Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Current Perspective on Established and Emerging Molecular Genetic Defects
- PMID: 26387786
- PMCID: PMC4822159
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.22904
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Current Perspective on Established and Emerging Molecular Genetic Defects
Abstract
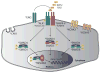
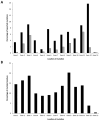
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is an often fatal disorder resulting from several causes including heterogeneous genetic defects. While mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II (BMPR2) gene are the single most common causal factor for hereditary cases, pathogenic mutations have been observed in approximately 25% of idiopathic PAH patients without a prior family history of disease. Additional defects of the transforming growth factor beta pathway have been implicated in disease pathogenesis. Specifically, studies have confirmed activin A receptor type II-like 1 (ACVRL1), endoglin (ENG), and members of the SMAD family as contributing to PAH both with and without associated clinical phenotypes. Most recently, next-generation sequencing has identified novel, rare genetic variation implicated in the PAH disease spectrum. Of importance, several identified genetic factors converge on related pathways and provide significant insight into the development, maintenance, and pathogenetic transformation of the pulmonary vascular bed. Together, these analyses represent the largest comprehensive compilation of BMPR2 and associated genetic risk factors for PAH, comprising known and novel variation. Additionally, with the inclusion of an allelic series of locus-specific variation in BMPR2, these data provide a key resource in data interpretation and development of contemporary therapeutic and diagnostic tools.
Keywords: ACVRL1; BMPR2; CAV1; EIF2AK4; ENG; KCNA5; KCNK3; SMAD1; SMAD4; SMAD9; haploinsufficiency; locus heterogeneity.
© 2015 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
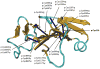
Similar articles
-
Defining the clinical validity of genes reported to cause pulmonary arterial hypertension.Genet Med. 2023 Nov;25(11):100925. doi: 10.1016/j.gim.2023.100925. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Genet Med. 2023. PMID: 37422716 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Dec 24;62(25 Suppl):D13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.035. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24355637 Review.
-
Genetic variants in a Polish population of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: sequencing of BMPR2, ALK1, and ENG genes.Kardiol Pol. 2018;76(5):852-859. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2018.0034. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Kardiol Pol. 2018. PMID: 29350394
-
Clinical and molecular genetic features of hereditary pulmonary arterial hypertension.Compr Physiol. 2011 Oct;1(4):1721-8. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c100063. Compr Physiol. 2011. PMID: 23733703 Review.
-
Genetic analyses in a cohort of 191 pulmonary arterial hypertension patients.Respir Res. 2018 May 9;19(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0789-9. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29743074 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of Genetic Predisposition in the Sex Bias of Pulmonary Pathophysiology, as a Function of Estrogens : Sex Matters in the Prevalence of Lung Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1303:107-127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63046-1_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33788190
-
In Search of the Second Hit in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Circ Res. 2019 Jan 4;124(1):6-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314270. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 30605416 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sotatercept analog suppresses inflammation to reverse experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension.Sci Rep. 2022 May 12;12(1):7803. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11435-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35551212 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetics of pulmonary hypertension in children.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022 Aug;75:101936. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2022.101936. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022. PMID: 35772304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Mutation Annotation and Pedigree for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients in Han Chinese Patients.Glob Heart. 2021 Oct 18;16(1):70. doi: 10.5334/gh.1002. eCollection 2021. Glob Heart. 2021. PMID: 34900561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdalla SA, Gallione CJ, Barst RJ, Horn EM, Knowles JA, Marchuk DA, Letarte M, Morse JH. Primary pulmonary hypertension in families with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Eur Respir J. 2004;23:373–377. - PubMed
-
- Aldred MA, Vijayakrishnan J, James V, Soubrier F, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Martensson G, Galie N, Manes A, Corris P, Simonneau G, Humbert M, Morrell NW, et al. BMPR2 gene rearrangements account for a significant proportion of mutations in familial and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:212–213. - PubMed
-
- Aldred MA, Machado RD, James V, Morrell NW, Trembath RC. Characterization of the BMPR2 5′-untranslated region and a novel mutation in pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:819–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

