Exome sequencing reveals de novo WDR45 mutations causing a phenotypically distinct, X-linked dominant form of NBIA
- PMID: 23176820
- PMCID: PMC3516593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.10.019
Exome sequencing reveals de novo WDR45 mutations causing a phenotypically distinct, X-linked dominant form of NBIA
Abstract
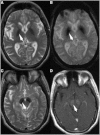
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) is a group of genetic disorders characterized by abnormal iron deposition in the basal ganglia. We report that de novo mutations in WDR45, a gene located at Xp11.23 and encoding a beta-propeller scaffold protein with a putative role in autophagy, cause a distinctive NBIA phenotype. The clinical features include early-onset global developmental delay and further neurological deterioration (parkinsonism, dystonia, and dementia developing by early adulthood). Brain MRI revealed evidence of iron deposition in the substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Males and females are phenotypically similar, an observation that might be explained by somatic mosaicism in surviving males and germline or somatic mutations in females, as well as skewing of X chromosome inactivation. This clinically recognizable disorder is among the more common forms of NBIA, and we suggest that it be named accordingly as beta-propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Neurodegenerative disorder with brain iron accumulation previously known as SENDA syndrome now genetically determined.Mov Disord. 2013 Jul;28(8):1051-2. doi: 10.1002/mds.25424. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 23868373 No abstract available.
-
Autophagy and neurodegeneration - genetic findings in SENDA syndrome, a subtype of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation, provide a novel link.Mov Disord. 2013 Jul;28(8):1050. doi: 10.1002/mds.25563. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 23939684 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
β-Propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration: a new X-linked dominant disorder with brain iron accumulation.Brain. 2013 Jun;136(Pt 6):1708-17. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt095. Epub 2013 May 17. Brain. 2013. PMID: 23687123 Free PMC article.
-
Exome sequencing reveals a novel WDR45 frameshift mutation and inherited POLR3A heterozygous variants in a female with a complex phenotype and mixed brain MRI findings.Eur J Med Genet. 2015 Aug;58(8):381-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2015.05.009. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Eur J Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 26096995
-
Elevation of neuron specific enolase and brain iron deposition on susceptibility-weighted imaging as diagnostic clues for beta-propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration in early childhood: Additional case report and review of the literature.Am J Med Genet A. 2016 Feb;170A(2):322-328. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37432. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Am J Med Genet A. 2016. PMID: 26481852 Review.
-
A novel WDR45 mutation in a patient with β-propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration.Neurol Genet. 2016 Dec 5;3(1):e124. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000124. eCollection 2017 Feb. Neurol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27957548 Free PMC article.
-
WDR45 mutations in three male patients with West syndrome.J Hum Genet. 2016 Jul;61(7):653-61. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.27. Epub 2016 Mar 31. J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27030146 Review.
Cited by
-
WDR45, one gene associated with multiple neurodevelopmental disorders.Autophagy. 2021 Dec;17(12):3908-3923. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1899669. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33843443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy and neurodegeneration.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jan;125(1):65-74. doi: 10.1172/JCI73944. Epub 2015 Jan 2. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25654552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted sequencing of 351 candidate genes for epileptic encephalopathy in a large cohort of patients.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2016 Jul 30;4(5):568-80. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.235. eCollection 2016 Sep. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2016. PMID: 27652284 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Intellectual Disability Genes in Female Patients with a Skewed X-Inactivation Pattern.Hum Mutat. 2016 Aug;37(8):804-11. doi: 10.1002/humu.23012. Epub 2016 May 25. Hum Mutat. 2016. PMID: 27159028 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Based Analysis of De Novo Variants in Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Dec 5;105(6):1274-1285. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31785789 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

