Mutations in FKBP14 cause a variant of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with progressive kyphoscoliosis, myopathy, and hearing loss
- PMID: 22265013
- PMCID: PMC3276673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.12.004
Mutations in FKBP14 cause a variant of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with progressive kyphoscoliosis, myopathy, and hearing loss
Abstract
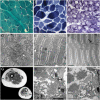
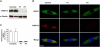
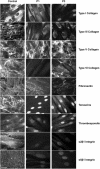
We report on an autosomal-recessive variant of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) characterized by severe muscle hypotonia at birth, progressive scoliosis, joint hypermobility, hyperelastic skin, myopathy, sensorineural hearing impairment, and normal pyridinoline excretion in urine. Clinically, the disorder shares many features with the kyphoscoliotic type of EDS (EDS VIA) and Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy. Linkage analysis in a large Tyrolean kindred identified a homozygous frameshift mutation in FKBP14 in two affected individuals. Based on the cardinal clinical characteristics of the disorder, four additional individuals originating from different European countries were identified who carried either homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in FKBP14. FKBP14 belongs to the family of FK506-binding peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases (PPIases). ER-resident FKBPs have been suggested to act as folding catalysts by accelerating cis-trans isomerization of peptidyl-prolyl bonds and to act occasionally also as chaperones. We demonstrate that FKBP14 is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and that deficiency of FKBP14 leads to enlarged ER cisterns in dermal fibroblasts in vivo. Furthermore, indirect immunofluorescence of FKBP14-deficient fibroblasts indicated an altered assembly of the extracellular matrix in vitro. These findings suggest that a disturbance of protein folding in the ER affecting one or more components of the extracellular matrix might cause the generalized connective tissue involvement in this disorder. FKBP14 mutation analysis should be considered in all individuals with apparent kyphoscoliotic type of EDS and normal urinary pyridinoline excretion, in particular in conjunction with sensorineural hearing impairment.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptome Profiling of Primary Skin Fibroblasts Reveal Distinct Molecular Features Between PLOD1- and FKBP14-Kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jul 8;10(7):517. doi: 10.3390/genes10070517. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31288483 Free PMC article.
-
A cohort of 17 patients with kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by biallelic mutations in FKBP14: expansion of the clinical and mutational spectrum and description of the natural history.Genet Med. 2018 Jan;20(1):42-54. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.70. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Genet Med. 2018. PMID: 28617417 Free PMC article.
-
Further delineation of FKBP14-related Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: A patient with early vascular complications and non-progressive kyphoscoliosis, and literature review.Am J Med Genet A. 2016 Aug;170(8):2031-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37728. Epub 2016 May 5. Am J Med Genet A. 2016. PMID: 27149304 Review.
-
FKBP14 kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome in adolescent patient: the first Colombian report.Arch Argent Pediatr. 2019 Jun 1;117(3):e274-e278. doi: 10.5546/aap.2019.eng.e274. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31063316 English, Spanish.
-
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome related to FKBP14 mutations: detailed cutaneous phenotype.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017 Jan;42(1):64-67. doi: 10.1111/ced.12983. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27905128 Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging role of peptidyl-prolyl isomerase chaperones in tau oligomerization, amyloid processing, and Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem. 2015 Apr;133(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13033. Epub 2015 Feb 24. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25628064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Further Evidence of a Recessive Variant in COL1A1 as an Underlying Cause of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A Report of a Saudi Founder Mutation.Glob Med Genet. 2020 Dec;7(4):109-112. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1722873. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Glob Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 33693443 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP52 in Neuronal Signaling and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Microtubule Story.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 3;23(3):1738. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031738. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brittle cornea syndrome: recognition, molecular diagnosis and management.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013 May 4;8:68. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-8-68. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013. PMID: 23642083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ehlers-danlos syndrome, hypermobility type: an underdiagnosed hereditary connective tissue disorder with mucocutaneous, articular, and systemic manifestations.ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:751768. doi: 10.5402/2012/751768. Epub 2012 Nov 22. ISRN Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 23227356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinmann B., Royce P.M., Superti-Furga A. The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. In: Royce P.M., Steinmann B., editors. Connective Tissue and Its Heritable Disorders. 2nd ed. Wiley-Liss; New York: 2002. pp. 431–523.
-
- Beighton P., De Paepe A., Steinmann B., Tsipouras P., Wenstrup R.J., Ehlers-Danlos National Foundation (USA) and Ehlers-Danlos Support Group (UK) Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1998;77:31–37. - PubMed
-
- Kivirikko K.I., Pihlajaniemi T. Collagen hydroxylases and the protein disulfide isomerase subunit of prolyl 4-hydroxylases. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 1998;72:325–398. - PubMed
-
- Giunta C., Randolph A., Al-Gazali L.I., Brunner H.G., Kraenzlin M.E., Steinmann B. Nevo syndrome is allelic to the kyphoscoliotic type of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS VIA) Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2005;133A:158–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

