Germline ETV6 Mutations Confer Susceptibility to Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 26102509
- PMCID: PMC4477877
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005262
Germline ETV6 Mutations Confer Susceptibility to Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Thrombocytopenia
Abstract
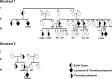
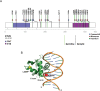
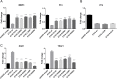
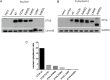
Somatic mutations affecting ETV6 often occur in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the most common childhood malignancy. The genetic factors that predispose to ALL remain poorly understood. Here we identify a novel germline ETV6 p. L349P mutation in a kindred affected by thrombocytopenia and ALL. A second ETV6 p. N385fs mutation was identified in an unrelated kindred characterized by thrombocytopenia, ALL and secondary myelodysplasia/acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemic cells from the proband in the second kindred showed deletion of wild type ETV6 with retention of the ETV6 p. N385fs. Enforced expression of the ETV6 mutants revealed normal transcript and protein levels, but impaired nuclear localization. Accordingly, these mutants exhibited significantly reduced ability to regulate the transcription of ETV6 target genes. Our findings highlight a novel role for ETV6 in leukemia predisposition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Germline deletion of ETV6 in familial acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood Adv. 2019 Apr 9;3(7):1039-1046. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018030635. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30940639 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of ETV6-mediated predisposition to childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 2021 Jan 21;137(3):364-373. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006164. Blood. 2021. PMID: 32693409 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of germline ETV6 W380R mutation causing inherited thrombocytopenia and secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia or essential thrombocythemia.Platelets. 2021 Aug 18;32(6):838-841. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2020.1802416. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Platelets. 2021. PMID: 32819174
-
Germline ETV6 mutations and predisposition to hematological malignancies.Int J Hematol. 2017 Aug;106(2):189-195. doi: 10.1007/s12185-017-2259-4. Epub 2017 May 29. Int J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28555414 Review.
-
Detection of a new heterozygous germline ETV6 mutation in a case with hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Eur J Haematol. 2018 Jan;100(1):104-107. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12981. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Eur J Haematol. 2018. PMID: 29034503 Review.
Cited by
-
ETV6-related thrombocytopenia: dominant negative effect of mutations as common pathogenic mechanism.Haematologica. 2022 Sep 1;107(9):2249-2254. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.280729. Haematologica. 2022. PMID: 35586967 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
TP53, ETV6 and RUNX1 germline variants in a case series of patients developing secondary neoplasms after treatment for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Haematologica. 2019 Sep;104(9):e402-e405. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.205849. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 31289210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
ETV6-NTRK3 induces aggressive acute lymphoblastic leukemia highly sensitive to selective TRK inhibition.Blood. 2018 Aug 23;132(8):861-865. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-849554. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29880614 Free PMC article.
-
ETV6: A Candidate Gene for Predisposition to "Blend Pedigrees"? A Case Report from the NEXT-Famly Clinical Trial.Case Rep Hematol. 2020 Jan 11;2020:2795656. doi: 10.1155/2020/2795656. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32148977 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide Association Study of Platelet Count Identifies Ancestry-Specific Loci in Hispanic/Latino Americans.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Feb 4;98(2):229-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.12.003. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 26805783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malkin D, Nichols KE, Zelley K, Schiffman JD (2014) Predisposition to pediatric and hematologic cancers: a moving target. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book: e44-55. - PubMed
-
- Pui C-H (2012) Childhood leukemias Cambridge, UK; New York: Cambridge University Press; xi, 880 p., 824 p. of col. plates p.
-
- Arepally G, Rebbeck TR, Song W, Gilliland G, Maris JM, et al. (1998) Evidence for genetic homogeneity in a familial platelet disorder with predisposition to acute myelogenous leukemia (FPD/AML). Blood 92: 2600–2602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM92666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK099808/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA178800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA178800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA036401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA36401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30 CA08748-40/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM092666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA036401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007266/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

