The 10 top-cited authors who published papers in journal medicine since 2000 using the betweenness centrality to identify unique names: Bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 37352024
- PMCID: PMC10289667
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034050
The 10 top-cited authors who published papers in journal medicine since 2000 using the betweenness centrality to identify unique names: Bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Numerous studies have explored the most productive and influential authors in a specific field. However, 2 challenges arise when conducting such research. First, some authors may have identical names in the study data, and second, the contributions of coauthors may vary in the article by line, requiring consideration. Failure to address these issues may result in biased research findings. Our objective was to illustrate how the author-weighted scheme (AWS) and betweenness centrality (BC) can be employed to identify the 10 most frequently cited authors in a particular journal and analyze their research themes.
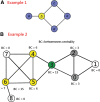
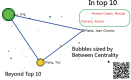
Methods: We collected 24,058 abstracts from the PubMed library between 2000 and 2020 using the keyword "Medicine [Journal]." Author names, countries/regions, and medical subject headings (MeSH terms) were collected. The AWS to identify the top 10 authors with a higher x-index was applied. To address the issue of authors with identical names affiliated with different research institutes, we utilized the BC method. Social network analysis (SNA) was conducted, and 10 major clusters were identified to highlight authors with a higher x-index within the corresponding clusters. We utilized SNA to analyze the MeSH terms from articles of the 10 top-cited authors to identify their research themes.
Results: Our findings revealed the following: within the top 10 cited authors, 2 authors from China shared identical names with Jing Li and Tao-Wang; JA Winkelstein from Maryland (US) had the highest x-index (15.58); Chia-Hung Kao from Taiwan was the most prolific author, having published 115 articles in Medicine since 2003; and the 3 primary research themes, namely, complications, etiology, and epidemiology, were identified using MeSH terms from the 10 most frequently cited authors.
Conclusions: Using AWS and BC, we identified the top 10 most cited authors. The research methods we utilized in this study (BC and AWS) have the potential to be applied to other bibliometric analyses in the future.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Most-Cited Authors Who Published Papers in JMIR mHealth and uHealth Using the Authorship-Weighted Scheme: Bibliometric Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 May 7;8(5):e11567. doi: 10.2196/11567. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 32379053 Free PMC article.
-
Whether article types of a scholarly journal are different in cited metrics using cluster analysis of MeSH terms to display: A bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(43):e17631. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017631. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31651878 Free PMC article.
-
Using the Kano model to display the most cited authors and affiliated countries in schizophrenia research.Schizophr Res. 2020 Feb;216:422-428. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2019.10.058. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Schizophr Res. 2020. PMID: 31862218
-
Using Kano diagrams to display the most cited article types, affiliated countries, authors and MeSH terms on spinal surgery in recent 12 years.Eur J Med Res. 2021 Feb 23;26(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40001-021-00494-x. Eur J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33622416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of the Most Cited Articles in Neurocritical Care Research.Neurocrit Care. 2019 Oct;31(2):365-372. doi: 10.1007/s12028-019-00731-6. Neurocrit Care. 2019. PMID: 31087256 Review.
References
-
- Ahmad P, Dummer P, Noorani T, et al. . The top 50 most-cited articles published in the International Endodontic Journal. Int Endod J. 2019;52:803–18. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S, et al. . Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis incitespace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12:593–608. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

