High-frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 27043185
- PMCID: PMC6516956
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004085.pub4
High-frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
Background: High-frequency oscillation (HFO) is an alternative to conventional mechanical ventilation that is sometimes used to treat people with acute respiratory distress syndrome, but effects on oxygenation, mortality and adverse clinical outcomes are uncertain. This review was originally published in 2004 and was updated in 2013 and again in 2015.
Objectives: To determine the effects of HFO compared to conventional mechanical ventilation on physiological outcomes, clinical outcomes, and mortality when used for the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Search methods: We electronically searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (Ovid), MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE (Ovid), and ISI, from inception to December 2015. We conducted the original search in 2002. We manually searched reference lists from included studies and review articles; searched conference proceedings of the American Thoracic Society (1994 to 2015), Society of Critical Care Medicine (1994 to 2015), European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (1994 to 2015), and American College of Chest Physicians (1994 to 2015); contacted clinical experts in the field; and searched for unpublished and ongoing trials in clinicaltrials.gov and controlled-trials.com.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing treatment using HFO with conventional mechanical ventilation for children and adults diagnosed with ARDS.
Data collection and analysis: Three review authors independently extracted data on clinical, physiological, and safety outcomes according to a predefined protocol. We contacted investigators of all included studies to clarify methods and obtain additional data. We used random-effects models in the analyses.
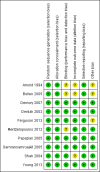
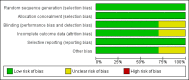
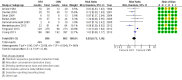
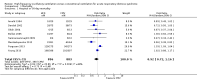
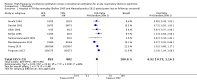
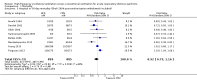
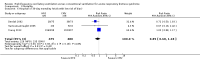
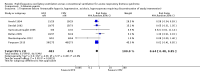
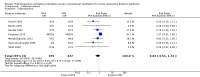
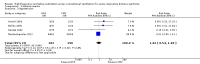
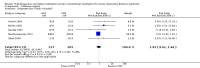
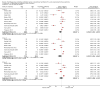
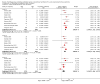
Main results: We include 10 RCTs (n = 1850); almost all participants had moderate or severe ARDS. For the primary analysis, the risk of bias was low in three studies and unclear in five studies; the overall quality of evidence was very low due to imprecision, inconsistency, indirectness and methodologic limitations. In participants randomized to HFO, there was no significant difference in hospital or 30-day mortality (risk ratio (RR) 0.92, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.72 to 1.16; P = 0.46, I² = 66%; 8 trials, 1779 participants, 807 deaths) compared with conventional ventilation. One large multicentre RCT was terminated early because of increased mortality in participants randomized to HFO compared to mechanical ventilation with low tidal volume and high positive end expiratory pressure, with HFO reserved only as a rescue therapy. We found substantial between-trial statistical heterogeneity (I² = 0% to 66%) for clinical outcomes, including mortality.
Authors' conclusions: The findings of this systematic review suggest that HFO does not reduce hospital and 30-day mortality due to ARDS; the quality of evidence was very low. Our findings do not support the use of HFO as a first-line strategy in people undergoing mechanical ventilation for ARDS.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the Cochrane online conflicts of interest form and declare the following:
Sachin Sud: nothing to declare. Maneesh Sud: nothing to declare. Jan O Friedrich: no financial interests to declare; Dr. Friedrich is a co‐investigators for the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) funded OSCILLATE study, which was included in this review (Ferguson 2013). CareFusion (formerly SensorMedics) is providing study oscillators to some of the hospitals involved in the OSCILLATE study for the duration of the study. Hannah Wunsch: nothing to declare. Maureen O Meade:no financial interests to declare; Dr. Meade is a primary investigator for the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) funded OSCILLATE study, which was included in this review (Ferguson 2013). CareFusion (formerly SensorMedics) is providing study oscillators to some of the hospitals involved in the OSCILLATE study for the duration of the study. Niall D Ferguson:no financial interests to declare; Dr. Ferguson is a primary investigator for the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) funded OSCILLATE study, which was included in this review (Ferguson 2013). CareFusion (formerly SensorMedics) is providing study oscillators to some of the hospitals involved in the OSCILLATE study for the duration of the study. Neill KJ Adhikari: no financial interests to declare; Dr. Adhikari is a co‐investigators for the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) funded OSCILLATE study, which was included in this review (Ferguson 2013). CareFusion (formerly SensorMedics) is providing study oscillators to some of the hospitals involved in the OSCILLATE study for the duration of the study.
Four of the seven authors (JOF, NKJA, NDF, MOM) co‐authored one of the included studies Ferguson 2013 and were not involved in the acquisition and interpretation of data, or the assessment of risk of bias for this study (which was performed by SS and MS). JOF verified the calculation of ratio of means (which was first performed independently by SS and MS), for physiologic outcomes for all studies, including Ferguson 2013.
Figures








Update of
-
High-frequency ventilation versus conventional ventilation for treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Feb 28;(2):CD004085. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004085.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 04;4:CD004085. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004085.pub4. PMID: 23450549 Updated. Review.
Similar articles
-
High-frequency ventilation versus conventional ventilation for treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Feb 28;(2):CD004085. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004085.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 04;4:CD004085. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004085.pub4. PMID: 23450549 Updated. Review.
-
Recruitment manoeuvres for adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome receiving mechanical ventilation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 17;11(11):CD006667. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006667.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27855477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pressure-controlled versus volume-controlled ventilation for acute respiratory failure due to acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 14;1(1):CD008807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008807.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25586462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prone position for acute respiratory failure in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 13;2015(11):CD008095. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008095.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26561745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung protective ventilation strategy for the acute respiratory distress syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Feb 28;2013(2):CD003844. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003844.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23450544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Salvage therapies for refractory hypoxemia in ARDS.Respir Med. 2018 Aug;141:150-158. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.06.030. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 30053961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical Ventilation and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygena tion in Acute Respiratory Insufficiency.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Dec 14;115(50):840-847. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.0840. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018. PMID: 30722839 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Microcirculation With Handheld Vital Microscopy in Critically Ill Neonates and Children: Evolution of the Technique and Its Potential for Critical Care.Front Pediatr. 2019 Jul 9;7:273. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00273. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31338353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-frequency oscillatory ventilation: A narrative review.Can J Respir Ther. 2019 May 2;55:40-46. doi: 10.29390/cjrt-2019-004. eCollection 2019. Can J Respir Ther. 2019. PMID: 31297448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of hypercapnia in critically ill mechanically ventilated patients-A narrative review of literature.J Intensive Care Soc. 2020 Nov;21(4):327-333. doi: 10.1177/1751143720915666. Epub 2020 Mar 30. J Intensive Care Soc. 2020. PMID: 34093735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arnold 1994 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Arnold JH, Hanson JH, Toro‐Figuero LO, Gutierrez J, Berens RJ, Anglin DL. Prospective, randomized comparison of high‐frequency oscillatory ventilation and conventional mechanical ventilation in pediatric respiratory failure. Critical Care Medicine 1994;22(10):1530‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bollen 2005 {published and unpublished data}
Demory 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Demory D, Michelet P, Arnal JM, Donati S, Forel JM, Gainnier M, et al. High‐frequency oscillatory ventilation following prone positioning prevents a further impairment in oxygenation. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35(1):106‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Derdak 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Derdak S, Mehta S, Stewart TE, Smith T, Rogers M, Buchman TG, et al. High‐frequency oscillatory ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults: a randomized, controlled trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;166(6):801‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ferguson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson N, Mehta S, Slutsky A, Stewart T, Hand L, Zhou Q, et al. Conversion from ventilation to high frequency oscillation ‐ physiologic responses in a pilot randomized trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2009;179:A3651.
-
- Ferguson ND, Cook DJ, Guyatt GH, Mehta S, Hand L, Austin P, et al. High‐frequency oscillation in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;368(9):795‐805. - PubMed
-
- Hand L, Matte A, Marie C, Ethier C, Lazosky L, Clarke F, et al. Results of a pilot randomized trial of High Frequency Oscillation in adults with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Critical Care Canada Forum (www.criticalcarecanada.com/abstracts/2009/high‐frequency‐oscillation.php). Toronto, Canada, 2009.
-
- Meade MO, Cook DJ, Mehta S, Arabi YM, Keenan S, Ronco JJ, et al. A multicentre pilot randomized trial of high frequency oscillation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2009; Vol. 179:A1559.
Mentzelopoulos 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Malachias S, Kokkoris S, Zakynthinos S, Mentzelopoulos SD. High frequency oscillation and tracheal gas insufflations for severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Results from a single‐center, phase II, randomized controlled trial [NCT00416260]. Intensive Care Medicine 2009;35 Suppl 1:S6.
-
- Mentzelopoulos SD, Malachias S, Tzoufi M, Markaki V, Zervakis D, Pitaridis M. High frequency oscillation and tracheal gas insufflation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Medicine 2007;33 Suppl 2:S142.
-
- Mentzelopoulos SD, Malachias S, Zintzaras E, Kokkoris S, Zakynthinos E, Makris D, et al. Intermittent recruitment with high‐frequency oscillation/tracheal gas insufflation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. European Respiratory Journal 2012;39(3):635‐47. - PubMed
Papazian 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Papazian L, Gainnier M, Marin V, Donati S, Arnal JM, Demory D, et al. Comparison of prone positioning and high‐frequency oscillatory ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 2005;33(10):2162‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Samransamruajkit 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Samransamruajkit R, Prapphal N, Deelodegenavong J, Poovorawan Y. Plasma soluble intercellular adhesion molecule‐1 (sICAM‐1) in pediatric ARDS during high frequency oscillatory ventilation: a predictor of mortality. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology 2005; Vol. 23, issue 4:181‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Samransamruajkit R, Prapphal N, Deerojanawong J, Vanapongtipagorn P, Poovorawan Y. Soluble Intercellular Adhesion Molecule‐1 (sICAM‐1) in pediatric ARDS during high frequency oscillatory ventilation; Randomized controlled trial, a predictor of mortality. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2003;167:A999. - PubMed
Shah 2004 {unpublished data only}
-
- Shah SB, Findlay GP, Jackson SK, Smithies MN. Prospective study comparing HFOV versus CMV in patients with ARDS. Intensive Care Medicine 2004;30 Suppl 1:S84.
-
- Shah SB, Jackson SK, Findlay GP, Smithies MN. Prospective study comparing high frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) versus conventional (CMV) in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [abstract]. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 2005;2:A847.
-
- Shah SB, Jackson SK, Findlay GP, Smithies MN. Ventilator induced lung injury comparing high frequency oscillator ventilation versus conventional mechanical ventilation [abstract]. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 2005;2:A251.
Young 2013 {published data only}
-
- Young D, Lamb SE, Shah S, MacKenzie I, Tunnicliffe W, Lall R, et al. High‐frequency oscillation for acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;368(9):806‐13. - PubMed
-
- Young JD. Conventional positive pressure ventilation or High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV) for adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN10416500 [accessed 1 August 2010].
References to studies excluded from this review
Carlon 1983 {published data only}
-
- Carlon GC, Howland WS, Ray C, Miodownik S, Griffin JP, Groeger JS. High‐frequency jet ventilation. A prospective randomized evaluation. Chest 1983;84(5):551‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dobyns 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dobyns EL, Anas NG, Fortenberry JD, Deshpande J, Cornfield DN, Tasker RC, et al. Interactive effects of high‐frequency oscillatory ventilation and inhaled nitric oxide in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure in pediatrics. Critical Care Medicine 2002;30(11):2425‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fessler 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fessler HE, Hager DN, Brower RG. Feasibility of very high‐frequency ventilation in adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 2008;36(4):1043‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hurst 1984 {published data only}
-
- Hurst JM, DeHaven CB. Adult respiratory distress syndrome: improved oxygenation during high‐frequency jet ventilation/continuous positive airway pressure. Surgery 1984;96(4):764‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hurst 1990 {published data only}
Mentzelopoulos 2007a {published data only}
-
- Mentzelopoulos SD, Roussos C, Koutsoukou A, Sourlas S, Malachias S, Lachana A, et al. Acute effects of combined high‐frequency oscillation and tracheal gas insufflation in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35(6):1500‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mentzelopoulos 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mentzelopoulos SD, Malachias S, Kokkoris S, Roussos C, Zakynthinos SG. Comparison of high‐frequency oscillation and tracheal gas insufflation versus standard high‐frequency oscillation at two levels of tracheal pressure. Critical Care Medicine 2010;36(5):810‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vrettou 2014 {published data only}
-
- Vrettou CS, Zakynthinos SG, Malachias S, Mentzelopoulos SD. The effect of high‐frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with tracheal gas insufflation on extravascular lung water in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized, crossover, physiologic study. Journal of Critical Care 2014;29(4):568‐73. - PubMed
Additional references
Adhikari 2007
Albuali 2007
-
- Albuali WH, Singh RN, Fraser DD, Seabrook JA, Kavanagh BP, Parshuram CS, et al. Have changes in ventilation practice improved outcome in children with acute lung injury?. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2007; Vol. 8, issue 4:324‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Amato 1998
-
- Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, Magaldi RB, Schettino GP, Lorenzi‐Filho G, et al. Effect of a protective‐ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(6):347‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Angus 2001
-
- Angus DC, Musthafa AA, Clermont G, Griffin MF, Linde‐Zwirble WT, Dremsizov TT, et al. Quality‐adjusted survival in the first year after the acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2001;163(6):1389‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ARDS Definition Task Force 2012
-
- ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, Fan E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012;307(23):2526‐33. - PubMed
ARDS Network 2000
-
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. New England Journal of Medicine 2000;342(18):1301‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Artigas 1998
-
- Artigas A, Bernard GR, Carlet J, Dreyfuss D, Gattinoni L, Hudson L, et al. The American‐European Consensus Conference on ARDS, part 2: Ventilatory, pharmacologic, supportive therapy, study design strategies, and issues related to recovery and remodeling. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1998;157(4 Pt 1):1332‐47. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Begg 1994
-
- Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994;50(4):1088‐101. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bein 2007
-
- Bein T, Ritzka M, Schmidt F, Taeger K. Positioning therapy in intensive care medicine in Germany. Results of a national survey [German]. Anaesthesist 2007;56(3):226‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Berlin 1997
-
- Berlin JA. Does blinding of readers affect the results of meta‐analyses? University of Pennsylvania Meta‐analysis Blinding Study Group. Lancet 1997;350(9072):185‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bernard 2008
-
- Bernard GR. PEEP guided by esophageal pressure‐‐any added value?. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;359(20):2166‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Briel 2010
-
- Briel M, Meade M, Mercat A, Brower RG, Talmor D, Walter SD, et al. Higher vs lower positive end‐expiratory pressure in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: systematic review and meta‐analysis. JAMA 2010;303(9):865‐73. - PubMed
Brochard 1998
-
- Brochard L, Roudot‐Thoraval F, Roupie E, Delclaux C, Chastre J, Fernandez‐Mondejar E, et al. Tidal volume reduction for prevention of ventilator‐induced lung injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Multicenter Trial Group on Tidal Volume reduction in ARDS. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1998;158(6):1831‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brun‐Buisson 2004
-
- Brun‐Buisson C, Minelli C, Bertolini G, Brazzi L, Pimentel J, Lewandowski K, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of acute lung injury in European intensive care units. Results from the ALIVE study. Intensive Care Medicine 2004;30(1):51‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cartotto 2004
-
- Cartotto R, Ellis S, Gomez M, Cooper A, Smith T. High frequency oscillatory ventilation in burn patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Burns 2004;30(5):453‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chalmers 1983
-
- Chalmers TC, Celano P, Sacks HS, Smith H Jr. Bias in treatment assignment in controlled clinical trials. New England Journal of Medicine 1983;309(22):1358‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chan 2005
-
- Chan KP, Stewart TE. Clinical use of high‐frequency oscillatory ventilation in adult patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 2005;33(3 Suppl):S170‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cheung 2006
-
- Cheung AM, Tansey CM, Tomlinson G, Diaz‐Granados N, Matte A, Barr A, et al. Two‐year outcomes, health care use, and costs of survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006;174(5):538‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cools 2015
Dominguez‐Cherit 2009
-
- Dominguez‐Cherit G, Lapinsky SE, Macias AE, Pinto R, Espinosa‐Perez L, Torre A, et al. Critically Ill patients with 2009 influenza A(H1N1) in Mexico. JAMA 2009;302(17):1880‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dreyfuss 1988
-
- Dreyfuss D, Soler P, Basset G, Saumon G. High inflation pressure pulmonary edema. Respective effects of high airway pressure, high tidal volume, and positive end‐expiratory pressure. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1988;137(5):1159‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ferguson 2005
-
- Ferguson ND, Chiche JD, Kacmarek RM, Hallett DC, Mehta S, Findlay GP, et al. Combining high‐frequency oscillatory ventilation and recruitment maneuvers in adults with early acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Treatment with Oscillation and an Open Lung Strategy (TOOLS) Trial pilot study. Critical Care Medicine 2005;33(3):479‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ferguson 2008
-
- Ferguson ND, Slutsky AS. Point: High‐frequency ventilation is the optimal physiological approach to ventilate ARDS patients. Journal of Applied Physiology 2008;104(4):1230‐1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Finkielman 2006
Flori 2005
-
- Flori HR, Glidden DV, Rutherford GW, Matthay MA. Pediatric acute lung injury: prospective evaluation of risk factors associated with mortality. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2005;171(9):995‐1001. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fort 1997
-
- Fort P, Farmer C, Westerman J, Johannigman J, Beninati W, Dolan S, et al. High‐frequency oscillatory ventilation for adult respiratory distress syndrome‐‐a pilot study. Critical Care Medicine 1997;25(6):937‐47. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Friedrich 2008
Gattinoni 2005
-
- Gattinoni L, Pesenti A. The concept of "baby lung". Intensive Care Medicine 2005;31(6):776‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gattinoni 2006
-
- Gattinoni L, Caironi P, Cressoni M, Chiumello D, Ranieri VM, Quintel M, et al. Lung recruitment in patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(17):1775‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Guérin 2013
-
- Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard JC, Beuret P, Gacouin A, Boulain T, et al. PROSEVA Study Group. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;368(23):2159‐68. - PubMed
Hager 2007
-
- Hager DN, Fessler HE, Kaczka DW, Shanholtz CB, Fuld MK, Simon BA, et al. Tidal volume delivery during high‐frequency oscillatory ventilation in adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35(6):1522‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hanson 2006
-
- Hanson JH, Flori H. Application of the acute respiratory distress syndrome network low‐tidal volume strategy to pediatric acute lung injury. Respiratory Care Clinics of North America 2006;12(3):349‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Haynes 2005
Henderson 2015
Herridge 2003
-
- Herridge MS, Cheung AM, Tansey CM, Matte‐Martyn A, Diaz‐Granados N, Al‐Saidi F, et al. One‐year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348(8):683‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Herridge 2011
-
- Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, Tomlinson G, Diaz‐Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2011;364(14):1293‐304. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kacmarek 2008
-
- Kacmarek RM. Counterpoint: High‐frequency ventilation is not the optimal physiological approach to ventilate ARDS patients. Journal of Applied Physiology 2008;104(4):1232‐3; discussion 1233‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kumar 2009
-
- Kumar A, Zarychanski R, Pinto R, Cook DJ, Marshall J, Lacroix J, et al. Critically ill patients with 2009 influenza A(H1N1) infection in Canada. JAMA 2009;302(17):1872‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Leonet 2002
-
- Leonet S, Fontaine C, Moraine JJ, Vincent JL. Prone positioning in acute respiratory failure: survey of Belgian ICU nurses. Intensive Care Medicine 2002;28(5):576‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Macaskill 2001
-
- Macaskill P, Walter SD, Irwig L. A comparison of methods to detect publication bias in meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(4):641‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meade 1997
-
- Meade MO, Richardson WS. Selecting and appraising studies for a systematic review. Annals of Internal Medicine 1997;127(7):531‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meade 2008
-
- Meade MO, Cook DJ, Guyatt GH, Slutsky AS, Arabi YM, Cooper DJ, et al. Ventilation strategy using low tidal volumes, recruitment maneuvers, and high positive end‐expiratory pressure for acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008;299(6):637‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehta 2001
-
- Mehta S, Lapinsky SE, Hallett DC, Merker D, Groll RJ, Cooper AB, et al. Prospective trial of high‐frequency oscillation in adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 2001;29(7):1360‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehta 2004
-
- Mehta S, Granton J, MacDonald RJ, Bowman D, Matte‐Martyn A, Bachman T, et al. High‐frequency oscillatory ventilation in adults: the Toronto experience. Chest 2004;126(2):518‐27. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mercat 2008
-
- Mercat A, Richard JC, Vielle B, Jaber S, Osman D, Diehl JL, et al. Positive end‐expiratory pressure setting in adults with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008;299(6):646‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Miller 2008
-
- Miller MP, Sagy M. Pressure characteristics of mechanical ventilation and incidence of pneumothorax before and after the implementation of protective lung strategies in the management of pediatric patients with severe ARDS. Chest 2008;134(5):969‐73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moher 2015
Montgomery 1985
-
- Montgomery AB, Stager MA, Carrico CJ, Hudson LD. Causes of mortality in patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1985;132(3):485‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Montori 2005
-
- Montori VM, Devereaux PJ, Adhikari NK, Burns KE, Eggert CH, Briel M, et al. Randomized trials stopped early for benefit: a systematic review. JAMA 2005;294(17):2203‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Muellenbach 2007
-
- Muellenbach RM, Kredel M, Said HM, Klosterhalfen B, Zollhoefer B, Wunder C, et al. High‐frequency oscillatory ventilation reduces lung inflammation: a large‐animal 24‐h model of respiratory distress. Intensive Care Medicine 2007;33(8):1423‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Muscedere 1994
-
- Muscedere JG, Mullen JB, Gan K, Slutsky AS. Tidal ventilation at low airway pressures can augment lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1994;149(5):1327‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Peek 2009
-
- Peek GJ, Mugford M, Tiruvoipati R, Wilson A, Allen E, Thalanany MM, et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009;374(9698):1351‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Peters 2006
-
- Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta‐analysis. JAMA 2006;295(6):676‐80. - PubMed
Phua 2009
-
- Phua J, Badia JR, Adhikari NK, Friedrich JO, Fowler RA, Singh JM, et al. Has mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome decreased over time?: A systematic review. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2009;179(3):220‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ranieri 1999
-
- Ranieri VM, Suter PM, Tortorella C, Tullio R, Dayer JM, Brienza A, et al. Effect of mechanical ventilation on inflammatory mediators in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999;282(1):54‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rimensberger 2003
Rubenfeld 2005
-
- Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353(16):1685‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2008
Sedeek 2003
-
- Sedeek KA, Takeuchi M, Suchodolski K, Vargas SO, Shimaoka M, Schnitzer JJ, et al. Open‐lung protective ventilation with pressure control ventilation, high‐frequency oscillation, and intratracheal pulmonary ventilation results in similar gas exchange, hemodynamics, and lung mechanics. Anesthesiology 2003;99(5):1102‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Slutsky 2002
-
- Slutsky AS, Drazen JM. Ventilation with small tidal volumes. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;347(9):630‐1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Slutsky 2009
-
- Slutsky AS. Improving outcomes in critically ill patients: the seduction of physiology. JAMA 2009;302(18):2030‐2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stapleton 2005
-
- Stapleton RD, Wang BM, Hudson LD, Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell ES, Steinberg KP. Causes and timing of death in patients with ARDS. Chest 2005;128(2):525‐32. - PubMed
Stata 9.2 [Computer program]
-
- StataCorp LP. Stata 9.2. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP, 2006.
Stewart 1998
-
- Stewart TE, Meade MO, Cook DJ, Granton JT, Hodder RV, Lapinsky SE, et al. Evaluation of a ventilation strategy to prevent barotrauma in patients at high risk for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pressure‐ and Volume‐Limited Ventilation Strategy Group. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(6):355‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sud 2008
-
- Sud S, Sud M, Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK. Effect of prone positioning in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome and high Simplified Acute Physiology Score II. Critical Care Medicine 2008;36(9):2711‐2; author reply 2712‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sud 2010a
-
- Sud S, Friedrich JO, Taccone P, Polli F, Adhikari NK, Latini R, et al. Prone ventilation reduces mortality in patients with acute respiratory failure and severe hypoxemia: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Intensive Care Medicine 2010;36(4):585‐99. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sud 2014
-
- Sud S, Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK, Taccone P, Mancebo J, Polli F, et al. Effect of prone positioning during mechanical ventilation on mortality among patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2014;186(10):E381‐90. - PMC - PubMed
Taccone 2009
-
- Taccone P, Pesenti A, Latini R, Polli F, Vagginelli F, Mietto C, et al. Prone positioning in patients with moderate and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009;302(18):1977‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Villar 2006
-
- Villar J, Kacmarek RM, Perez‐Mendez L, Aguirre‐Jaime A. A high positive end‐expiratory pressure, low tidal volume ventilatory strategy improves outcome in persistent acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized, controlled trial. Critical Care Medicine 2006;34(5):1311‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Sud 2007
-
- Sud S, Adhikari N, Ferguson ND, Friedrich JO, Sud M, Meade MO. High‐frequency oscillatory ventilation for ARDS: a meta‐analysis. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35(12 Suppl):A225.
Sud 2010b
-
- Sud S, Sud M, Friedrich JO, Meade MO, Ferguson ND, Wunsch H, et al. High frequency oscillation in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): systematic review and meta‐analysis. BMJ 2010;340:c2327. [1468‐5833: (Electronic)] - PubMed
Sud 2013
-
- Sud S, Sud M, Friedrich JO, Meade MO, Ferguson ND, Wunsch H, et al. High‐frequency ventilation versus conventional ventilation for treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004085.pub3] - DOI - PubMed
Wunsch 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

