Overall survival in the SIMPLIFY-1 and SIMPLIFY-2 phase 3 trials of momelotinib in patients with myelofibrosis
- PMID: 35869266
- PMCID: PMC9417985
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-022-01637-7
Overall survival in the SIMPLIFY-1 and SIMPLIFY-2 phase 3 trials of momelotinib in patients with myelofibrosis
Abstract
Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) approved for myelofibrosis provide spleen and symptom improvements but do not address anemia, a negative prognostic factor. Momelotinib, an inhibitor of ACVR1/ALK2, JAK1 and JAK2, demonstrated activity against anemia, symptoms, and splenomegaly in the phase 3 SIMPLIFY trials. Here, we report mature overall survival (OS) and leukemia-free survival (LFS) from both studies, and retrospective analyses of baseline characteristics and efficacy endpoints for OS associations. Survival distributions were similar between JAKi-naïve patients randomized to momelotinib, or ruxolitinib then momelotinib, in SIMPLIFY-1 (OS HR = 1.02 [0.73, 1.43]; LFS HR = 1.08 [0.78, 1.50]). Two-year OS and LFS were 81.6% and 80.7% with momelotinib and 80.6% and 79.3% with ruxolitinib then momelotinib. In ruxolitinib-exposed patients in SIMPLIFY-2, two-year OS and LFS were 65.8% and 64.2% with momelotinib and 61.2% and 59.7% with best available therapy then momelotinib (OS HR = 0.98 [0.59, 1.62]; LFS HR = 0.97 [0.59, 1.60]). Baseline transfusion independence (TI) was associated with improved survival in both studies (SIMPLIFY-1 HR = 0.474, p = 0.0001; SIMPLIFY-2 HR = 0.226, p = 0.0005). Week 24 TI response in JAKi-naïve, momelotinib-randomized patients was associated with improved OS in univariate (HR = 0.323; p < 0.0001) and multivariate (HR = 0.311; p < 0.0001) analyses. These findings underscore the importance of achieving or maintaining TI in myelofibrosis, supporting the clinical relevance of momelotinib's pro-erythropoietic mechanism of action, and potentially informing treatment decision-making.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ruben Mesa has received grants or contracts from Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incye, AbbVie, Samus, Genotech, Promedior, CTI Biopharma, Constellation, and National Cancer Institute; and consulting fees from Novartis, Sierra Oncology, LaJolla, and Constellation. Claire Harrison has received grants or contracts from Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Constellation, and Novartis; consulting fees from Keros, Galecto, AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals, and Roche; payments or honoraria from Novartis, Celgene, CTI Biopharma, AbbVie, Janssen, and Constellation; support to attending meetings from Novartis; and has participated on Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards for Galecto, CTI Biopharma, Roche, Geron, Promedior, AbbVie, AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals, and Sierra Oncology, in addition to leadership or fiduciary roles in EHA and MPN Voice. Stephen T. Oh has received consulting fees from CTI Biopharma, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Blueprint Medicines, AbbVie, Sierra Oncology, Disc Medicine, Constellation, and PharmaEssentia. Aaron T. Gerds has participated in Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards at Sierra Oncology, CTI Biopharma, Incyte, AbbVie, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Morphosys, Novartis, and PharmEssentia. Vikas Gupta has received consulting fees from Novartis, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sierra Oncology, AbbVie, Constellation, and Pfizer; payment or honoraria from Novartis, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Constellation; and has participated on Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards for Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, AbbVie, and Pfizer. John Catalano states no conflicts of interest. Francisco Cervantes has received consulting feeds from Bristol-Myers Squibb; payment or honoraria from Pfizer; and support for attending meetings from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Timothy Devos has received consulting fees for Novartis, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Morphosys, and AbbVie. Marek Hus states no conflicts of interest. Jean-Jacques Kiladjian has received consulting fees from Novartis, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals; payment or honoraria from Novartis; and has participated in Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards for Incyte. Ewa Lech-Maranda has participated in Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards for AbbVie, Roche, Gilead, and Novartis. Donal McLornan has received research funding from Novartis; royalties from a book on myelofibrosis; payment or honoraria from Nocartis, Jazz, and AbbVie, and has participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board for the UK ALLRIC trial. Alessandro M. Vannucchi has received payment or honoraria from Novartis, AbbVie, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals; participated in Data Safety Monitoring and Advisory Boards with Incyte, Novartis, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, GlaxoSmithKline, and AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals. Uwe Platzbecker has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Novartis, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Curis, and Geron; payment or honoraria from Novartis, Takeda, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals; and has participated on Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards for Novartis, AbbVie, and Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb. Mei Huang, Bryan Strouse, and Barbara Klencke are employees of and claim stock options from Sierra Oncology. Srdan Verstovsek has received consulting fees from Sierra Oncology.
Figures
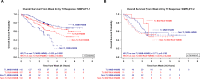

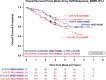
Similar articles
-
Momelotinib versus Continued Ruxolitinib or Best Available Therapy in JAK Inhibitor-Experienced Patients with Myelofibrosis and Anemia: Subgroup Analysis of SIMPLIFY-2.Adv Ther. 2024 Sep;41(9):3722-3735. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02928-4. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 38990433 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Momelotinib versus ruxolitinib in JAK inhibitor-naïve patients with myelofibrosis: an efficacy/safety analysis in the Japanese subgroup of the phase 3 randomized SIMPLIFY-1 trial.Int J Hematol. 2024 Sep;120(3):314-324. doi: 10.1007/s12185-024-03822-z. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Int J Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39110143 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
SIMPLIFY-1: A Phase III Randomized Trial of Momelotinib Versus Ruxolitinib in Janus Kinase Inhibitor-Naïve Patients With Myelofibrosis.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec 1;35(34):3844-3850. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.4418. Epub 2017 Sep 20. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28930494 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Momelotinib: an emerging treatment for myelofibrosis patients with anemia.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Jan 19;15(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01157-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35045875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Momelotinib for the treatment of myelofibrosis with anemia.Future Oncol. 2022 Jun;18(20):2559-2571. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0276. Epub 2022 May 23. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35603634 Review.
Cited by
-
Upfront allogeneic transplantation versus JAK inhibitor therapy for patients with myelofibrosis: a North American collaborative study.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024 Feb;59(2):196-202. doi: 10.1038/s41409-023-02146-6. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024. PMID: 37938736 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Treatment Options for Myelofibrosis: Focus on Anemia.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023 Jun 28;19:535-547. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S386802. eCollection 2023. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023. PMID: 37404252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of classical Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms in Asia: consensus of the Asian Myeloid Working Group.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Dec;23(8):4199-4217. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01189-9. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37747591 Review.
-
Momelotinib: Mechanism of action, clinical, and translational science.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Aug;17(8):e70018. doi: 10.1111/cts.70018. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39189872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK/STAT pathway: Extracellular signals, diseases, immunity, and therapeutic regimens.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 23;11:1110765. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1110765. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36911202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cervantes F, Dupriez B, Pereira A, Passamonti F, Reilly JT, Morra E, et al. New prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis based on a study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood. 2009;113:2895–901. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-170449. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Passamonti F, Cervantes F, Vannucchi AM, Morra E, Rumi E, Pereira A, et al. A dynamic prognostic model to predict survival in primary myelofibrosis: A study by the IWG-MRT (International Working Group for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment) Blood. 2010;115:1703–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-245837. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gangat N, Caramazza D, Vaidya R, George G, Begna K, Schwager S, et al. DIPSS Plus: A refined dynamic international prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis that incorporates prognostic information from karyotype, platelet count, and transfusion status. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:392–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.2446. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

