Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome with simultaneous hyperplastic polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract: case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 32171268
- PMCID: PMC7071710
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-020-0991-8
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome with simultaneous hyperplastic polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract: case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (BHDS) is a rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis characterized by benign growth of the hair follicles, the presence of pulmonary cysts, spontaneous pneumothorax, and bilateral renal tumors that are usually hybrid oncocytic or multifocal chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. The diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of a pathogenic variant in the tumor suppressor folliculin (FLCN) gene mapped at 17p11.2. Although the dermatological lesions typical of BHDS are benign and only cause aesthetic concerns, and the pulmonary manifestations are controllable, the greater tendency of patients with this syndrome to present benign or malignant renal tumors, often bilateral and multifocal, makes the diagnosis of this syndrome important for the prognosis of the patients. The objective was to report the case of a patient with BHDS, without pulmonary manifestations and with hyperplastic polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract, and to perform a literature review.
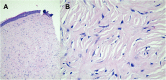
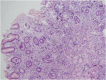
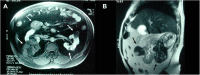
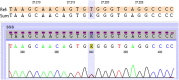
Case presentation: A 60-year-old man complained of abdominal pain and diarrhoea for 2 months. Physical examination was normal except for the presence of normochromic papules in the frontal region of the face associated with hyperkeratotic and hyperchromic papules in the dorsal region. The excisional biopsies of the skin lesions indicated trichodiscomas. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, enteroscopy, and colonoscopy showed the presence of hyperplastic polyps in the stomach, duodenum, jejunum, colon, and rectum. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen revealed multiple expansive solid lesions in both kidneys, with necrotic and calcified areas. Renal magnetic resonance angiography also showed a solid lesion in the right kidney measuring 5 cm in diameter and another solid lesion in the left kidney measuring 8 cm in diameter, both suggestive of renal angiomyolipoma. CT scans of the skull, chest, and temporal bones were normal. The genetic study revealed the presence of a variant of FLCN in the intron 13.
Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of BHDS with the simultaneous finding of gastrointestinal hyperplastic polyposis, which may represent a possible phenotypic expression of this syndrome that has not yet been described.
Keywords: Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome; FLCN gene; Pneumothorax; Polyps; Skin neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comment on Balsamo et al.: "Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome with simultaneous hyperplastic polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract: case report and review of the literature".BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Apr 15;15(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01233-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35428236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relevance of Family History Taking in the Detection and Management of Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome.Respiration. 2019;98(2):125-132. doi: 10.1159/000498973. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Respiration. 2019. PMID: 31266032
-
Heterozygous germline FLCN mutation in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome with bilateral renal hybrid oncocytic/chromophobe tumor and unilateral renal chromophobe cell carcinoma: a case report.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun;149(6):2319-2325. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04417-z. Epub 2022 Oct 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36258004
-
A case of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome implying reduced or no wild-type folliculin without mutated protein is pathogenic.Eur J Med Genet. 2020 Apr;63(4):103820. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2019.103820. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Eur J Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 31778855
-
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: Clinical and molecular aspects of recently identified kidney cancer syndrome.Int J Urol. 2016 Mar;23(3):204-10. doi: 10.1111/iju.13015. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Int J Urol. 2016. PMID: 26608100 Review.
Cited by
-
Comment on Balsamo et al.: Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome with simultaneous hyperplastic polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract: case report and review of the literature.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Apr 15;15(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01229-5. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35428286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Novel Pathogenic Folliculin Variant in a Chinese Family With Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome (Hornstein-Knickenberg Syndrome).Front Genet. 2020 Nov 2;11:565566. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.565566. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33240319 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of MET-variant digestive tract tumors.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):4338-4353. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i11.4338. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39554732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Toro JR, Wei MH, Glenn GM, Weinreich M, Toure O, Vocke C, Turner M, Choyke P, Merino MJ, Pinto PA, Steinberg SM, Schmidt LS, Linehan WM. BHD mutations, clinical and molecular genetic investigations of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: a new series of 50 families and a review of published reports. J Med Genet. 2008;45:321–331. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2007.054304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

