A systematic review of the botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological profile of Dracaena cochinchinensis, a plant source of the ethnomedicine "dragon's blood"
- PMID: 25054444
- PMCID: PMC6270834
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules190710650
A systematic review of the botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological profile of Dracaena cochinchinensis, a plant source of the ethnomedicine "dragon's blood"
Abstract
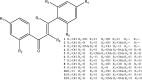
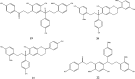
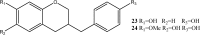
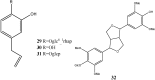
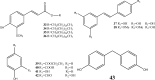
"Dragon's blood" is the name given to a deep red resin obtained from a variety of plant sources. The resin extracted from stems of Dracaena cochinchinensis is one such source of "dragon's blood". It has a reputation for facilitating blood circulation and dispersing blood stasis. In traditional Chinese medicine, this resinous medicine is commonly prescribed to invigorate blood circulation for the treatment of traumatic injuries, blood stasis and pain. Modern pharmacological studies have found that this resinous medicine has anti-bacterial, anti-spasmodic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-diabetic, and anti-tumor activities, while it is also known to enhance immune function, promote skin repair, stop bleeding and enhance blood circulation. Various compounds have been isolated from the plant, including loureirin A, loureirin B, loureirin C, cochinchinenin, socotrin-4'-ol, 4',7-dihydroxyflavan, 4-methylcholest-7-ene-3-ol, ethylparaben, resveratrol, and hydroxyphenol. The present review summarizes current knowledge concerning the botany, phytochemistry, pharmacological effects, toxicology studies and clinical applications of this resinous medicine as derived from D. cochinchinenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

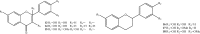
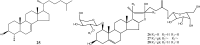
Similar articles
-
Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of Dracaena cinnabari Resin.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jul 22;2021:8561696. doi: 10.1155/2021/8561696. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34337055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural potential therapeutic agents of neurodegenerative diseases from the traditional herbal medicine Chinese dragon's blood.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 28;152(3):508-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.032. Epub 2014 Feb 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24509154
-
Modulation of dragon's blood on tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons and identification of its material basis for efficacy.Sci China C Life Sci. 2006 Jun;49(3):274-85. doi: 10.1007/s11427-006-0274-4. Sci China C Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16856497
-
Comparison of the chemical profiles and anti-platelet aggregation effects of two "Dragon's Blood" drugs used in traditional Chinese medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Jan 27;133(2):796-802. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.11.008. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21073937
-
Phenolic constituents, pharmacological activities, quality control, and metabolism of Dracaena species: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Nov 15;244:112138. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112138. Epub 2019 Aug 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31390529 Review.
Cited by
-
Dragon's Blood Regulates Rac1-WAVE2-Arp2/3 Signaling Pathway to Protect Rat Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction Induced by Simulated Microgravity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 8;22(5):2722. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052722. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800361 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo transcriptome characterization of Dracaena cambodiana and analysis of genes involved in flavonoid accumulation during formation of dragon's blood.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 6;6:38315. doi: 10.1038/srep38315. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27922066 Free PMC article.
-
Daemonorops draco Blume Induces Apoptosis Against Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via Regulation of the miR-216b/c-Jun.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 9;12:808174. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.808174. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35356209 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of Dracaena cinnabari Resin.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jul 22;2021:8561696. doi: 10.1155/2021/8561696. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34337055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunosuppressive effects and mechanisms of loureirin B on collagen-induced arthritis in rats.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 24;14:1094649. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1094649. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37168850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- State Bureau of Environmental Protection of China. Institute of Botany Chinese Academy of Sciences . List of Vulnerable and Threatened Species of China. Science Press; Beijing, China: 1987.
-
- Editorial Board of Flora of China. Chinese Academy of Sciences . Flora of China. Volume 14. Science Press; Beijing, China: 1980. pp. 276–277.
-
- Medical Plant Image Database from School of Chinese Medicine in Hong Kong Baptist University. [(accessed on 6 July 2014)]. Available online: http://library.hkbu.edu.hk/electronic/libdbs/mpd/index.html.
-
- Cai X.T., Xu Z.F. A study on the resource of Chinese dragon’s blood. Yunnan Zhi Wu Yan Jiu. 1979;1:1–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

