Look Alike, Sound Alike: Phenocopies in Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
- PMID: 33198123
- PMCID: PMC7696007
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17228363
Look Alike, Sound Alike: Phenocopies in Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
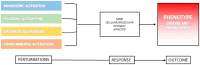
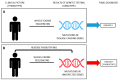
Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) is a clinical picture defined by the lack of response to standard steroid treatment, frequently progressing toward end-stage kidney disease. The genetic basis of SRNS has been thoroughly explored since the end of the 1990s and especially with the advent of next-generation sequencing. Genetic forms represent about 30% of cases of SRNS. However, recent evidence supports the hypothesis that "phenocopies" could account for a non-negligible fraction of SRNS patients who are currently classified as non-genetic, paving the way for a more comprehensive understanding of the genetic background of the disease. The identification of phenocopies is mandatory in order to provide patients with appropriate clinical management and to inform therapy. Extended genetic testing including phenocopy genes, coupled with reverse phenotyping, is recommended for all young patients with SRNS to avoid unnecessary and potentially harmful diagnostic procedures and treatment, and for the reclassification of the disease. The aim of this work is to review the main steps of the evolution of genetic testing in SRNS, demonstrating how a paradigm shifting from "forward" to "reverse" genetics could significantly improve the identification of the molecular mechanisms of the disease, as well as the overall clinical management of affected patients.
Keywords: genetics; phenocopies; steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome; whole-exome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetics of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a review of mutation spectrum and suggested approach for genetic testing.Acta Paediatr. 2013 Sep;102(9):844-56. doi: 10.1111/apa.12317. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Acta Paediatr. 2013. PMID: 23772861 Review.
-
Clinical genetic testing using a custom-designed steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome gene panel: analysis and recommendations.J Med Genet. 2017 Dec;54(12):795-804. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-104811. Epub 2017 Aug 5. J Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 28780565 Free PMC article.
-
Causal and putative pathogenic mutations identified in 39% of children with primary steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in South Africa.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Oct;181(10):3595-3606. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04581-x. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35920919 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid detection of monogenic causes of childhood-onset steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Jun 6;9(6):1109-16. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09010813. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24742477 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in the genomic era.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Nov;34(11):2279-2293. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-4093-1. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30280213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Genetic Characterization of Patients with Bartter and Gitelman Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 18;23(10):5641. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105641. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628451 Free PMC article.
-
Defining diagnostic trajectories in patients with podocytopathies.Clin Kidney J. 2022 May 3;15(11):2006-2019. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfac123. eCollection 2022 Nov. Clin Kidney J. 2022. PMID: 36325008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Clinical and Genetic Features in Chinese Children With Steroid-Resistant or Early-Onset Nephrotic Syndrome: A Multicenter Cohort Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 9;9:885178. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.885178. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35755072 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics and pathogenesis of CAKUT.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023 Nov;19(11):709-720. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00742-9. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37524861 Review.
-
Reverse phenotyping facilitates disease allele calling in exome sequencing of patients with CAKUT.Genet Med. 2022 Feb;24(2):307-318. doi: 10.1016/j.gim.2021.09.010. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Genet Med. 2022. PMID: 34906515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Report, North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies: NAPRTCS Annual Transplant. [(accessed on 1 September 2020)]; Available online: http://we.emmes.com/study/ped/annlrept/annualrept2014.pdf.
-
- Landini S., Mazzinghi B., Becherucci F., Allinovi M., Provenzano A., Palazzo V., Ravaglia F., Artuso R., Bosi E., Stagi S., et al. Reverse Phenotyping after Whole-Exome Sequencing in Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020;15:89–100. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06060519. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

