A review of prospective Clinical Trials for neurogenic bladder: Pharmaceuticals
- PMID: 25247085
- PMCID: PMC4165668
- DOI: 10.5173/ceju.2014.03.art11
A review of prospective Clinical Trials for neurogenic bladder: Pharmaceuticals
Abstract
Introduction: The neurogenic urinary bladder is defined as a dysfunctional bladder associated with a known neurological injury. We review the data from good quality clinical trials looking at drug therapy for the neurogenic bladder.
Materials and methods: IN ORDER TO IDENTIFY AS MANY PROSPECTIVE TRIALS AS POSSIBLE, WE PERFORMED INTERNET SEARCHES, USING THE SAME SEARCH STRING: Urinary Bladder, neurogenic (MESH). In each case, the search was limited to clinical trial, prospective trial, subjects were human and the language was English. There was no year limit for our search. The next step was duplicate removal, which led to a final number of 580 papers. We defined clear inclusion criteria for the papers.
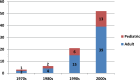
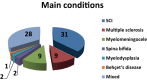
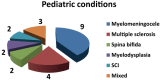
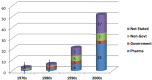
Results: A total of 82 full text papers were reviewed and analyzed according to the previously mentioned algorithm. The oldest two prospective clinical trials date back to 1976, with an obvious increase in number of trials each year, reaching more than five trials per year after 2001, which demonstrates increased interest toward the subject. The total number of patients included in the trials is 3904, 888 of which are children. The male: female ratio is close to 1, although there were 9 studies where no information regarding the sex of the patients was available.
Conclusions: Our analysis stresses the acute need for good quality trials looking at the drugs used for the management of the patients with neurogenic bladders, with adequate statistical power to support the data they present.
Keywords: antimuscarinics; botulinum toxin; clinical trial; drug therapy; neurogenic bladder.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A review of prospective Clinical Trials for neurogenic bladder: The place of surgery, experimental techniques and devices.Cent European J Urol. 2014;67(3):270-6. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2014.03.art12. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Cent European J Urol. 2014. PMID: 25247086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botulinum toxin injections for adults with overactive bladder syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;(12):CD005493. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005493.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 22161392 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin A intradetrusor injections in adults with neurogenic detrusor overactivity/neurogenic overactive bladder: a systematic review.Drugs. 2013 Jul;73(10):1055-66. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0068-5. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23775527 Review.
-
Use of botulinum toxin in individuals with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: state of the art review.J Spinal Cord Med. 2013 Sep;36(5):402-19. doi: 10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000116. J Spinal Cord Med. 2013. PMID: 23941788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botulinum injection is useless on fibrotic neuropathic bladders.J Pediatr Urol. 2015 Feb;11(1):27.e1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2014.08.009. Epub 2014 Sep 28. J Pediatr Urol. 2015. PMID: 25448589
Cited by
-
Angiogenic systemic response to the hypoxic microenvironment in prostate tumorigenesis: A pilot study.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Sep 1;26(4):483. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12182. eCollection 2023 Oct. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37753291 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of pharmacotherapy on prostate volume, prostate perfusion and prostate-specific antigen (prostate morphometric parameters) in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and benign prostatic obstruction. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cent European J Urol. 2021;74(3):388-421. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2021.132.R1. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Cent European J Urol. 2021. PMID: 34729231 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue Fixation System ligament repair cures major pelvic organ prolapse in ageing women with minimal complications - a 10-year Japanese experience in 960 women.Cent European J Urol. 2021;74(4):552-562. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2021.0208. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Cent European J Urol. 2021. PMID: 35083076 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo onset and duration of action varies for botulinum neurotoxin A subtypes 1-5.Toxicon. 2015 Dec 1;107(Pt A):37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.06.021. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Toxicon. 2015. PMID: 26130522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klausner AP, Steers WD. The neurogenic bladder: an update with management strategies for primary care physicians. Med Clin North Am. 2011;95:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Wyndaele JJ, Kovindha A, Madersbacher H, Radziszewski P, Ruffion A, Schurch B, et al. Committe 10 on Neurogenic Bladder and Bowel of the International Consultation on Incontinence 2008–2009. Neurologic urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Novara G, Galfano A, Secco S, D'Elia C, Cavalleri S, Ficarra V, Artibani W. A systematic review and meta–analysis of randomized controlled trials with antimuscarinic drugs for overactive bladder. Eur Urol. 2008;54:740–763. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials