Structural Basis for the Versatile and Methylation-Dependent Binding of CTCF to DNA
- PMID: 28529057
- PMCID: PMC5542067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.004
Structural Basis for the Versatile and Methylation-Dependent Binding of CTCF to DNA
Abstract
The multidomain CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF), containing a tandem array of 11 zinc fingers (ZFs), modulates the three-dimensional organization of chromatin. We crystallized the human CTCF DNA-binding domain in complex with a known CTCF-binding site. While ZF2 does not make sequence-specific contacts, each finger of ZF3-7 contacts three bases of the 15-bp consensus sequence. Each conserved nucleotide makes base-specific hydrogen bonds with a particular residue. Most of the variable base pairs within the core sequence also engage in interactions with the protein. These interactions compensate for deviations from the consensus sequence, allowing CTCF to adapt to sequence variations. CTCF is sensitive to cytosine methylation at position 2, but insensitive at position 12 of the 15-bp core sequence. These differences can be rationalized structurally. Although included in crystallizations, ZF10 and ZF11 are not visible, while ZF8 and ZF9 span the backbone of the DNA duplex, conferring no sequence specificity but adding to overall binding stability.
Keywords: C2H2 zinc-finger arrays; CTCF; DNA methylation; DNA-binding adaptability to sequence variations; epigenetics; protein-DNA recognition.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
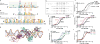

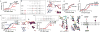

Similar articles
-
Structures of CTCF-DNA complexes including all 11 zinc fingers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Sep 8;51(16):8447-8462. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad594. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37439339 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into methylated DNA recognition by the C-terminal zinc fingers of the DNA reader protein ZBTB38.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 21;293(51):19835-19843. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005147. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30355731 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of directional CTCF recognition of a diverse range of genomic sites.Cell Res. 2017 Nov;27(11):1365-1377. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.131. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 29076501 Free PMC article.
-
Does CTCF mediate between nuclear organization and gene expression?Bioessays. 2010 Jan;32(1):37-50. doi: 10.1002/bies.200900118. Bioessays. 2010. PMID: 20020479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CTCF is a uniquely versatile transcription regulator linked to epigenetics and disease.Trends Genet. 2001 Sep;17(9):520-7. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(01)02366-6. Trends Genet. 2001. PMID: 11525835 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of DNA Methylation on TFs in Human Embryonic Stem Cells.Front Genet. 2021 Feb 23;12:639461. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.639461. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33708244 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial patterns of CTCF sites define the anatomy of TADs and their boundaries.Genome Biol. 2020 Aug 12;21(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02108-x. Genome Biol. 2020. PMID: 32782014 Free PMC article.
-
Brain and cancer associated binding domain mutations provide insight into CTCF's relationship with chromatin and its ability to act as a chromatin organizer.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 19:rs.3.rs-4670379. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4670379/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 39070636 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Neural network modeling of differential binding between wild-type and mutant CTCF reveals putative binding preferences for zinc fingers 1-2.BMC Genomics. 2022 Apr 12;23(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08486-9. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35410161 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF: an R/bioconductor data package of human and mouse CTCF binding sites.Bioinform Adv. 2022 Dec 16;2(1):vbac097. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbac097. eCollection 2022. Bioinform Adv. 2022. PMID: 36699364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell AC, Felsenfeld G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature. 2000;405:482–485. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

