Ciliary Dyneins and Dynein Related Ciliopathies
- PMID: 34440654
- PMCID: PMC8391580
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10081885
Ciliary Dyneins and Dynein Related Ciliopathies
Abstract
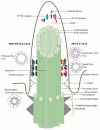
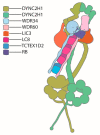
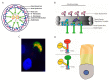
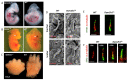
Although ubiquitously present, the relevance of cilia for vertebrate development and health has long been underrated. However, the aberration or dysfunction of ciliary structures or components results in a large heterogeneous group of disorders in mammals, termed ciliopathies. The majority of human ciliopathy cases are caused by malfunction of the ciliary dynein motor activity, powering retrograde intraflagellar transport (enabled by the cytoplasmic dynein-2 complex) or axonemal movement (axonemal dynein complexes). Despite a partially shared evolutionary developmental path and shared ciliary localization, the cytoplasmic dynein-2 and axonemal dynein functions are markedly different: while cytoplasmic dynein-2 complex dysfunction results in an ultra-rare syndromal skeleto-renal phenotype with a high lethality, axonemal dynein dysfunction is associated with a motile cilia dysfunction disorder, primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) or Kartagener syndrome, causing recurrent airway infection, degenerative lung disease, laterality defects, and infertility. In this review, we provide an overview of ciliary dynein complex compositions, their functions, clinical disease hallmarks of ciliary dynein disorders, presumed underlying pathomechanisms, and novel developments in the field.
Keywords: cilium; dynein; intraflagellar transport; primary ciliary dyskinesia; short rib polydactyly syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CCDC151 mutations cause primary ciliary dyskinesia by disruption of the outer dynein arm docking complex formation.Am J Hum Genet. 2014 Sep 4;95(3):257-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.08.005. Am J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 25192045 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic aspects of primary ciliary dyskinesia/Kartagener syndrome.Genet Med. 2009 Jul;11(7):473-87. doi: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181a53562. Genet Med. 2009. PMID: 19606528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C11orf70 Mutations Disrupting the Intraflagellar Transport-Dependent Assembly of Multiple Axonemal Dyneins Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia.Am J Hum Genet. 2018 May 3;102(5):956-972. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.03.024. Am J Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29727692 Free PMC article.
-
Primary ciliary dyskinesia and associated sensory ciliopathies.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016;10(5):569-76. doi: 10.1586/17476348.2016.1165612. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 26967669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNAH11 Localization in the Proximal Region of Respiratory Cilia Defines Distinct Outer Dynein Arm Complexes.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Aug;55(2):213-24. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0353OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26909801 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biochemically validated structural model of the 15-subunit intraflagellar transport complex IFT-B.EMBO J. 2022 Dec 15;41(24):e112440. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112440. Epub 2022 Nov 10. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 36354106 Free PMC article.
-
PCD Genes-From Patients to Model Organisms and Back to Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 3;23(3):1749. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031749. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and Function of Dynein's Non-Catalytic Subunits.Cells. 2024 Feb 11;13(4):330. doi: 10.3390/cells13040330. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38391943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bi-allelic variants in DNAH3 cause male infertility with asthenoteratozoospermia in humans and mice.Hum Reprod Open. 2024 Jan 11;2024(1):hoae003. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoae003. eCollection 2024. Hum Reprod Open. 2024. PMID: 38312775 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog Morphogens Act as Growth Factors Critical to Pre- and Postnatal Cardiac Development and Maturation: How Primary Cilia Mediate Their Signal Transduction.Cells. 2022 Jun 9;11(12):1879. doi: 10.3390/cells11121879. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

