
Abstract
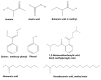
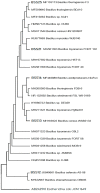
Bacillus species produce different classes of antimicrobial and antioxidant substances: peptides or proteins with different structural compositions and molecular masses and a broad range of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), some of which may serve as biomarkers for microorganism identification. The aim of this study is the identification of biologically active compounds synthesized by five Bacillus species using gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The current study profoundly enhances the knowledge of antibacterial and antioxidant metabolites ensuring the unambiguous identification of VOCs produced by some Bacillus species, which were isolated from vegetable samples of potato, carrot, and tomato. Phylogenetic and biochemical studies were used to identify the bacterial isolates after culturing. Phylogenetic analysis proved that five bacterial isolates BSS12, BSS13, BSS16, BSS21, and BSS25 showed 99% nucleotide sequence similarities with Bacillus safensis AS-08, Bacillus cereus WAB2133, Bacillus acidiproducens NiuFun, Bacillus toyonesis FORT 102, and Bacillus thuringiensis F3, respectively. The crude extract was prepared from bacterial isolates to assess the antibiotic resistance potency and the antimicrobial potential against various targeted multidrug-resistant strains, including yeast strains such as Candida albicans, Candida krusei, and bacterial strains of Enterococcus hirae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus group B, Streptococcus mutans, Shigella sonnei, Salmonella enteritidis, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus vulgaris. GC-MS analysis of bacterial strains found that VOCs from Bacillus species come in a variety of chemical forms, such as ketones, alcohols, terpenoids, alkenes, etc. Overall, 69 volatile organic compounds were identified from five Bacillus species, and all five were found to share different chemical classes of volatile organic components, which have a variety of pharmacological applications. However, eight antibacterial compounds with different concentrations were commonly found in all five species: acetoin, acetic acid, butanoic acid, 2-methyl-, oxime-, methoxy-phenyl, phenol, 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester, nonanoic acid, and hexadecanoic acid, methyl. The present study has demonstrated that bacterial isolates BSS25, BSS21, and BSS16 display potent inhibitory effects against Candida albicans, while BSS25, BSS21, and BSS13 exhibit the ability to restrain the growth and activity of Candida krusei. Notably, BSS25 and BSS21 are the only isolates that demonstrate substantial inhibitory activity against Klebsiella aerogenes. This disparity in inhibitory effects could be attributed to the higher concentrations of acetoin in BSS25 and BSS21, whereas BSS16 and BSS13 have relatively elevated levels of butanoic acid, 2-methyl-. Certainly, the presence of acetoin and butanoic acid, 2-methyl-, contributes to the enhanced antibacterial potential of these bacterial strains, in conjunction with other organic volatile compounds and peptides, among other factors. The biology and physiology of Bacillus can be better understood using these results, which can also be used to create novel biotechnological procedures and applications. Moreover, because of its exceptional ability to synthesize and produce a variety of different antibacterial compounds, Bacillus species can serve as natural and universal carriers for antibiotic compounds in the form of probiotic cultures and strains to fight different pathogens, including mycobacteria.
Keywords: Bacillus acidiproducens; Bacillus cereus; Bacillus safensis; Bacillus subtilis; Bacillus thuringiensis; Bacillus toyonensis; GC–MC analysis; antimicrobial activity; volatile organic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Characterization of Some Bacillus Species from Vegetables and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiotic Potency.Molecules. 2023 Apr 4;28(7):3210. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073210. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049972 Free PMC article.
-
GC-MS analysis of volatile organic compounds from Bambara groundnut rhizobacteria and their antibacterial properties.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 May 27;35(6):83. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2660-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31134356 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of bioactive compounds extracted from Streptomyces africanus strain E2 isolated from Moroccan soil.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 9;14(1):27372. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77729-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39521814 Free PMC article.
-
Volatile metabolites of pathogens: a systematic review.PLoS Pathog. 2013 May;9(5):e1003311. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003311. Epub 2013 May 9. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23675295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Arthrospira (Former Spirulina) and Dunaliella Related to Recognized Antimicrobial Bioactive Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 19;25(10):5548. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105548. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Volatile Organic Compounds Produced by Co-Culture of Burkholderia vietnamiensis B418 with Trichoderma harzianum T11-W Exhibits Improved Antagonistic Activities against Fungal Phytopathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):11097. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011097. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456879 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus megaterium: Evaluation of Chemical Nature of Metabolites and Their Antioxidant and Agronomics Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 12;25(6):3235. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063235. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542209 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Weevil (Sitophilus oryzae L.) Gut Bacteria Inhibit Growth of Aspergillus flavus and Degrade Aflatoxin B1.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 May 24;10(6):377. doi: 10.3390/jof10060377. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921363 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

