Speech production deficits in early readers: predictors of risk
- PMID: 22448102
- PMCID: PMC3303057
- DOI: 10.1007/s11145-011-9300-4
Speech production deficits in early readers: predictors of risk
Abstract
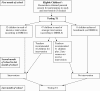
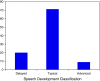
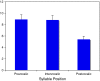
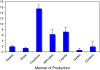
Speech problems and reading disorders are linked, suggesting that speech problems may potentially be an early marker of later difficulty in associating graphemes with phonemes. Current norms suggest that complete mastery of the production of the consonant phonemes in English occurs in most children at around 6-7 years. Many children enter formal schooling (kindergarten) around 5 years of age with near-adult levels of speech production. Given that previous research has shown that speech production abilities and phonological awareness skills are linked in preschool children, we set out to examine whether this pattern also holds for children just beginning to learn to read, as suggested by the critical age hypothesis. In the present study, using a diverse sample, we explored whether expressive phonological skills in 92 5-year-old children at the beginning and end of kindergarten were associated with early reading skills. Speech errors were coded according to whether they were developmentally appropriate, position within the syllable, manner of production of the target sounds, and whether the error involved a substitution, omission, or addition of a speech sound. At the beginning of the school year, children with significant early reading deficits on a predictively normed test (DIBELS) made more speech errors than children who were at grade level. Most of these errors were typical of kindergarten children (e.g., substitutions involving fricatives), but reading-delayed children made more of these errors than children who entered kindergarten with grade level skills. The reading-delayed children also made more atypical errors, consistent with our previous findings about preschoolers. Children who made no speech errors at the beginning of kindergarten had superior early reading abilities, and improvements in speech errors over the course of the year were significantly correlated with year-end reading skills. The role of expressive vocabulary and working memory were also explored, and appear to account for some of these findings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preschool speech error patterns predict articulation and phonological awareness outcomes in children with histories of speech sound disorders.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013 May;22(2):173-84. doi: 10.1044/1058-0360(2012/12-0022). Epub 2012 Nov 26. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23184137 Free PMC article.
-
Phonological awareness, reading accuracy and spelling ability of children with inconsistent phonological disorder.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2008 May-Jun;43(3):300-22. doi: 10.1080/13682820701445032. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2008. PMID: 17852519
-
Characteristics of speech errors produced by children with and without delayed phonological awareness skills.Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2007 Jan;38(1):60-71. doi: 10.1044/0161-1461(2007/006). Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2007. PMID: 17218536
-
Infant brain responses associated with reading-related skills before school and at school age.Neurophysiol Clin. 2012 Jan-Feb;42(1-2):35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neucli.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Sep 17. Neurophysiol Clin. 2012. PMID: 22200340 Review.
-
Developmental dyslexia: a motor-articulatory feedback hypothesis.Ann Neurol. 1996 Mar;39(3):407-12. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390323. Ann Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8602765 Review.
Cited by
-
Preschool speech error patterns predict articulation and phonological awareness outcomes in children with histories of speech sound disorders.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013 May;22(2):173-84. doi: 10.1044/1058-0360(2012/12-0022). Epub 2012 Nov 26. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23184137 Free PMC article.
-
Reading skills of students with speech sound disorders at three stages of literacy development.Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2013 Oct;44(4):360-73. doi: 10.1044/0161-1461(2013/12-0015). Epub 2013 Jul 5. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2013. PMID: 23833280 Free PMC article.
-
Morphosyntactic profiles among preschoolers with and without speech sound disorders.Clin Linguist Phon. 2024 Oct 2;38(10):987-1005. doi: 10.1080/02699206.2023.2286883. Epub 2023 Dec 3. Clin Linguist Phon. 2024. PMID: 38044123
-
Increased Response to Altered Auditory Feedback in Dyslexia: A Weaker Sensorimotor Magnet Implied in the Phonological Deficit.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017 Mar 1;60(3):654-667. doi: 10.1044/2016_JSLHR-L-16-0201. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 28257585 Free PMC article.
-
Speech Error Variability and Phonological Awareness in Preschoolers.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2023 Jan 11;32(1):246-263. doi: 10.1044/2022_AJSLP-22-00031. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36580542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al Otaiba S, Torgesen J. Effects from intensive standardized kindergarten and first-grade interventions for the prevention of reading difficulty. In: Jimerson SR, Burns MK, Van Der Heyden AM, editors. Handbook of response to intervention. The science and practice of assessment and intervention. New York, NY: Springer; 2007. pp. 212–222.
-
- Anthony JL, Francis DJ. Development of phonological awareness. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 2005;14(5):255–259. doi: 10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00376.x. - DOI
-
- Baddeley AD. Human memory: Theory and practice. Hove, England: Erlbaum; 1986.
-
- Berninger VW, Abbott RD, Thomson J, Wagner R, Swanson HL, Wijsman EM, Raskind W. Modeling phonological core deficits within a working memory achitecture in children and adults with developmental dyslexia. Scientific Studies of Reading. 2006;10(2):165–198. doi: 10.1207/s1532799xssr1002_3. - DOI
