Audit and feedback to improve laboratory test and transfusion ordering in critical care: a systematic review
- PMID: 32560666
- PMCID: PMC7303577
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-020-00981-5
Audit and feedback to improve laboratory test and transfusion ordering in critical care: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Laboratory tests and transfusions are sometimes ordered inappropriately, particularly in the critical care setting, which sees frequent use of both. Audit and Feedback (A&F) is a potentially useful intervention for modifying healthcare provider behaviors, but its application to the complex, team-based environment of critical care is not well understood. We conducted a systematic review of the literature on A&F interventions for improving test or transfusion ordering in the critical care setting.
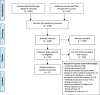
Methods: Five databases, two registries, and the bibliographies of relevant articles were searched. We included critical care studies that assessed the use of A&F targeting healthcare provider behaviors, alone or in combination with other interventions to improve test and transfusion ordering, as compared to historical practice, no intervention, or another healthcare behaviour change intervention. Studies were included only if they reported laboratory test or transfusion orders, or the appropriateness of orders, as outcomes. There were no restrictions based on study design, date of publication, or follow-up time. Intervention characteristics and absolute differences in outcomes were summarized. The quality of individual studies was assessed using a modified version of the Effective Practice and Organisation of Care Cochrane Review Group's criteria.
Results: We identified 16 studies, including 13 uncontrolled before-after studies, one randomized controlled trial, one controlled before-after study, and one controlled clinical trial (quasi-experimental). These studies described 17 interventions, mostly (88%) multifaceted interventions with an A&F component. Feedback was most often provided in a written format only (41%), more than once (53%), and most often only provided data aggregated to the group-level (41%). Most studies saw a change in the hypothesized direction, but not all studies provided statistical analyses to formally test improvement. Overall study quality was low, with studies often lacking a concurrent control group.
Conclusions: Our review summarizes characteristics of A&F interventions implemented in the critical care context, points to some mechanisms by which A&F might be made more effective in this setting, and provides an overview of how the appropriateness of orders was reported. Our findings suggest that A&F can be effective in the context of critical care; however, further research is required to characterize approaches that optimize the effectiveness in this setting alongside more rigorous evaluation methods.
Trial registration: PROSPERO CRD42016051941.
Keywords: Audit; Critical Care; Feedback; Intensive Care; Laboratory Utilization; Test Use; Transfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How well do critical care audit and feedback interventions adhere to best practice? Development and application of the REFLECT-52 evaluation tool.Implement Sci. 2021 Aug 17;16(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13012-021-01145-9. Implement Sci. 2021. PMID: 34404449 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
The evaluation of enhanced feedback interventions to reduce unnecessary blood transfusions (AFFINITIE): protocol for two linked cluster randomised factorial controlled trials.Implement Sci. 2017 Jul 3;12(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0614-8. Implement Sci. 2017. PMID: 28673310 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Enhanced feedback interventions to promote evidence-based blood transfusion guidance and reduce unnecessary use of blood components: the AFFINITIE research programme including two cluster factorial RCTs.Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2022 Mar. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2022 Mar. PMID: 35377572 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
A systematic review of electronic audit and feedback: intervention effectiveness and use of behaviour change theory.Implement Sci. 2017 May 12;12(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0590-z. Implement Sci. 2017. PMID: 28494799 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of de-implementation of low-value healthcare practices: an overview of systematic reviews.Implement Sci. 2024 Aug 5;19(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13012-024-01384-6. Implement Sci. 2024. PMID: 39103927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How well do critical care audit and feedback interventions adhere to best practice? Development and application of the REFLECT-52 evaluation tool.Implement Sci. 2021 Aug 17;16(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13012-021-01145-9. Implement Sci. 2021. PMID: 34404449 Free PMC article.
-
Audit and feedback interventions involving pharmacists to influence prescribing behaviour in general practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Fam Pract. 2023 Dec 22;40(5-6):615-628. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmac150. Fam Pract. 2023. PMID: 36633309 Free PMC article.
-
A descriptive study of routine laboratory testing in intensive care unit in nearly 140,000 patient stays.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 13;12(1):21526. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25961-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36513742 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the Gaps Between Best-Practice Implementation Strategies and Real-world Implementation: Qualitative Study Among Family Physicians Who Engaged With Audit and Feedback Reports.JMIR Hum Factors. 2023 Jan 6;10:e38736. doi: 10.2196/38736. JMIR Hum Factors. 2023. PMID: 36607715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Australian Association of Pathology Practices Inc. An analysis of pathology test use in australia. Family Medicine Research Centre, University of Sydney; 2011.
-
- Lewandrowski K, Baron J, Dighe A. Utilization management in the clinical laboratory: an introduction and overview. In: Lewandrowski K, Sluss P, editors. Utilization Management in the Clinical Laboratory and Other Ancillary Services. Springer, Cham; 2017.
-
- Ezzie ME, Aberegg SK, O’Brien JM. Laboratory Testing in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Clin. 2007;23(3):435–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical