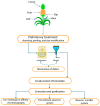
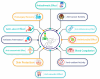
Bromelain a Potential Bioactive Compound: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective
- PMID: 33917319
- PMCID: PMC8067380
- DOI: 10.3390/life11040317
Bromelain a Potential Bioactive Compound: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective
Erratum in
-
Correction: Chakraborty et al. Bromelain a Potential Bioactive Compound: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective. Life 2021, 11, 317.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 7;14(4):483. doi: 10.3390/life14040483. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672810 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Bromelain is an effective chemoresponsive proteolytic enzyme derived from pineapple stems. It contains several thiol endopeptidases and is extracted and purified via several methods. It is most commonly used as an anti-inflammatory agent, though scientists have also discovered its potential as an anticancer and antimicrobial agent. It has been reported as having positive effects on the respiratory, digestive, and circulatory systems, and potentially on the immune system. It is a natural remedy for easing arthritis symptoms, including joint pain and stiffness. This review details bromelain's varied uses in healthcare, its low toxicity, and its relationship to nanoparticles. The door of infinite possibilities will be opened up if further extensive research is carried out on this pineapple-derived enzyme.
Keywords: Ananas comosus; bromelain; nanoparticles; pineapple; proteolytic enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bromelain, a Group of Pineapple Proteolytic Complex Enzymes (Ananas comosus) and Their Possible Therapeutic and Clinical Effects. A Summary.Foods. 2021 Sep 23;10(10):2249. doi: 10.3390/foods10102249. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34681298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic uses of pineapple-extracted bromelain in surgical care - A review.J Pak Med Assoc. 2017 Jan;67(1):121-125. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28065968
-
The proteolytic system of pineapple stems revisited: Purification and characterization of multiple catalytically active forms.Phytochemistry. 2017 Jun;138:29-51. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.02.019. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Phytochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28238440
-
CHEMICAL MODIFICATION OF BROMELAIN WITH DEXTRAN ALDEHYDE AND ITS POTENTIAL MEDICAL APPLICATION.Georgian Med News. 2021 Jun;(315):185-189. Georgian Med News. 2021. PMID: 34365448
-
Current Uses of Bromelain in Children: A Narrative Review.Children (Basel). 2024 Mar 21;11(3):377. doi: 10.3390/children11030377. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti‑angiogenic and cytotoxic evaluation of green‑synthesized Fe2ZnO4 nanoparticles against MCF‑7 cell line.Biomed Rep. 2024 Jan 10;20(3):36. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1724. eCollection 2024 Mar. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38343659 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Bromelain in Alveolar Ridge Preservation.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 3;11(11):1542. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111542. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358197 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in Asagirt District, Northeastern Ethiopia.Trop Med Health. 2023 Jan 9;51(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s41182-023-00493-0. Trop Med Health. 2023. PMID: 36617576 Free PMC article.
-
How Do Herbal Cigarettes Compare To Tobacco? A Comprehensive Review of Their Sensory Characters, Phytochemicals, and Functional Properties.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 6;7(50):45797-45809. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04708. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36570239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the Potential of Enzymes as Inhaled Therapeutics in Respiratory Tract Diseases: A Review of the Literature.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 17;10(6):1440. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061440. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740461 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heinicke R.M., Gortner W.A. Stem bromelain—A new protease preparation from pineapple plants. Econ. Bot. 1957;11:225–234. doi: 10.1007/BF02860437. - DOI
-
- Tayab M.A., Chowdhury K.A.A., Jabed M., Mohammed Tareq S., Kamal A.T.M.M., Islam M.N., Uddin A.M.K., Hossain M.A., Emran T.B., Simal-Gandara J. Antioxidant-Rich Woodfordia fruticosa Leaf Extract Alleviates Depressive-Like Behaviors and Impede Hyperglycemia. Plants. 2021;10:287. doi: 10.3390/plants10020287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mamo J., Assefa F. Antibacterial and Anticancer Property of Bromelain: A Plant Protease Enzyme from Pineapples (Ananas comosus) Curr. Trends Biomed. Eng. Biosci. 2019;19:60–68.
-
- Manzoor Z., Nawaz A., Mukhtar H., Haq I. Bromelain: Methods of Extraction, Purification and Therapeutic Applications. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2016;59:e16150010. doi: 10.1590/1678-4324-2016150010. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources