A review of recent publication trends from top publishing countries
- PMID: 30261915
- PMCID: PMC6161455
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-018-0819-1
A review of recent publication trends from top publishing countries
Abstract
Background: Evidence-based medicine relies on current best evidence from the medical literature, the patient's history, and the clinician's own experience to provide the best care for patients. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis are considered the highest levels of evidence for informing clinical decisions. Recently, reports have shown an increase in the number but a decrease in quality of meta-analysis publications. We reviewed publication trends and determined the countries with the most journal articles and types of publications in PubMed from 1995 to 2015.
Methods: We examined journal entries in PubMed from 1995 to 2015 from top publishing countries for total number of publications and citations in core clinical journals and in specific publication types (systematic reviews, meta-analysis, randomized controlled trials).
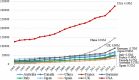
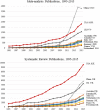
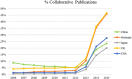
Results: Yearly, only 30 countries generated 94.6% of all publications and 98.1% of core clinical journals worldwide. All publication types increased but with a significant increase in meta-analysis publications from China. Collaborative and co-authored papers among the 30 countries also showed an increasing trend.
Conclusion: The USA leads in all publication citations and specific publication types, except for meta-analysis where China publishes more. Collaborative publishing among international collaborators is also increasing.
Keywords: Collaborative publishing; Evidence-based medicine; Meta-analysis; PubMed; Publication type; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orthopedics research output from China, USA, UK, Japan, Germany and France: A 10-year survey of the literature.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016 Nov;102(7):939-945. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27296711
-
Scientific publication in obstetrics and gynecology from Mainland China and other top-ranking countries: A 10-year survey of the literature.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019 Mar;45(3):695-704. doi: 10.1111/jog.13849. Epub 2018 Nov 4. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019. PMID: 30393998
-
Publication Trends in Acupuncture Research: A 20-Year Bibliometric Analysis Based on PubMed.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 14;11(12):e0168123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168123. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27973611 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific research output in orthopaedics from China and other top-ranking countries: a 10-year survey of the literature.BMJ Open. 2016 Sep 16;6(9):e011605. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011605. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27638493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
China's Contribution to Anesthesiology Research: A 10-Year Survey of the Literature.Anesth Analg. 2016 May;122(5):1640-5. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001225. Anesth Analg. 2016. PMID: 27003916 Review.
Cited by
-
COVID 19 Scoping: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021 Nov;13(Suppl 2):S938-S942. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_387_21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021. PMID: 35017902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Summary on Tuberculosis Vaccine Development-Where to Go?J Pers Med. 2023 Feb 24;13(3):408. doi: 10.3390/jpm13030408. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36983589 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic reviews: Not always a pain.Interv Pain Med. 2022 Aug 15;1(Suppl 2):100128. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2022.100128. eCollection 2022. Interv Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 39239125 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Literature on Physical Activity and COVID-19.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 10;19(12):7116. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127116. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742364 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Research on the Use of the Nine Hole Peg Test.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 15;19(16):10080. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191610080. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36011713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

