De-DUFing the DUFs: Deciphering distant evolutionary relationships of Domains of Unknown Function using sensitive homology detection methods
- PMID: 26228684
- PMCID: PMC4520260
- DOI: 10.1186/s13062-015-0069-2
De-DUFing the DUFs: Deciphering distant evolutionary relationships of Domains of Unknown Function using sensitive homology detection methods
Abstract
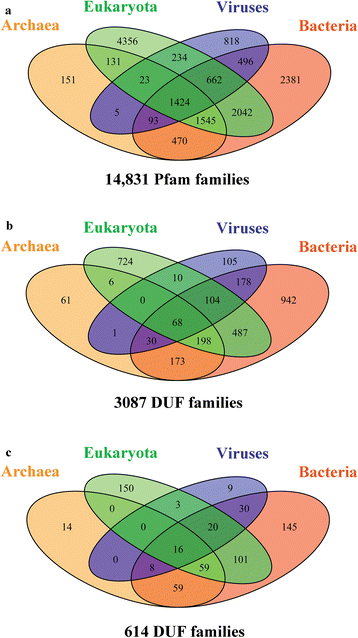
Background: In the post-genomic era where sequences are being determined at a rapid rate, we are highly reliant on computational methods for their tentative biochemical characterization. The Pfam database currently contains 3,786 families corresponding to "Domains of Unknown Function" (DUF) or "Uncharacterized Protein Family" (UPF), of which 3,087 families have no reported three-dimensional structure, constituting almost one-fourth of the known protein families in search for both structure and function.
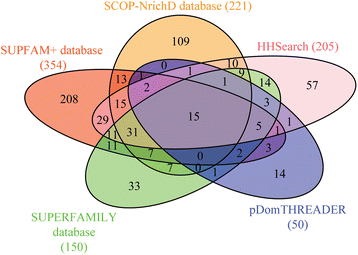
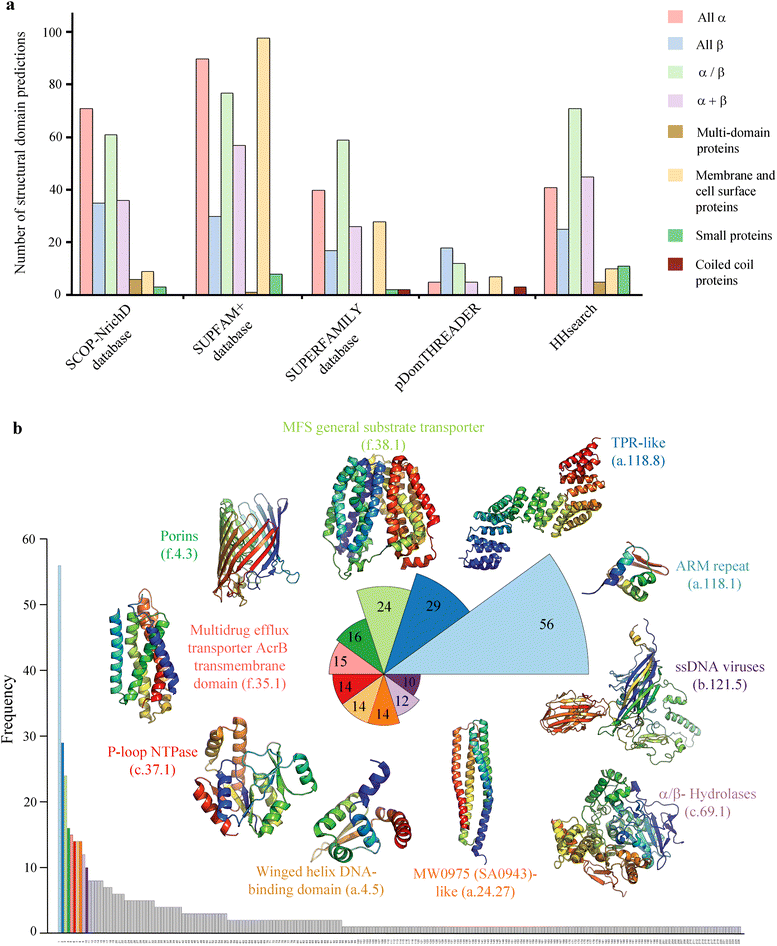
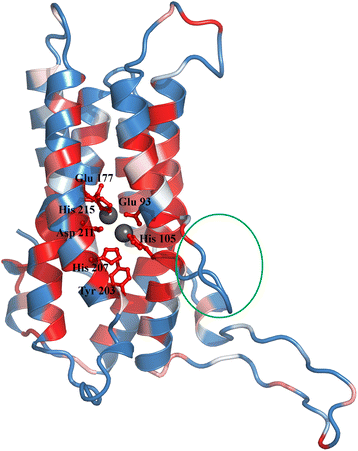
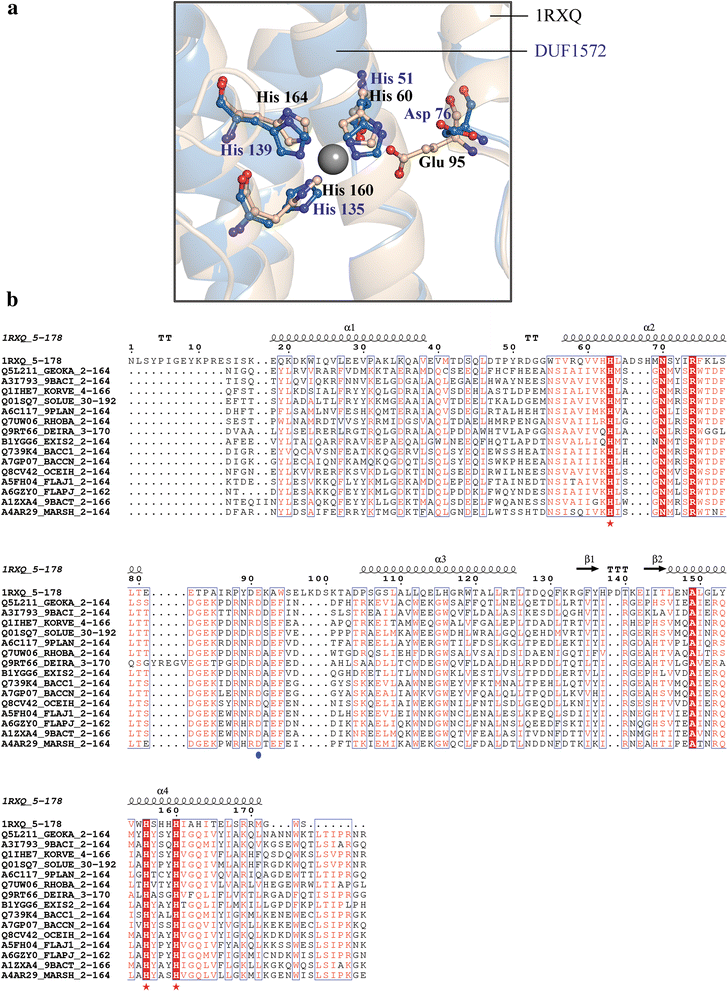
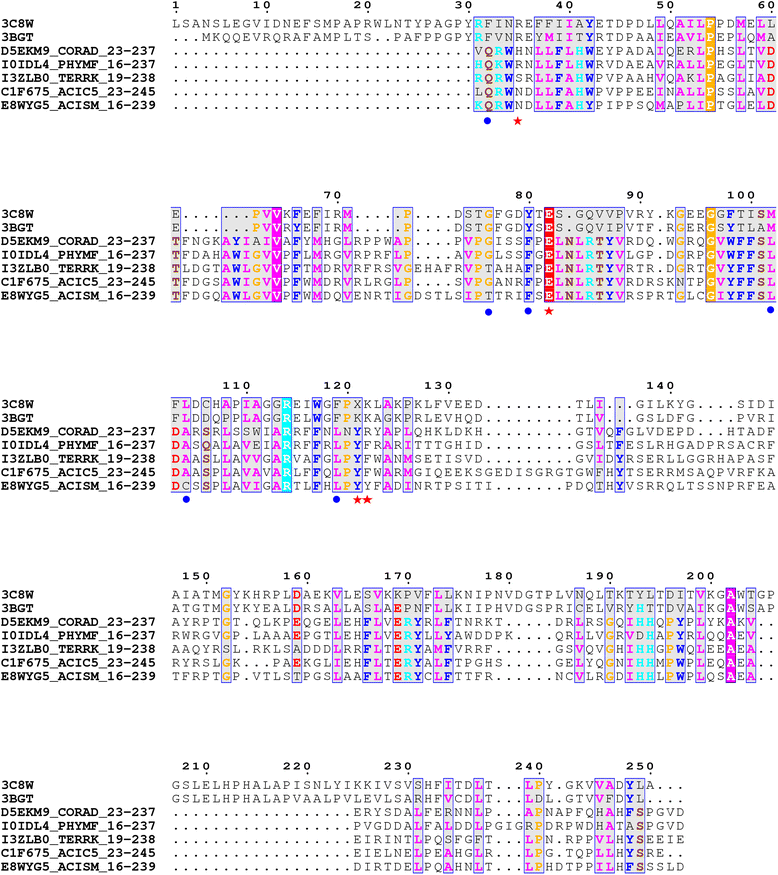
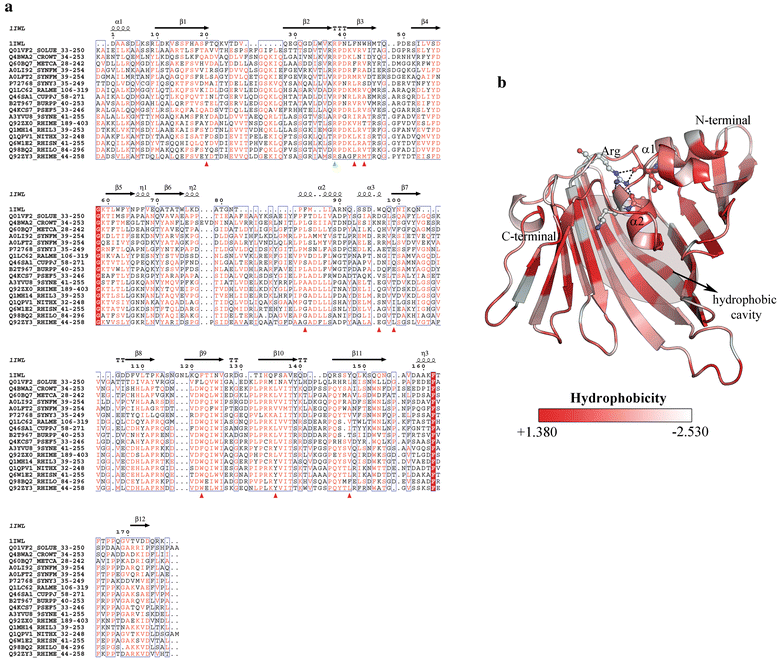
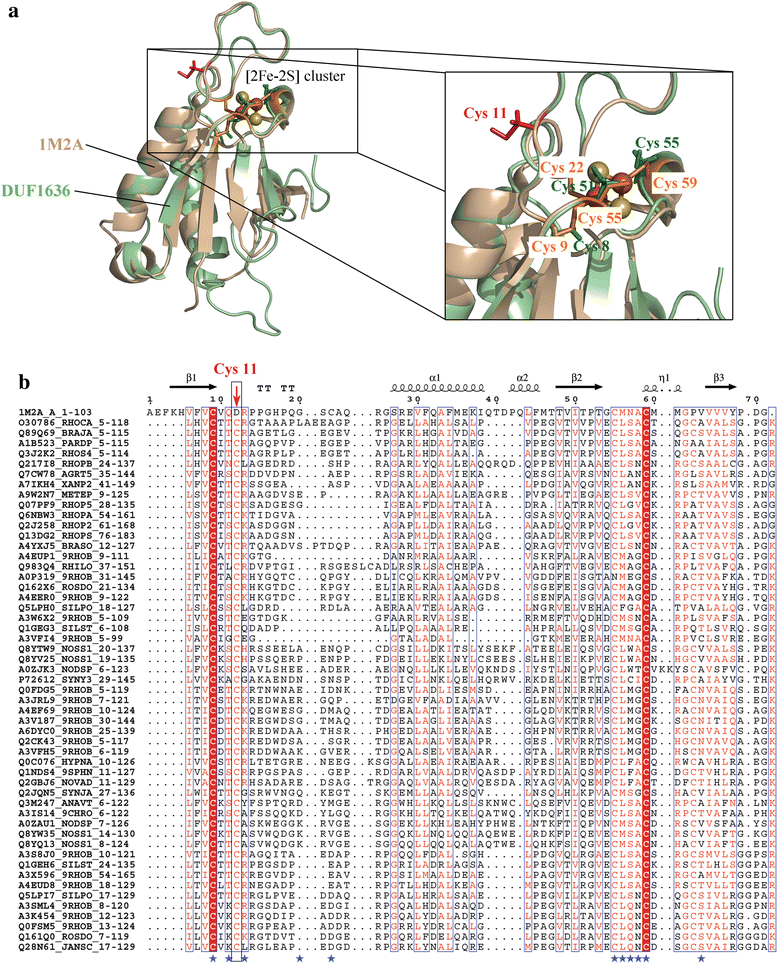
Results: We applied a 'computational structural genomics' approach using five state-of-the-art remote similarity detection methods to detect the relationship between uncharacterized DUFs and domain families of known structures. The association with a structural domain family could serve as a start point in elucidating the function of a DUF. Amongst these five methods, searches in SCOP-NrichD database have been applied for the first time. Predictions were classified into high, medium and low- confidence based on the consensus of results from various approaches and also annotated with enzyme and Gene ontology terms. 614 uncharacterized DUFs could be associated with a known structural domain, of which high confidence predictions, involving at least four methods, were made for 54 families. These structure-function relationships for the 614 DUF families can be accessed on-line at http://proline.biochem.iisc.ernet.in/RHD_DUFS/ . For potential enzymes in this set, we assessed their compatibility with the associated fold and performed detailed structural and functional annotation by examining alignments and extent of conservation of functional residues. Detailed discussion is provided for interesting assignments for DUF3050, DUF1636, DUF1572, DUF2092 and DUF659.
Conclusions: This study provides insights into the structure and potential function for nearly 20 % of the DUFs. Use of different computational approaches enables us to reliably recognize distant relationships, especially when they converge to a common assignment because the methods are often complementary. We observe that while pointers to the structural domain can offer the right clues to the function of a protein, recognition of its precise functional role is still 'non-trivial' with many DUF domains conserving only some of the critical residues. It is not clear whether these are functional vestiges or instances involving alternate substrates and interacting partners.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SUPFAM--a database of potential protein superfamily relationships derived by comparing sequence-based and structure-based families: implications for structural genomics and function annotation in genomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):289-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.289. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11752317 Free PMC article.
-
NrichD database: sequence databases enriched with computationally designed protein-like sequences aid in remote homology detection.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D300-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku888. Epub 2014 Sep 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25262355 Free PMC article.
-
SUPFAM: a database of sequence superfamilies of protein domains.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Mar 15;5:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-28. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15113407 Free PMC article.
-
Domain of unknown function (DUF) proteins in plants: function and perspective.Protoplasma. 2024 May;261(3):397-410. doi: 10.1007/s00709-023-01917-8. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Protoplasma. 2024. PMID: 38158398 Review.
-
Unraveling the Diverse Roles of Neglected Genes Containing Domains of Unknown Function (DUFs): Progress and Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4187. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044187. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
REL2, A Gene Encoding An Unknown Function Protein which Contains DUF630 and DUF632 Domains Controls Leaf Rolling in Rice.Rice (N Y). 2016 Dec;9(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12284-016-0105-6. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Rice (N Y). 2016. PMID: 27473144 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine-Rich Small Proteins with a Domain of Unknown Function, DUF1127, Play a Role in Phosphate and Carbon Metabolism of Agrobacterium tumefaciens.J Bacteriol. 2020 Oct 22;202(22):e00309-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00309-20. Print 2020 Oct 22. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 33093235 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of conserved DUF177A protein in plastid 23S rRNA accumulation and plant embryogenesis.J Exp Bot. 2016 Oct;67(18):5447-5460. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw311. Epub 2016 Aug 29. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27574185 Free PMC article.
-
TIM29 is required for enhanced stem cell activity during regeneration in the flatworm Macrostomum lignano.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1166. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80682-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441924 Free PMC article.
-
A DUF4148 family protein produced inside RAW264.7 cells is a critical Burkholderia pseudomallei virulence factor.Virulence. 2020 Dec;11(1):1041-1058. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1806675. Virulence. 2020. PMID: 32835600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eisenhaber F. A decade after the first full human genome sequencing: when will we understand our own genome? J Bioinform Comput Biol.10(5):1271001. doi:10.1142/S0219720012710011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

