Asparagine Synthetase Deficiency causes reduced proliferation of cells under conditions of limited asparagine
- PMID: 26318253
- PMCID: PMC10152381
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.08.007
Asparagine Synthetase Deficiency causes reduced proliferation of cells under conditions of limited asparagine
Abstract
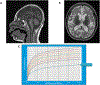
Asparagine Synthetase Deficiency is a recently described cause of profound intellectual disability, marked progressive cerebral atrophy and variable seizure disorder. To date there has been limited functional data explaining the underlying pathophysiology. We report a new case with compound heterozygous mutations in the ASNS gene (NM_183356.3:c. [866G>C]; [1010C>T]). Both variants alter evolutionarily conserved amino acids and were predicted to be pathogenic based on in silico protein modelling that suggests disruption of the critical ATP binding site of the ASNS enzyme. In patient fibroblasts, ASNS expression as well as protein and mRNA stability are not affected by these variants. However, there is markedly reduced proliferation of patient fibroblasts when cultured in asparagine-limited growth medium, compared to parental and wild type fibroblasts. Restricting asparagine replicates the physiology within the blood-brain-barrier, with limited transfer of dietary derived asparagine, resulting in reliance of neuronal cells on intracellular asparagine synthesis by the ASNS enzyme. These functional studies offer insight into the underlying pathophysiology of the dramatic progressive cerebral atrophy associated with Asparagine Synthetase Deficiency.
Keywords: ATP binding; Asparagine; Epileptic encephalopathy; Exome sequencing; Intellectual disability.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

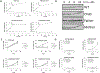
Similar articles
-
Asparagine synthetase: Function, structure, and role in disease.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 8;292(49):19952-19958. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R117.819060. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29084849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular characterization of two novel asparagine synthetase gene mutations linked to asparagine synthetase deficiency.J Biol Chem. 2022 Sep;298(9):102385. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102385. Epub 2022 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35985424 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Enzyme Activity and Cellular Function for the N80S and S480F Asparagine Synthetase Variants Expressed in a Child with Asparagine Synthetase Deficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):559. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010559. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613999 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagine synthetase deficiency detected by whole exome sequencing causes congenital microcephaly, epileptic encephalopathy and psychomotor delay.Metab Brain Dis. 2015 Jun;30(3):687-94. doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9618-0. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Metab Brain Dis. 2015. PMID: 25227173 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagine Synthetase deficiency-report of a novel mutation and review of literature.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Dec;32(6):1889-1900. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0073-6. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 28776279 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal deficiency of ARV1 causes an autosomal recessive epileptic encephalopathy.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Jul 15;25(14):3042-3054. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw157. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27270415 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagine synthetase: Function, structure, and role in disease.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 8;292(49):19952-19958. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R117.819060. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29084849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating exome sequencing into a diagnostic pathway for epileptic encephalopathy: Evidence of clinical utility and cost effectiveness.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2018 Mar;6(2):186-199. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.355. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2018. PMID: 29314763 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy suppression potentiates the anti-glioblastoma effect of asparaginase in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 20;8(53):91052-91066. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19409. eCollection 2017 Oct 31. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29207624 Free PMC article.
-
A novel compound heterozygous missense mutation in ASNS broadens the spectrum of asparagine synthetase deficiency.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Jun;8(6):e1235. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1235. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32255274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ruzzo EK, Capo-Chichi JM, Ben-Zeev B, Chitayat D, Mao H, Pappas AL, Hitomi Y, Lu YF, Yao X, Hamdan FF, Pelak K, Reznik-Wolf H, Bar-Joseph I, Oz-Levi D, Lev D, Lerman-Sagie T, Leshinsky-Silver E, Anikster Y, Ben-Asher E, Olender T, Colleaux L, Décarie JC, Blaser S, Banwell B, Joshi RB, He XP, Patry L, Silver RJ, Dobrzeniecka S, Islam MS, Hasnat A, Samuels ME, Aryal DK, Rodriguiz RM, Jiang YH, Wetsel WC, McNamara JO, Rouleau GA, Silver DL, Lancet D, Pras E, Mitchell GA, Michaud JL, Goldstein DB, Deficiency of asparagine synthetase causes congenital microcephaly and a progressive form of encephalopathy, Neuron 80 (2013)429–441. - PMC - PubMed
Web References
-
- CADD. http://cadd.gs.washington.edu/
- EXAC http://exac.broadinstitute.org;
- dbSNP http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP;
- EVS http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/;
- 1000 Genomes http://www.1000genomes.org;
- PROVEAN. http://provean.jcvi.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

