Oenococcus oeni Exopolysaccharide Biosynthesis, a Tool to Improve Malolactic Starter Performance
- PMID: 29946314
- PMCID: PMC6006919
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01276
Oenococcus oeni Exopolysaccharide Biosynthesis, a Tool to Improve Malolactic Starter Performance
Abstract
Oenococcus oeni is the lactic acid bacterium that most commonly drives malolactic fermentation (MLF) in wine. Though the importance of MLF in terms of wine microbial stability and sensory improvement is well established, it remains a winemaking step not so easy to control. O. oeni displays many adaptation tools to resist the harsh wine conditions which explain its natural dominance at this stage of winemaking. Previous findings showed that capsular polysaccharides and endogenous produced dextran increased the survival rate and the conservation time of malolactic starters. In this paper, we showed that exopolysaccharides specific production rates were increased in the presence of single stressors relevant to wine (pH, ethanol). The transcription of the associated genes was investigated in distinct O. oeni strains. The conditions in which eps genes and EPS synthesis were most stimulated were then evaluated for the production of freeze dried malolactic starters, for acclimation procedures and for MLF efficiency. Sensory analysis tests on the resulting wines were finally performed.
Keywords: Oenococcus oeni; exopolysaccharides; malolactic fermentation; stress; wine.
Figures

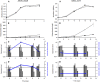
 ) and on glucose+sucrose medium (
) and on glucose+sucrose medium ( ). (B) Polysaccharide concentration (n = 3) on glucose medium (
). (B) Polysaccharide concentration (n = 3) on glucose medium ( ) and on glucose+sucrose medium (
) and on glucose+sucrose medium ( ). (C,D), Expression level relative to gyrA (2ΔCT) at the indicated time: the genes are described in the following order: pgm, ldh, wobA, wzx and dsrO. The blue point represents the expression ratio between wzx and wobA: relative gene expression on glucose medium (C) and on glucose+sucrose medium (D).
). (C,D), Expression level relative to gyrA (2ΔCT) at the indicated time: the genes are described in the following order: pgm, ldh, wobA, wzx and dsrO. The blue point represents the expression ratio between wzx and wobA: relative gene expression on glucose medium (C) and on glucose+sucrose medium (D).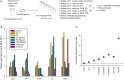
 acclimation to wine performed in standard conditions.
acclimation to wine performed in standard conditions.  acclimation to wine performed in the presence of 5 g/l sucrose.
acclimation to wine performed in the presence of 5 g/l sucrose.
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Transcriptomic Response to SO2 by Oenococcus oeni Growing in Continuous Culture.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0115421. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01154-21. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34612664 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and technological properties of Oenococcus oeni strains from wine spontaneous malolactic fermentations: a framework for selection of new starter cultures.J Appl Microbiol. 2010 Jan;108(1):285-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04428.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19614854
-
Effect of Biofilm Formation by Oenococcus oeni on Malolactic Fermentation and the Release of Aromatic Compounds in Wine.Front Microbiol. 2016 Apr 27;7:613. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00613. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27199942 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Oenococcus oeni to overcome challenges of wine malolactic fermentation.Trends Biotechnol. 2015 Sep;33(9):547-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jul 18. Trends Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26197706 Review.
-
Genomic variations of Oenococcus oeni strains and the potential to impact on malolactic fermentation and aroma compounds in wine.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Nov;92(3):441-7. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3546-2. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21870044 Review.
Cited by
-
Exopolysaccharides Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria in Wine and Other Fermented Beverages: For Better or for Worse?Foods. 2021 Sep 17;10(9):2204. doi: 10.3390/foods10092204. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34574312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterologous Expression of Argininosuccinate Synthase From Oenococcus oeni Enhances the Acid Resistance of Lactobacillus plantarum.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 21;10:1393. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01393. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31293541 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Transcriptomic Response to SO2 by Oenococcus oeni Growing in Continuous Culture.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0115421. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01154-21. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34612664 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Pediococcus ethanolidurans CUPV141: A β-D-glucan- and Heteropolysaccharide-Producing Bacterium.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 4;9:2041. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02041. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30233527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antalick G., Perello M. C., de Revel G. (2010). Development, validation and application of a specific method for the quantitative determination of wine esters by headspace-solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 121, 1236–1245. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.01.011 - DOI
-
- Assad-García J. S., Bonnin-Jusserand M., Garmyn D., Guzzo J., Alexandre H., Grandvalet C. (2008). An improved protocol for electroporation of Oenococcus oeni ATCC BAA-1163 using ethanol as immediate membrane fluidizing agent. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 47, 333–338. 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02435.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

