Regulatory cohesion of cell cycle and cell differentiation through interlinked phosphorylation and second messenger networks
- PMID: 21855795
- PMCID: PMC3298681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.07.018
Regulatory cohesion of cell cycle and cell differentiation through interlinked phosphorylation and second messenger networks
Abstract
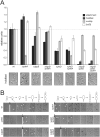
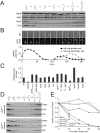
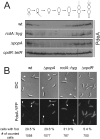
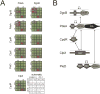
In Caulobacter crescentus, phosphorylation of key regulators is coordinated with the second messenger cyclic di-GMP to drive cell-cycle progression and differentiation. The diguanylate cyclase PleD directs pole morphogenesis, while the c-di-GMP effector PopA initiates degradation of the replication inhibitor CtrA by the AAA+ protease ClpXP to license S phase entry. Here, we establish a direct link between PleD and PopA reliant on the phosphodiesterase PdeA and the diguanylate cyclase DgcB. PdeA antagonizes DgcB activity until the G1-S transition, when PdeA is degraded by the ClpXP protease. The unopposed DgcB activity, together with PleD activation, upshifts c-di-GMP to drive PopA-dependent CtrA degradation and S phase entry. PdeA degradation requires CpdR, a response regulator that delivers PdeA to the ClpXP protease in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Thus, CpdR serves as a crucial link between phosphorylation pathways and c-di-GMP metabolism to mediate protein degradation events that irreversibly and coordinately drive bacterial cell-cycle progression and development.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation and polar sequestration of PopA, a c-di-GMP effector protein involved in Caulobacter crescentus cell cycle control.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Nov;94(3):580-94. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12777. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25171231
-
Cell cycle-dependent adaptor complex for ClpXP-mediated proteolysis directly integrates phosphorylation and second messenger signals.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Sep 30;111(39):14229-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1407862111. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25197043 Free PMC article.
-
Second messenger-mediated spatiotemporal control of protein degradation regulates bacterial cell cycle progression.Genes Dev. 2009 Jan 1;23(1):93-104. doi: 10.1101/gad.502409. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19136627 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory circuits in Caulobacter.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000 Apr;3(2):171-6. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00071-0. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10744989 Review.
-
Two-component signaling systems and cell cycle control in Caulobacter crescentus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:122-30. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792685 Review.
Cited by
-
The Protein Quality Control Network in Caulobacter crescentus.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 30;8:682967. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.682967. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33996917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Systems Approaches Reveal a Multistage Mode of Action of a Marine Antimicrobial Peptide against Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Its Protective Effect against Bacterial Peritonitis and Endotoxemia.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Dec 27;61(1):e01056-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01056-16. Print 2017 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27795369 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of high-specificity cyclic diguanylate signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 31;109(31):12746-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115663109. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22802636 Free PMC article.
-
Bypassing the need for subcellular localization of a polysaccharide export-anchor complex by overexpressing its protein subunits.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Jul;89(2):350-71. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12281. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23714375 Free PMC article.
-
More than Enzymes That Make or Break Cyclic Di-GMP-Local Signaling in the Interactome of GGDEF/EAL Domain Proteins of Escherichia coli.mBio. 2017 Oct 10;8(5):e01639-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01639-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29018125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldridge P, Paul R, Goymer P, Rainey P, Jenal U. Role of the GGDEF regulator PleD in polar development of Caulobacter crescentus. Mol Microbiol. 2003;47:1695–1708. - PubMed
-
- Bateman JM, McNeill H. Temporal control of differentiation by the insulin receptor/tor pathway in Drosophila. Cell. 2004;119:87–96. - PubMed
-
- Biondi EG, Reisinger SJ, Skerker JM, Arif M, Perchuk BS, Ryan KR, Laub MT. Regulation of the bacterial cell cycle by an integrated genetic circuit. Nature. 2006;444:899–904. - PubMed
-
- Boehm A, Kaiser M, Li H, Spangler C, Kasper CA, Ackermann M, Kaever V, Sourjik V, Roth V, Jenal U. Second messenger-mediated adjustment of bacterial swimming velocity. Cell. 2010;141:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Boehm A, Steiner S, Zaehringer F, Casanova A, Hamburger F, Ritz D, Keck W, Ackermann M, Schirmer T, Jenal U. Second messenger signalling governs Escherichia coli biofilm induction upon ribosomal stress. Mol Microbiol. 2009;72:1500–1516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 GM084157-02/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM084157-03/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM084157/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-082899/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM082899/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-049224/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM049224/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM082899-05/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- GM-084157/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 GM084157/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM084157-04/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

