Assessing the roles and challenges of librarians in dental systematic and scoping reviews
- PMID: 33424464
- PMCID: PMC7772970
- DOI: 10.5195/jmla.2021.1031
Assessing the roles and challenges of librarians in dental systematic and scoping reviews
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to determine the scope of experience, roles, and challenges that librarians face in participating in dental and oral health systematic and scoping reviews to inform outreach efforts to researchers and identify areas for librarian professional development.
Methods: The authors developed a twenty-three-item survey based on the findings of two recent articles about health sciences librarians' roles and challenges in conducting systematic and scoping reviews. The survey was distributed via electronic mailing lists to librarians who were likely to have participated in conducting dental systematic and scoping reviews.
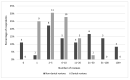
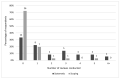
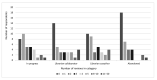
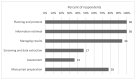
Results: While survey respondents reported participating in many dental reviews, they participated more commonly in systematic reviews than in scoping reviews. Also, they worked less commonly on dental and oral health reviews than on non-dental reviews. Librarian roles in dental reviews tended to follow traditional librarian roles: all respondents had participated in planning and information retrieval stages, whereas fewer respondents had participated in screening and assessing articles. The most frequently reported challenges involved the lead reviewer or review team rather than the librarians themselves, with time- and methodology-related challenges being most common.
Conclusions: Although librarians might not be highly involved in dental and oral health systematic and scoping reviews, more librarian participation in these reviews, either as methodologists or information experts, may improve their reviews' overall quality.
Copyright © 2021 Nena Schvaneveldt, Elizabeth M. Stellrecht.
Figures
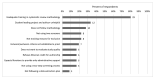
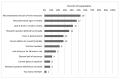
Similar articles
-
Benchmarking veterinary librarians' participation in systematic reviews and scoping reviews.J Med Libr Assoc. 2019 Oct;107(4):499-507. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2019.710. Epub 2019 Oct 1. J Med Libr Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31607807 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring conceptual and theoretical frameworks for nurse practitioner education: a scoping review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):146-55. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2150. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571290
-
Roles for librarians in systematic reviews: a scoping review.J Med Libr Assoc. 2018 Jan;106(1):46-56. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2018.82. Epub 2018 Jan 2. J Med Libr Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29339933 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The relationship between methodological quality and the use of retracted publications in evidence syntheses.Syst Rev. 2023 Sep 20;12(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s13643-023-02316-z. Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37730590 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of librarian involvement on the quality of systematic reviews in dental medicine.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 1;16(9):e0256833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256833. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34469487 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review support received and needed by researchers: a survey of libraries supporting Ontario medical schools.J Can Health Libr Assoc. 2021 Dec 1;42(3):154-163. doi: 10.29173/jchla29571. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Can Health Libr Assoc. 2021. PMID: 35949251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arksey H, O'Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32. DOI: 10.1080/1364557032000119616. - DOI
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S eds. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions [Internet]. Version 6 London, UK: Cochrane Collaboration; 2019. [cited 15 Oct 2020]. <http://handbook.cochrane.org>.
-
- Page MJ, Shamseer L, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Sampson M, Tricco AC, Catalá-López F, Li L, Reid EK, Sarkis-Onofre R, Moher D. Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews of biomedical research: a cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2016;13(5):e1002028 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002028. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
