A case report of familial 4q13.3 microdeletion in three individuals with syndromic intellectual disability
- PMID: 32299451
- PMCID: PMC7160938
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-020-0711-4
A case report of familial 4q13.3 microdeletion in three individuals with syndromic intellectual disability
Abstract
Background: Interstitial 4q deletions are rare chromosomal alterations. Most of the previously reported deletions involving the 4q13.3 region are large chromosomal alterations with a common loss of band 4q21 resulting in marked growth restriction, severe intellectual disability, and absent or severely delayed speech. A microdeletion of 4q13.3 hasn't been previously reported. We discuss the involvement of genes and the observed phenotype, comparing it with that of previously reported patients.
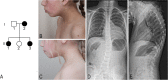
Case presentation: We report on a 4q13.3 microdeletion detected in three affected individuals of a Lithuanian family. The clinical features of two affected children and their affected mother are very similar and include short stature, congenital heart defect, skeletal anomalies, minor facial anomalies, delayed puberty, and intellectual disability. Whole genome SNP microarray analysis of one child revealed an interstitial 4q13.3 microdeletion, 1.56 Mb in size. FISH analysis confirmed the deletion in the proband and identified the same deletion in her affected sib and mother, while it was not detected in a healthy sib. Deletion includes ADAMTS3, ANKRD17, COX18, GC, and NPFFR2 protein-coding genes.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that 4q13.3 microdeletion is a cause of a recognizable phenotype of three affected individuals. The detected microdeletion is the smallest interstitial deletion in 4q13. We highlight ADAMTS3, ANKRD17 and RNU4ATAC9P as candidate genes for intellectual disability, growth retardation and congenital heart defect.
Keywords: 4q13.3 microdeletion; ADAMTS3; ANKRD17; COX18; Congenital anomalies; Intellectual disability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interstitial microdeletions including the chromosome band 4q13.2 and the UBA6 gene as possible causes of intellectual disability and behavior disorder.Am J Med Genet A. 2015 Dec;167A(12):3113-20. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37291. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Am J Med Genet A. 2015. PMID: 26284580
-
Clinical delineation of 18q11-q12 microdeletion: Intellectual disability, speech and behavioral disorders, and conotruncal heart defects.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Sep;7(9):e896. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.896. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31390163 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A novel maternally-derived insertional translocation resulting in partial trisomy 4q13.2-q22.1 with complex translocation t(8;20) in a family with intellectual disability.Am J Med Genet A. 2012 Apr;158A(4):901-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35259. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Am J Med Genet A. 2012. PMID: 22419381
-
8.6Mb interstitial deletion of chromosome 4q13.3q21.23 in a boy with cognitive impairment, short stature, hearing loss, skeletal abnormalities and facial dysmorphism.Genet Couns. 2011;22(4):353-63. Genet Couns. 2011. PMID: 22303795 Review.
-
Coexistence of urogenital malformations in a female fetus with de novo 15q24 microdeletion and a literature review.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Jul;8(7):e1265. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1265. Epub 2020 May 13. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32400031 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterozygous ANKRD17 loss-of-function variants cause a syndrome with intellectual disability, speech delay, and dysmorphism.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Jun 3;108(6):1138-1150. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.04.007. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33909992 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 model of prostate cancer identifies Kmt2c deficiency as a metastatic driver by Odam/Cabs1 gene cluster expression.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 7;15(1):2088. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46370-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38453924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zollino M, Murdolo M, Marangi G, Pecile V, Galasso C, Mazzanti L, Neri G. On the nosology and pathogenesis of Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome: genotype–phenotype correlation analysis of 80 patients and literature review. In: American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C: Seminars in Medical Genetics: 2008: Wiley Online Library; 2008. p. 257–69. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ajmg.c.30190. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonnet C, Andrieux J, Béri-Dexheimer M, Leheup B, Boute O, Manouvrier S, Delobel B, Copin H, Receveur A, Mathieu M, et al. Microdeletion at chromosome 4q21 defines a new emerging syndrome with marked growth restriction, mental retardation and absent or severely delayed speech. J Med Genet. 2010;47(6):377. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2009.071902. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

